Authors: Eric Bediako and Aditya Bandikallu
Achieving a successful migration takes careful planning, attention to detail, and knowledge of the right steps to take when. This blog provides some guidance regarding factors that can lead to a successful VMware Workspace ONE® UEM on-premises to dedicated SaaS migration. It also identifies some of the blockers that can hinder your success. Do this correctly and your migration will go smoothly and quickly.
Blockers To Address
There are several blockers you may need to address before migrating your environments from on-premises to dedicated SaaS such as these configurations at the Global Organization Group (OG):
- Directory services
- Device management
- Email management
- Application management
- Complexities associated with multi-tenant architectures where there are multiple URLs as entry points.
Other potential blockers could be an unsupported version of Workspace ONE UEM and integration points (e.g., VMware Workspace ONE® Access™). Conducting a health check before migration will help to reveal issues that need to be resolved.
Migration Guidance
Let’s explore the recommended OG structure, best practices, pre-migration considerations, migration prerequisites, and a high-level remediation process for ensuring a successful migration.
VMware Professional Services has a process to identify and remediate some of the migration blockers. However, it’s important to ensure that all the necessary pre-migration steps are completed before migration. Otherwise, complications such as delays and escalations would be encountered. The end goal is to minimize remediations and to have a successful migration!
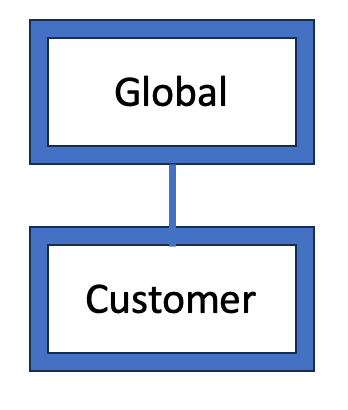
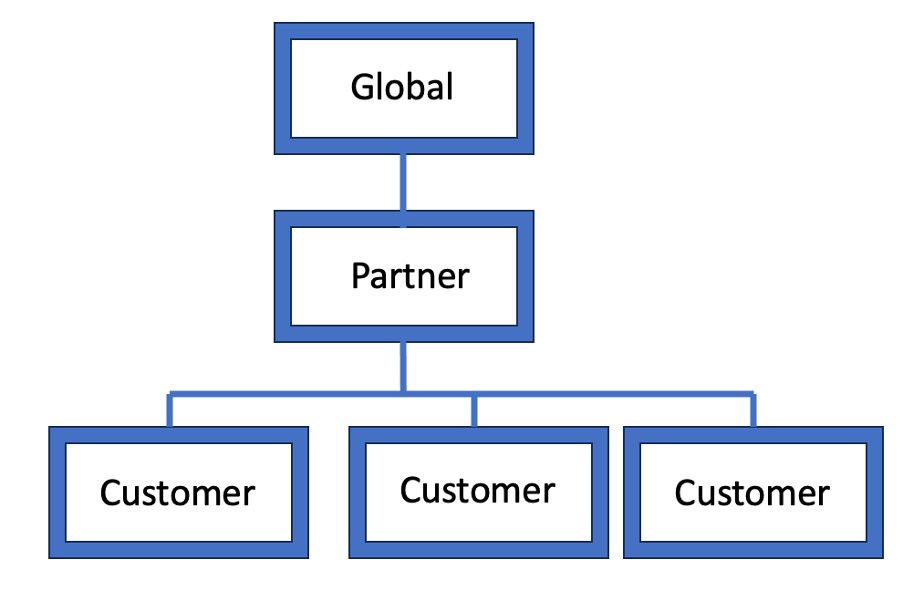
Recommended OG structure for Customer and Partner OG Type
Think of organization groups as individual branches on a family tree, with each leaf as a device user. Workspace ONE UEM identifies each leaf and establishes its standing in the family tree using OG. The type of an organization group can have an impact on what settings an administrator can configure.
