Today’s post explains how to establish certificate-based authentication for Microsoft Office 365 in VMware Identity Manager.
App Access & Management with VMware Workspace ONE |
| [tabs slidertype=”simple” fx=”slide”][tab]
VMware Workspace ONE unifies VMware Identity Manager access control and application management and VMware AirWatch unified endpoint management (UEM) technology into a single platform. Available as a cloud service or for on-premises deployments, the Workspace ONE platform enables IT to deliver and manage any app on any device. |
Office 365 Certificate Authentication with Identity Manager Overview |
| [tabs slidertype=”simple”] [tab]
Certificate-based authentication for Microsoft Office 365 provides employees seamless access to email and other resources. Relying on client certificates simplifies authentication by eliminating the need for employee username and password combinations. Pair certificate-based authentication for Office 365 with VMware Workspace ONE to streamline access for Windows, Android and iOS devices. [/tab] [/tabs] [tabs slidertype=”simple”] [tab] Benefits of Certificate-Based Authentication
[/tab] [/tabs] |
Office 365 Certificate Authentication with Identity Manager Configuration |
[tabs slidertype=”simple”] [tab]
Before You Begin
[/tab][/tabs] [tabs slidertype=”simple”] [tab] Configure Office 365 Certificate Authentication with Identity ManagerThe video at the top of this post provides a how-to demonstration of Office 365 certificate authentication with Identity Manager. For step-by-step instructions of the processes covered in the video, expand the drop-down menus. [/tab][/tabs] [learn_more caption=”Step 1: Download the Root & Intermediate CA Certificate”] Download Root & Intermediate CA CertificateTo configure a trusted CA in Azure, upload any applicable root and intermediate certificates for the CA issuing the user certificates.[/learn_more][learn_more caption=”Step 2: Install AzureAD PowerShell Module”] Install Azure AD PowerShell ModuleInstall Azure AD PowerShell Module 2.0.0.33 or higher for use configuring the Azure AD trusted CA.
[/learn_more][learn_more caption=”Step 3: Configure Azure AD Trusted CA”] Configure Azure AD Trusted CAAfter installing PowerShell, use it to connect with Azure AD and configure a trusted CA. Then, validate the CA’s configuration.
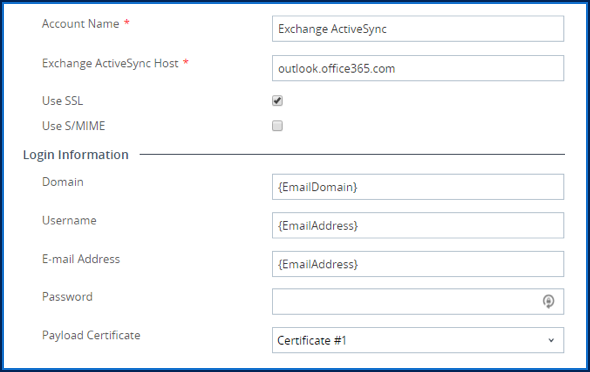
[/learn_more][learn_more caption=”Step 4: Configure the Certificate Template in AirWatch”] Configure the Certificate Template in AirWatchAfter configuring the trusted CA in PowerShell, configure a template that requests client certificates in the AirWatch console. Certificates must contain the Office 365 user principal name (UPN) to map correctly to devices. Add the Office 365 UPN as a subject alternative name (SAN) value in either the UPN or email (RFC822) field. [/learn_more][learn_more caption= “Step 5: Create an Exchange ActiveSync Profile in AirWatch”] Create an Exchange ActiveSync Profile in AirWatchAfter creating the certificate template in the AirWatch console, create a device profile that provisions user certificates to enrolled devices.
[/learn_more][learn_more caption= “Step 6: Create Authentication Policies for Fallback Flow”] Create Authentication Policies for Fallback FlowIn Azure, certificates created in a trusted CA, are Optional (back to IIS terminology). This means that authentication does not solely rely on certificates. In lieu of a certificate, Azure falls back to basic authentication. In turn, ActiveSync traffic falls back to the default WS-Federation active flow. To make sure only devices with valid certificates access Exchange Online, create policies to block off authentication via basic credentials. In the Identity Manager admin catalog, navigate to the Office 365 application. Then, from the access policies menu, create policies to either block all or only allow a subset of users/clients to authenticate with basic credentials. [/learn_more] |

 [/tab][/tabs]
[/tab][/tabs]