Introduction
VMware is pleased to announce the availability of VMware Telco Cloud Automation 2.1. This latest version of VMware Telco Cloud Automation—released on July 21st, 2021—focuses on key feature upgrades and new capabilities for Communication Service Providers. The new features central to Telco Cloud Automation 2.1 fall under several broader themes: application lifecycle management, improvements to CaaS automation, enhanced platform operability and the initial availability of Network Slicing for VMware Telco Cloud Automation.
Importantly, VMware Telco Cloud Automation 2.1’s improvements continue to serve as an integral, differentiating aspect of the VMware Telco Cloud Platform stack—offering a holistic, end-to-end, automation solution for Communication Service Providers regardless of their stage of network maturity (pictured in Figure 1 below). VMware Telco Cloud Automation supports 4G, VNF-based deployments, helps a Communication Service Provider modernize their networks to 5G, CNF-based environments and, for those Communication Service Providers already operating 5G, cloud-native networks, supports—through the VMware Telco Cloud Platform—new avenues to revenue with cutting-edge services like Network Slicing.
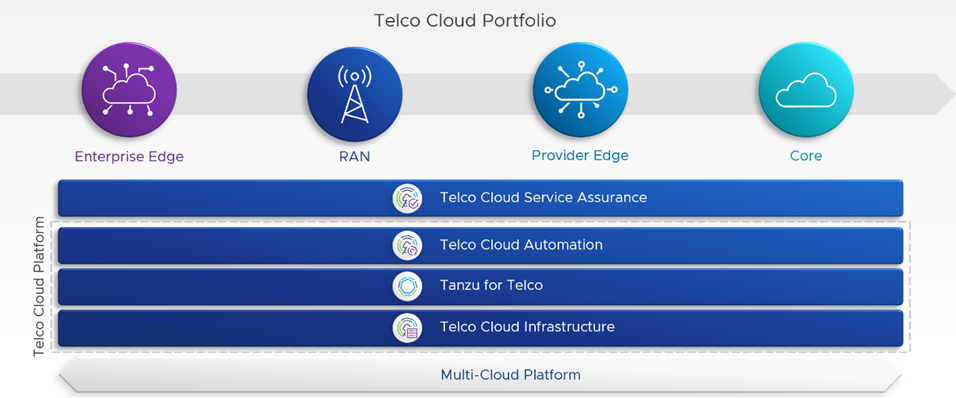
What’s more, with the improvements in VMware Telco Cloud Automation 2.1 as part of the Telco Cloud Platform stack, Communication Service Providers can better manage lifecycle management operations of VNFs and CNFs and, with its support for network slicing, network services chaining and a robust ecosystem of certified VNF and CNF partners, contributes to OpEx and CapEx savings and promotes SLA adherence (see Figures 2 and 3 for more detail). In the following, we offer a comprehensive overview of the new features and capabilities pertinent to the Telco Cloud Automation 2.1 release and how this latest launch improves both the functionality and business benefits of the VMware Telco Cloud Platform.