- Global – The top-most organization group. Usually, this group is called Global and has type Global. Hosted SaaS environments are not able to access this group.
- Customer – The top-level organization group for each customer.
- Partner – Top-level organization group for partners (third-party resellers of Workspace ONE UEM).
Refer to this KB article for best practices on structuring OGs in the Workspace ONE UEM Console.
Below is a high-level OG structure recommendation for customer and Managed Service Provider (MSP) managed environments:
Customer Managed Environment
MSP Managed Environment
Migration Best Practices
There cannot be any configurations set up at the Global OG. Configurations on the Global OG level should be moved to the target OG (e.g., Customer OG) level before migration. It is mandatory to move these configurations as access to the Global OG will be lost post-migration to dedicated SaaS. Configurations such as:
- Profiles
- Application Assignments
- Active Directory (AD)
- Apple Push Notification service (APNs)
- Apple Business Manager – Device Enrollment Program (DEP)
- Apple Business Manager – Volume Purchase Programme (VPP)
- Android Enterprise Mobility Management (EMM) Configuration
- Product Provisioning
- User Accounts
- Directory Services
- Email Management – VMware Workspace ONE® Secure Email Gateway™ / PowerShell
- Certificate Authority (CA)
- Syslog
- VMware Workspace ONE® Tunnel™
- VMware AirWatch® Mobile Access Gateway™
- VMware Unified Access Gateway™
- VMware AirWatch® Cloud Connector™
- Representational State Transfer Application Programming Interface (REST API)
- Event Notification Service (ENS)
- Email – Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP)
For some customers to perform this change, devices enrolled at the Global OG will need to be moved or re-enrolled to the target OG (e.g., Customer) on the on-premises environment before migration. Devices should never be left at Global OG. Generally, devices can be moved to the target OG if the users they are enrolled to exist at/above the target OG. If the users exist outside the target OG hierarchy, devices will likely have to be re-enrolled to users who exist at/above the target OG. There are certain scenarios where re-enrollment may be required even if the user exists at/above the target OG; for example, the same user has been added at the target OG (or an intermediate OG) and has a device enrolled there as well.
The trigger points to decide between going through a migration or building a new tenant in dedicated SaaS is ultimately your decision if the level of effort for remediation outweighs the benefits of re-enrolling devices from scratch.
Refer to this VMware doc for reasons not to enroll devices in the Global OG.
Considerations Before Migration
The purpose of the pre-migration considerations is to ensure a successful migration and reduce the risk of migration-related issues. Ultimately, those who fail to follow them have a higher percentage of having an unsuccessful migration which leads to remediation which can be time intensive. Preparation is essential to avoid costly delays.
Health check
A health check should be performed for the on-premises environment. It will help to reduce the time and effort required to diagnose basic infrastructure and configuration problems.
The health check at a minimum should assess the Workspace ONE UEM core components (Console, Device Services, API, Database) and available enterprise integration components (e.g., AirWatch Cloud Connector, Directory Services, VMware Workspace ONE® Access™, Workspace ONE Access Connector). The existing configuration (profiles, applications, compliance) should be reviewed against defined use cases. The health check should confirm the use cases for Workspace ONE UEM to ensure they are being achieved accurately and efficiently.
Examples of things to check:
- Ensure all Workspace ONE Components are fully functional.
- Monitor the Workspace ONE UEM database to ensure it’s fully functioning and healthy as recommended in this VMware doc.
- Check application server health by reviewing the event logs for the Workspace ONE UEM servers.
- Check if Active Directory integration is at the Global OG.
The Workspace ONE UEM Recommended Architecture offers generic guidelines and recommendations to improve performance, manageability, and scalability of the environment.
VMware Professional Services can help with our health check service (Assess Workspace ONE Technology Configuration Review) and provide assistance in the areas of recommendation during the health check.
