Check out our big, bulletproof guide to layered VMware solutions for securing remote desktop services hosts (RDSH).
Remote desktop services (RDS) bring users closer to the data center. However, attackers can misuse the infrastructure to collect information, abuse and hop around the data center.
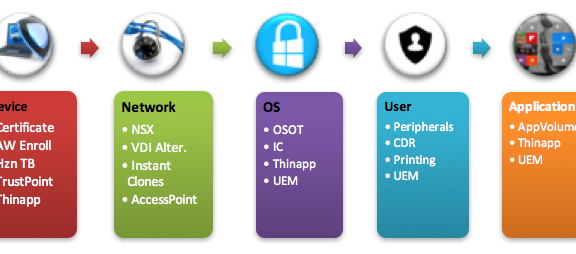
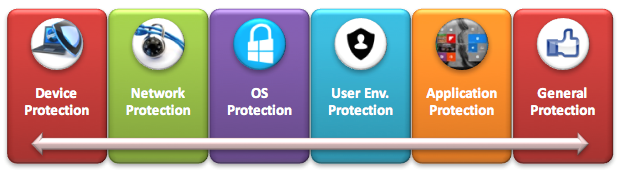
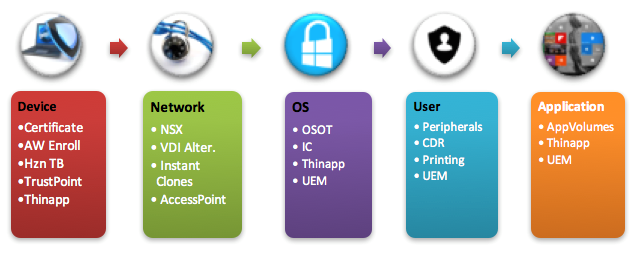
RDS bridge common physical security best practices and data center security principals and, thus, require unique security considerations. Here are different approaches to secure RDS farms with VMware solutions across the device, network, operating system (OS), user environment and applications.
Device Protection
- Client Device Certificate Authentication: VMware Access Point functions as a secure gateway for users who want to access remote desktops and apps outside the corporate firewall. A new feature in Access Point 2.6 and up silently authenticates only trusted client machines (endpoints that have the client device certificate installed). The certificate can be delivered as part of an enrollment process with VMware AirWatch. [Click here for setup of SSL certificates for Horizon View.]
- VMware Horizon Toolbox: The Horizon Toolbox 2.0 web portal is an extension to View in Horizon 6 and up. The included Device Access Policy limits access to the broker based on the media access control (MAC) address of the device. In a high-security environment, IT may want extra control on not only who connects to the system but also from which device. [Click here for Horizon 6 RDSH best practices.]
- VMware TrustPoint: TrustPoint’s out-of-the-box endpoint security capabilities include: quarantining machines, killing processes, disabling network connections, changing registry data, uninstalling applications, resetting credentials, shutting down systems and even reimaging Windows endpoints at scale.
- VMware ThinApp: Another option is to deliver your Horizon Client as a ThinApp isolated app. This ensures the Horizon Client will not be changed, nor its configurations that might allow the attacker to abuse its code.
Network Protection

- VMware NSX for Horizon: Create policies and security rules based on logical objects such as a specific virtual machine (VM) and/or folder to bring agility and control to your RDSH farm. This capability can complement a design with more security around farms and groups of VMs. In addition, micro-segmentation of the RDSH farm can make each RDS host operate on its own in a zero-trust network. No RDS host will be able to contact other RDS hosts over network or any other unnecessary enterprise resources. [Click here for a deep dive into VMware Horizon 6 with NSX.]
- Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) Alternative: RDSH aggregates multiple users under the same network. In case of compromised security, it is almost impossible to find out which user created the suspicious activity over the network. The only way to allow separation of each user to a different IP is migrating to a VDI model where more network security can be enforced.
- VMware Instant Clone Technology: Instant Clone Technology allows admins to rapidly clone and deploy a VM in less than a few seconds (“just in time”). For example, IT can decide to provision or decommission an RDS farm only around users’ login time. Because the servers don’t exist until IT deploys them—no IP addresses to ping until then, no MAC, nothing—there’s zero attack surface. (Note: Instant clones are not yet supported for RDSH servers).
- Access Point:Access Point acts as a proxy host for connections inside your company’s trusted network. This additional layer of security shields virtual desktops, application hosts and servers from the public-facing internet. The only remote desktop and application traffic that can enter the corporate data center is traffic on behalf of a strongly authenticated user.

OS/VM Protection
- VMware OS Optimization Tool: Optimize Windows 7, 8 and 10, as well as Windows Server 2008 and 2012, for View. With customizable templates, you can easily enable or disable Windows services and features (often enabled by default) to improve performance.
- Instant Clones & View Composer: In addition to the network benefits of Instant Clones, View Composer supports RDSH recomposing (cleaning and redeploying from a standard snapshot). The RDS farm stays clean and up-to-date based on the setup (e.g. force clean RDSH daily, weekly, etc.).