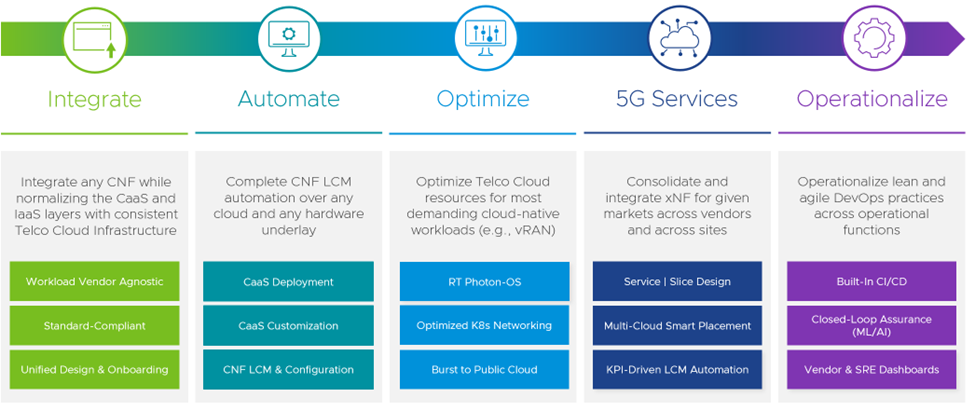
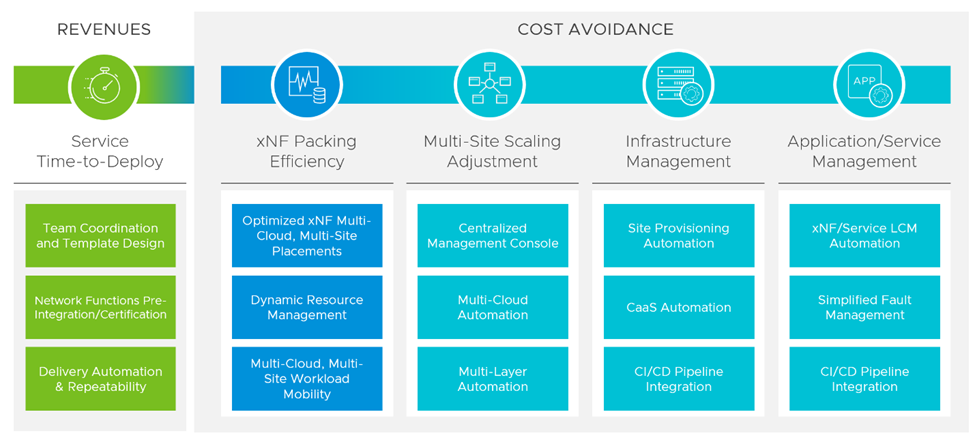
What’s New in Telco Cloud Automation 2.1?
Multi-Cloud Automation for VMware Cloud on AWS and Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS)
Driven by the need for business agility, acceleration in innovation and potential cost savings, Communication Service Providers are undertaking the task of constructing distributed, multi-cloud networks. Telco Cloud Automation enables Communication Service Providers to take full advantage of their multi-cloud ecosystem by providing a centralized management plane to manage distributed, multi-cloud workloads. As part of Telco Cloud Automation 2.1, Communication Service Providers can leverage Amazon Web Services’ (AWS) public cloud resources with VMware Cloud on AWS and/or EKS. Telco Cloud Automation 2.1 can provision cloud-native network functions directly on native Amazon EKS, bringing unified management of workloads on-premises and on public cloud infrastructures (depicted in Figure 4 below). As such, Telco Cloud Automation 2.1 offers multi-cloud consistency, easing workload onboarding, instantiation and lifecycle management while promoting mobility from the network core to edge to RAN, and from private to public clouds.
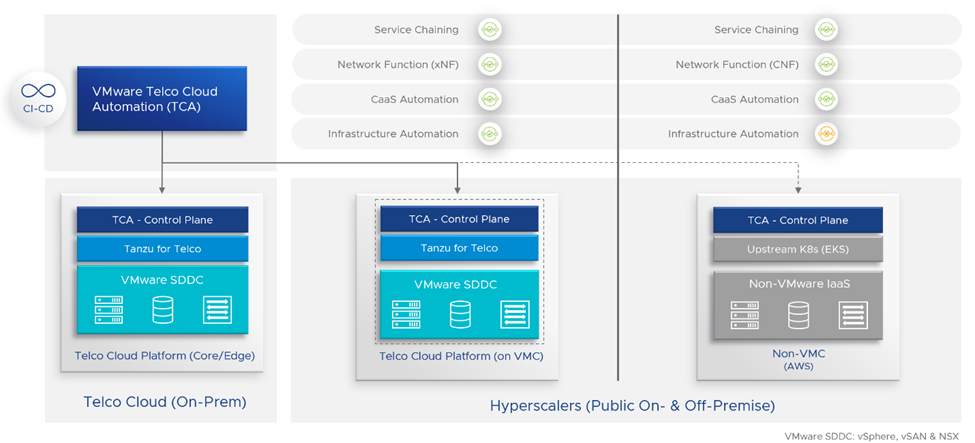
What’s more, Telco Cloud Automation 2.1 supports and manages EKS clusters running on vSphere (in Tech Preview). Telco Cloud Automation 2.1 can, as a result, manage CNFs running in an EKS-A environment. This improvement in EKS functionality allows the Communication Service Provider to extend the environments in which their workloads can be managed—eventually supporting lifecycle management of CNFs running on EKS-A—and offering new avenues for edge-based services.