Multiple Customer OGs
An on-premises environment with multiple Customer OGs where each of them has different management and enrollment URLs should be avoided. Workspace ONE UEM does not support different enrollment URLs. The recommendation is to consolidate against a single URL. The risk with the consolidation is that some of the devices may need to be re-enrolled.
It is not a good idea to migrate with multiple Customer OGs because the additional operational overhead to manage each Customer OG is impractical. Imagine needing separate infrastructure for enterprise integration components, and requiring unique user/administrator accounts, etc.
Workspace ONE UEM version
Your on-premises Workspace ONE UEM version should be supported and updated with all recommended patches. If the environment is not supported (including all gateway components) then it must be upgraded and validated before moving to the dedicated SaaS environment. Gateway components include Workspace ONE Secure Email Gateway and Workspace ONE Tunnel. Refer to this KB article for supported Workspace ONE UEM versions.
Licenses
Workspace ONE UEM on-premises licenses should be valid. If the on-premises licenses have expired, you will be unable to open support requests (SR).
- Pre-Migration
- If the on-premises licenses expire, you lose the ability to file support requests online or via Chat. You will need to either:
- Purchase additional support for the on-premises licenses so your online access is restored
- Get a Do Not Deny (DND) in place, so you can call in for support. If you call in with expired licenses, the Customer Support team will require the DND number before you will be able to file an SR via phone.
- The VMware sales team can work with VMware Renewals to obtain a DND if needed. Also note that the DND has a time limit and if it expires it has to be renewed.
- If the on-premises licenses expire, you lose the ability to file support requests online or via Chat. You will need to either:
- Post-Migration
- Post migration the SID (SaaS Tenant) has to be activated by VMware for SaaS support to be active. Your super user now needs to re-add all the correct admins to restore their support, as Admins are not carried over from the on-premises licenses to the SaaS support. Refer to this KB article for steps to add users to the SID once it is active.
It is important to ensure the type of VMware Workspace ONE® Intelligence™ services (Sandbox / Production) and licenses (Basic / Advanced) are collected. Workspace ONE Intelligence Sandbox is not supported for migration. All custom reports and templates, dashboards, and automation on Workspace ONE Intelligence will need to be rebuilt if the on-premises environment is connected to Sandbox Workspace ONE Intelligence environment.
Components
Components should be supported for migration, otherwise, re-install/re-configuration would be required, or an alternative component installed prior to migration.
The following components must be re-installed or re-configured or an alternative component installed in the environment vs. migrating.
| Component | Alternative Option/Solution Prior To Migration |
| Workspace ONE Access Connector | Rather than migration, requires reconfiguration of a new tenant. VMware Professional Services has an offering to do this including deployment of new Workspace ONE Access Connectors. |
| AirWatch Cloud Connector – new installs | Requires a new install of AirWatch Cloud Connector |
| Classic Workspace ONE Secure Email Gateway | Workspace ONE Secure Email Gateway v2 or Workspace ONE Secure Email Gateway on Unified Access Gateway should be setup |
| AirWatch Mobile Access Gateway | Unified Access Gateway should be setup |
| Push Relay Servers | Convert all Push Relay Servers to Pull Relay Servers |
| VMware Workspace ONE® Assist™ – on-premises | Workspace ONE Assist on-premises data will not be migrated. New licenses are required for the SaaS Workspace ONE Assist environment post-migration. Note: the data from the on-premises Workspace ONE Assist is not needed for Workspace ONE Assist to function. |
Integrations
Integrations with the following cannot be migrated to the new environment. They must be re-created post-migration.
- Workspace ONE Access
- Azure Active Directory
- Android Enterprise
- Apple Business Manager (VPP, DEP)
VMware Professional Services has a service that can re-configure what is in your on-premises environment to the new dedicated SaaS instance.
Migration Prerequisites
It is important to ensure that the migration pre-requisites are met to avoid any blockers:
- Secure File Transfer Protocol (SFTP) the SSL certificates
- No support for wildcard certificates / No support for certificates issued by Internal CA; must be a certificate issued by a trusted third-party CA.