- Disable vSphere Console Access: In VDI, the user’s session can be viewed from the vSphere console for administrators creating a security breach and privacy issues. This is disabled by default and can be managed under the GPO ADM or registry (Software\Policies\Teradici\PCoIP\pcoip_admin pcoip.enable_console_access=0).
- ThinApp Containerized Apps: ThinApp isolation benefits apps management and ensures local OS resources are not available to the app itself. If the app is isolated from the host, any changes, deletions or additions made by the app to the file system or registry are recorded in the sandbox, instead of to the host OS.
- Disable Peripherals on the VM: Any external device or external interface can be used to bypass all software and OS security, so peripherals should be individually managed and disabled. Extract devices such as USB and serial ports and CD and floppy disk drives from the VM settings, and manually disable capabilities like hot plugging and VMware Tools. [Quick Tips: On the VM advanced settings, set “devices.hotplug” to “disable.” Edit “HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\NetworkProvider\Order” delete the “vmhgfs” string.]
- VMware User Environment Manager (UEM): UEM simplifies end-user profile management, and, with the following features, gives you more control over the OS environment: DirectFlex, Environment Variables, application blocking (for example, regedit.exe, cmd.exe, powershell and other editors), hide drives, policy settings (such as hide “Run” and prohibit access to the control panel). Another best practice: Create a mandatory profile instead of using the defaults. (Note: This is officially supported by Microsoft only for Win2008R2 servers.)
Application Protection
- VMware App Volumes AppStacks: Read-only objects, AppStacks cannot be modified by the user (elevated or not) or the administrator. This helps you maintain a unified, standard RDS farm and protect the OS and application from malware attempting to hijack the app environment.
- NSX for App Volumes: NSX for App Volumes enables IT to manage network policies associated with apps in App Volumes.
- ThinApp Containerized Apps: ThinApp protects apps from modifications and changes while running. Just enable the “Delete sandbox on exit.” Once enabled, each time a user runs Chrome, it will be a new install, keeping it secure and fresh.
- UEM: The user’s profile also holds a link to the app, as the application loads it corresponds with the AppData required to run (unless you defined zero customization for user, which will mitigate this risk, as well). With UEM, control a big part of the user’s profile and AppData when considering the following options: 1) Control and enforce predefined settings and 2) DirectFlex profile delivery. For example, block advanced configuration and appearance with predefined settings and not saving user changes on log off. This way IT can control the profile the user gets upon login.
User Protection
- USB and Serial Redirection: Map required USB devices Vendor ID (VID) and Product ID (PID), and use the whitelisting option in the Horizon GPO. If not needed, you can block it entirely using the same GPO.
- Client Driver Redirection: This is another bridge from the client to the Datacenter. Block this feature, or even better, don’t install the agent.
- Disable Clipboard: Horizon View Client and Agent have corresponding GPO settings to allow one or bi-directional clipboard usage.
- Printing Redirection: Printing can be used as a channel to transfer data and exploit the system. Disable where needed or use network-managed printers.
- UEM: Part of the user is his or her profile (%APPDATA%), which is directly managed by UEM. To strengthen security, consider using UEM Profile Backups, predefined settings and advanced settings (exclusion of files based on size and date). In addition, use the “Remove local profile at logoff” feature to clear the local copy after logoff. UEM also has “Horizon Smart Policy” feature so you can control all of the above for PCoIP. Use it! [Click here for VMware UEM FlexEngine advanced settings.]
General Protection
- vRealize Log Insight Windows Agent: A Windows event channel is a pool for collecting related events in a Windows system. By default, the Log Insight Windows Agent collects events from the application, system and security channels. In a Windows system, applications can store log data in flat text files on the file system. The Log Insight Windows Agent can monitor directories and collect events from flat text log files.
- Antivirus with NSX Integration: With NSX, utilize the hypervisor level antivirus with third-party vendors. This offloading ensures each VM is protected and up-to-date with virus definition from the moment it’s created. [Click here for help installing NSX components.]
- Disable Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP): To make sure no RDP connections will override PCoIP and Blast protocols, disable the option to log in with RDP, even for administrators.
- Windows Updates: Regularly update your RDS server for critical and security updates. Refresh all servers from the image using Composer in a managed way and not individually with System Center Configuration Manager (SCCM) or Windows Server Update Services (WSUS), which can fail or be blocked by a malicious user.
- Remove Unnecessary Software: Remove unnecessary software like PowerShell, admin tools and debug tools.
- Disconnect Idle Sessions: With this internal tool, you can disconnect users not performing any jobs and idling on the system.
- Create a Group Policy Object (GPO): Check out this IT Blog for basic Group Policies to get started.
RDSH Security Checklist
[Note: These recommendations can be deployed individually or together but should be delivered on top of Microsoft security best practices concerning the New Technology File System (NTFS), ports, services, etc. In addition, follow security hardening guides, like VMware vSphere and NSX, and follow each product minimal user rights required.]