Network Slicing for VMware Telco Cloud Automation: End-to-End Orchestration with Network Slicing
As demands from customers to offer new, differentiated services increases, Communication Service Providers are searching for new ways to fulfill—and monetize—these requests. Network Slicing allows Communication Service Providers to create and monetize a new breed of services—from Massive Machine Type Communication (mMTC) or Ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communication (uRLLC) to enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB)—through standard frameworks to design, create, and manage network resources that can be packaged and exposed directly to the end users.
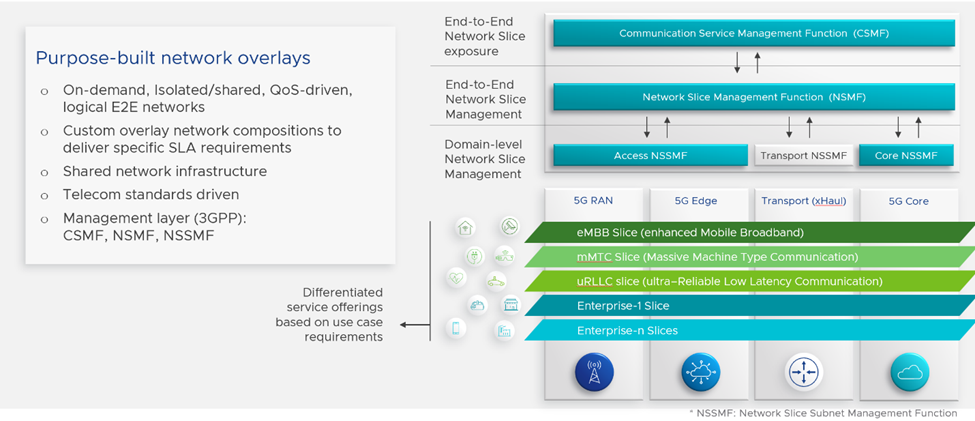
5G Network Slicing enables Communication Service Providers to create on-demand, isolated, end-to-end logical networks running on a shared and common infrastructure. These programmable overlay networks are associated with specific business purposes and follow a set of predefined SLAs with Quality-of-Service indicators (QoS) and security requirements. Network Slicing for VMware Telco Cloud Automation provides a standard way of managing and exposing network resources to the end user, while assuring the delivered slice’s purpose and characteristics (i.e., throughput, latency, geographical location, isolation level, etc.)
Network Slicing for VMware Telco Cloud Automation supports 3GPP standard-compliant Network Slicing management, enabling users to plan, design and instantiate end-to-end network slices across the RAN, edge, core and transport network domains, as illustrated in Figure 5 below. Network Slicing for VMware Telco Cloud Automation allows Communication Service Providers to unify these domains and close the gap between the endpoint consumed services and the required network resources, from physical or cloud infrastructure.
Support for VMware Integrated OpenStack (VIO)
Building on previous versions of VMware Telco Cloud Automation, VMware Telco Cloud Automation 2.1 continues to increase support of and integration with VMware Integrated OpenStack. With VMware Telco Cloud Automation 2.1, Communication Service Providers find improved integration with VMware Integrated OpenStack and support for its high-performance configuration settings. This integration, moreover, continues to cement VMware Telco Cloud Automation as a differentiating automation tool for NFVi as VMware Integrated OpenStack serves as an integral VIM in VMware Telco Cloud Platform’s NFV infrastructure. As such, VMware Telco Cloud Automation continues to offer robust support for 4G, VNF-based environments and can now support customers’ data-intensive applications and leverage Enhanced Platform Availability (EPA).[1] These automated VMware Integrated OpenStack configurations and customizations, in short, support new high-performance applications and allow the Communication Service Provider to monetize on related services (i.e., 4G vEPC, vIMS).