- Subject Alternate Name (SAN) certificates are supported / Personal Information Exchange (PFX) format required.
- Need to be prepared before the test run (pre-migration) as the certificates will be validated as part of the test run. The test run is VMware’s SaaS team’s internal validation of the dedicated SaaS environment that will be built for you before going to production.
- SFTP database backup for a dry run
- No service interruption required.
- Stop the scheduler service when taking the database backup.
- New up-to-date backup should be taken and uploaded to the SFTP before the dry run window.
- Global system admin account
- For VMware team verification purposes
- SFTP is prepared by VMware
- SFTP server is deployed on Amazon Web Services (AWS) Transfer Family. Secure Shel (SSH) Public key needs to be provided by you to deploy the SFTP.
- Refer to this Amazon doc for how to Generate SSH keys.
- SFTP access information to log in to the SFTP server created
- SFTP Endpoint URL (Host) provided by VMware.
- Username (cnxxxx-sftpuser) provided by VMware.
- SSH Private key (from the same key pair with your public key)
- On-premises architecture and deployment details
- Workspace ONE UEM version including patch version
- Number of devices
- Database size / MS SQL Version / Log File Size
- DNS Time To Live (TTL)
- Set to 5 minutes ahead of the migration window to ensure a smooth and short DNS migration from on-premise to SaaS.
- Firewall Rules preparation
- If IP whitelist is required as outlined in this KB article and this KB article.
VMware encourages you to download and execute a diagnostic script that will help identify settings in the existing environment that may have to be changed before the migration can take place. The diagnostic script is a set of read-only database queries used to identify the presence of configurations/settings/resources at Global OG, which will have to be addressed before an on-premises instance of Workspace ONE UEM can be migrated to SaaS. It includes queries to gather environment statistics (supplemental information used to guide remediation plans). The diagnostic script is available to download only from the myWorkspaceONE Resources portal. The download contains instructions on how to run the script.
The script will output a set of Pass/Fail results for each configuration based on whether it exists at the Global OG when it should not. It is recommended that the results be gathered in a single text/rpt file. Hitting Ctrl+T in SQL Studio (SSMS) before running the script will provide output in a single window which can then be saved as an .rpt file or copied to a text file.
Remediation Process
Each configuration/section covered by the diagnostic script comes with high-level guidance on remediation.
Data clean-up
Clearing stale/unused records helps reduce the complexity and risk involved in subsequent steps. For example, deleting unenrolled devices, inactive users, unused profiles, etc.
Devices
- Delete stale devices – defined as devices that are either not Enrolled or have not been seen for over x days (x can be 30, 60, or 90, for example).
- Delete devices enrolled to Inactive users.
- Move enrolled devices to the Target OG tree:
- Any device enrolled to a Global enrollment user of type Directory
- Any Apple device associated with a Global APNs for MDM token
- Any Android device associated with a Global Android EMM token
- Move enrolled devices to sibling(s) of the Target OG:
- Any device enrolled to a Global enrollment user of type Basic, which needs to reside at a sibling of the Target OG.
Administrators, enrollment users, and groups
- Delete enrollment users who are Inactive or have no enrolled devices; at the least, do so for Global enrollment users.
- Delete unused enrollment user groups; at the least, do so for Global enrollment user groups.
- Delete Inactive or unused Administrator accounts; at the least do so for Global admins of type Directory.
Directory Services
- If Directory Services have been configured at an OG where they are no longer required or in use, change the setting to Inherit.
- Administrators, Enrollment Users, and Groups imported through such a Directory Services configuration will have to be deleted first.
Resources – profiles, compliance policies, applications, and products and product components
- Delete Inactive or unused resources, including those which are assigned to devices but not required. At the least, do so for resources managed at Global.