Improved Platform Operability & RAN Performance
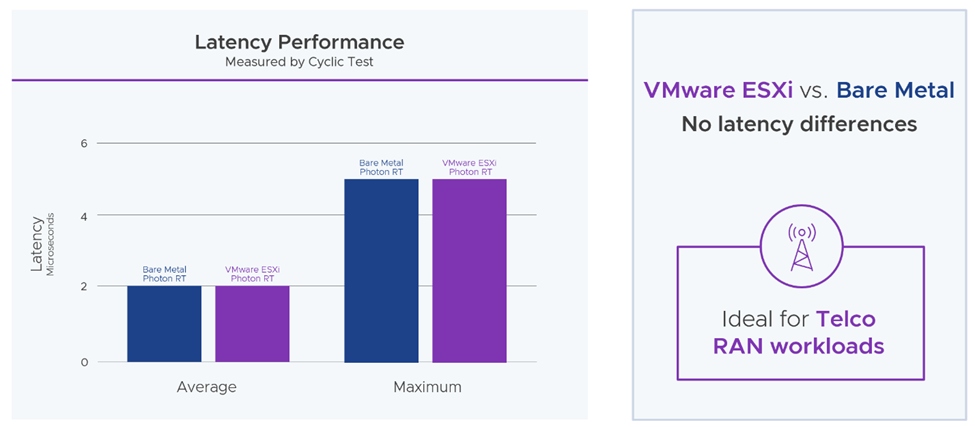
VMware Telco Cloud Automation 2.1, combined with VMware Telco Cloud Platform RAN, provides myriad RAN-specific automation benefits—offering Communication Service Providers an unprecedented ability to scale their RAN sites and modernize their networks. VMware Telco Cloud Automation, through VMware Telco Cloud Platform RAN, simplifies RAN operations with on-demand resource provisioning, reduces the time to deploy new RAN sites and decreases DU instantiation times with simplified template customization—all while achieving low-latency performance equal to bare metal (see Figure 6 below). As such, Communication Service Providers can scale new sites rapidly and with ease.
Telco Cloud Automation 2.1 also offers a broad range of platform operability enhancements. With this latest update, Communication Service Providers can integrate with an external Active Directory system for improved user authentication, in addition to vCenter Server authentication. Communication Service Providers will find new security upgrades like the ability to build an airgap server in an isolated environment with no internet connectivity. Scalability improvements also allow Communication Service Providers to support up to 25,000 CNFs.
As an additional security necessity and due to the shortage in IPv4 addresses, Communication Service Providers require IPv6 for VM and cloud-native use of Telco Cloud Automation. In other words, Communication Service Providers cannot use their network without additional IP addresses. IPv4 lacked the necessary scale that IPv6 now offers. The ability to scale and expand new networks and services with IPv6 allows Communication Service Providers to deploy Telco Cloud Automation 2.1 in an IPv6-only (IPv6 single-stack) network and, correspondingly, manage IPv6 infrastructure, CaaS, and VNFs and CNFs—improving security and scale of operations.
Advanced CaaS Operations
Updated CaaS API
Telco Cloud Automation 2.1 offers improved CaaS operability—upgrading the current CaaS infrastructure API version. With this upgrade, users now have increased control over cluster failures and can view the status of all the components at a granular level—giving them the ability to act on a failure while the cluster creation is in progress. Also, during the cluster creation process, the user can edit or delete a node pool or an add-on at any point in the event of an error.
Improved Lifecycle Management
Telco Cloud Automation 2.1 also supports the installation of AKO operator for clusters (AVI Load-Balancer Kubernetes Operator Lifecycle Management) and the installation of Tanzu Kubernetes Grid extensions like Prometheus and Fluentbit. Telco Cloud Automation 2.1’s support for these extensions improves lifecycle management operations of Kubernetes clusters.
Increased Cluster Monitoring & Security
With Telco Cloud Automation 2.1 the user can now diagnose issues and perform health checks on a CaaS Cluster or a Node Pool directly from the VMware Telco Cloud Automation UI. VMware Telco Cloud Automation provides users with separate diagnosis tests for Management Clusters, Workload Clusters, and Node Pools—enabling a thorough assessment throughout the stack.