- Unused VPP apps may need to be dissociated from the VPP token in Apple’s portal first.
Tags
- Delete any unused Tags managed at Global.
- If any Tags remaining at Global are in use, create a copy at the relevant OG(s) and add the necessary devices to each.
Smart Groups (SGs)
- Delete any Global SGs which either:
- Are not used in any assignment/exclusion
- Do not have any devices
- Delete SGs managed at an OG outside the Target OG tree, which are mapped to Global enrollment users and user groups. If they cannot be deleted, update them to remove the association with such users/groups.
- Create copies of any remaining Global SGs at the Target OG which are either:
- Associated with a Global enrollment user or user group, or
- Used to assign a resource to devices in the Target OG tree
- Create copies of any remaining Global SGs at siblings of the Target OG if they do not meet any of the previous criteria, and are used to assign a resource to devices outside the Target OG tree.
- Delete any Global SGs for whom copies were made at that Target OG or its siblings.
Console/REST API
Moving, re-creating, and updating records through the Console/REST API so any dependencies on the Global OG are removed. Records such as profiles, applications, Certificate Authorities (CAs), Certificate Templates (CTs), Android – EMM, and Apple DEP.
Resources – profiles, compliance policies, applications, and products and product components
- If any resources remain at Global, move or re-add them to/at the Target OG.
- Create copies of any such resources at siblings of the Target OG if needed.
Enterprise integration – CA and CTs
- Delete unused CAs/CTs managed at Global.
- Create a copy of each remaining CA/CT at the Target OG (and its siblings, if needed).
- Update the Credentials/SCEP payloads of corresponding Device/Product/SDK/Application profiles to leverage the newly created CA/CT and publish.
Organization Group type
- Ensure that the Target OG is of type Customer. Its siblings may also have to be set to type Customer.
- If any of their children are of type Customer, such OGs will have to be converted to type Container first.
Apple – DEP
- Clear the DEP token from Global and configure it at the Target OG.
Apple – Profile Signing Certificate
- Upload the SSL certificate at the Target OG, if it is currently residing at Global.
Android – EMM
- Clear the EMM token from Global and configure it at the Target OG.
Enterprise Integration – Syslog and Event Notifications
- Clear from Global and configure at the Target OG (and its siblings if needed).
- This step may be performed after Section C.
MemConfig
- Clear from Global and configure at the Target OG (and its siblings if needed).
While you may want to implement these steps yourself, it is recommended that you engage a VMware Professional Services subject matter expert for oversight to rectify your environment.
Database
This pertains to components/settings/artifacts which cannot be remediated through the Console/REST API. Database scripts are developed, tested, and backported on an as-needed basis and are typically reserved as a last resort. The scripts make changes through the database, but before making any changes read-only scripts are utilized to validate that previous steps have been executed successfully. For example, scripts to move the APNs for Mobile Device Management (MDM) token to the target OG and move the Directory Services configuration from Global OG to the target OG.
You will need a VMware Professional Services engagement to rectify your environment if this solution is needed.
Get help from the professionals
While you now have a better understanding of the considerations, steps, and common pitfalls to avoid when migrating from Workspace ONE UEM on-premises to dedicate SaaS – there’s a better way. VMware Professional Services performs these migrations all the time. We have the experience and subject matter experts that can help you successfully achieve your migration objectives. Just ask your VMware Sales Representative for more information on how we can help with your project.

Aditya is a Product Line Manager who joined VMware in 2014. Aditya worked in VMware Global Support in various roles spanning frontline tech support, account management, and escalation management where he helped resolve critical performance, architecture, and product escalations for customers spanning the breadth of the size and complexity spectrums. He has overseen the discovery, assessment, planning, and remediation of multiple on-premises environments to enable a hassle-free migration to SaaS whilst ensuring long-term success. Aditya recently moved to EUC Product Management, focusing on the Workspace ONE UEM core platform.