Telco Cloud Automation 2.1 also offers secure Kubectl access to enable restricted access to VMware Tanzu Kubernetes Grid through VMware Telco Cloud Automation—giving the operator the ability to issue one-time passwords and tokens with expiry dates and the ability to revoke them, if necessary. These monitoring and security enhancements give Communication Service Providers more control over the managed resources, allowing them to easily troubleshoot clusters.
Template Developer Guide
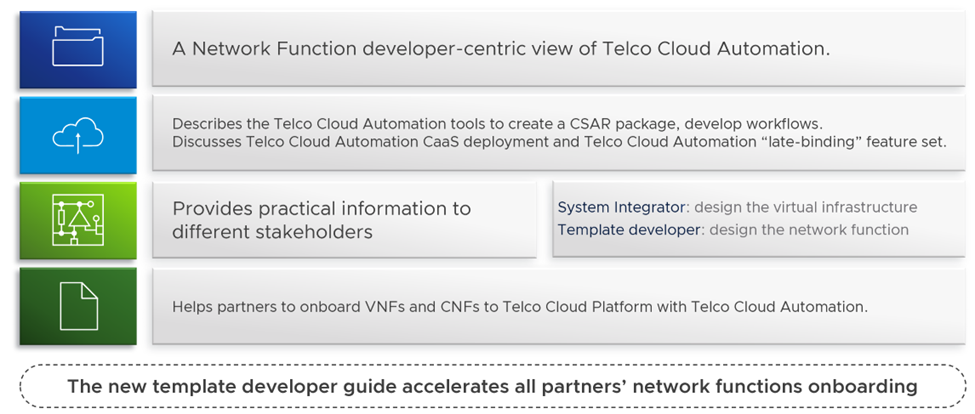
To improve and streamline the process for integrating and onboarding VNFs and CNFs to VMware Telco Cloud Automation, Telco Cloud Automation 2.1 offers a holistic document that details instructions for VNF and CNF vendors seeking integration with VMware Telco Cloud Automation (see Figure 7 below). The Template Developer Guide supports seamless package creation and allows Communication Service Providers to access new VNFs and CNFs with ease and will be woven into our Ready for Telco Cloud Program.
Partner Ecosystem (ISVs/NEPs)
A fundamental aspect of any orchestration solution is its ability to evolve in a multi-cloud, multi-vendor ecosystem. As an infrastructure provider for many years, VMware has a robust group of network function partners certified on its technology (260+ network functions certified from all major equipment providers—see Figure 8 below for additional detail). As part of Telco Cloud Automation’s efforts, many of these partners now integrate their VNFs and CNFs to both automation and infrastructure layers of the Telco Cloud. The certification process validates the partner network function CSAR package conformity and the crucial steps of onboarding and lifecycle management over the Telco Cloud platform. This important process allows Communication Service Providers to accelerate the deployment of their network functions and limits the risks associated with interoperability.

Conclusion
The confluence of the new features central to Telco Cloud Automation 2.1 provides comprehensive, centralized multi-layer automation for Communciation Service Providers at any stage of network development—from those deploying 4G-based VNFs to those seeking hybrid VNF/CNF deployments to those entirely cloud-native. VMware Telco Cloud Automation’s multi-layer, multi-domain management also, importantly, helps Communication Service Providers reduce costs and unlock incremental sources of revenue.
Coupled with the VMware Telco Cloud Platform, VMware Telco Cloud Automation establishes an open, disaggregated, vendor-agnostic ecosystem for Communication Service Providers to streamline 4G and 5G service delivery. From design to lifecycle management automation, VMware Telco Cloud Platform with VMware Telco Cloud Automation create a unified, developer-friendly architecture with key capabilities for resource optimization, operational consistency, multi-cloud mobility, and multi-layer automation. To manage the ballooning costs and complexities with rapidly-expanding networks, the integration of Telco Cloud Automation 2.1 with VMware Telco Cloud Platform empowers Communication Service Providers to modernize their network architectures, transform their businesses, and accelerate the delivery of disruptive, next-gen services.
[1] EPA, like “late-binding” for Kubernetes, allows a user to set customizable configurations for VMware Integrated OpenStack. In other words, EPA permits a user to create or edit an NF to enable certain advanced properties.
Discover more from VMware Telco Cloud Blog
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.







