VMware NSX Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) provides a robust solution for isolating, securing, and self-managing network resources in a private cloud environment. With the release of VMware Cloud Foundation (VCF) 5.2.1, VMware introduces new features that enhance multi-tenancy support and simplify network operations. In this blog, we explore how VMware NSX VPC helps you achieve an advanced Cloud Operating Model and the exciting new NSX VPC integration with vCenter introduced in VCF 5.2.1.
What is VMware NSX VPC?
VMware NSX VPC empowers enterprises to build isolated network environments within their VCF private cloud, much like Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs) in public clouds. Introduced in NSX 4.1.1, this feature allows each project, department, or tenant to define its own subnets, networking services (like NAT), firewall rules (Distributed and Perimeter), and an advanced load balancer like AVI. This simplifies network and security management, giving users a self-service model similar to public cloud environments.
With NSX VPC, each project, department, or tenant has its own networking policies and security controls. This isolation and flexibility are critical for organizations looking to adopt a cloud operating model strategy to enhance security, simplify network management, increase agility, and improve time to market.
NSX VPC in a private cloud enables:
- Simplified Network Consumption: Eliminate complex physical network configurations. VPCs streamline virtual network deployment and setup.
- Self-Service Model: Empower application owners with self-service capabilities for network provisioning, freeing up network teams for more strategic tasks.
- Multi-Tenancy: VPCs provide strong isolation between tenants, ensuring secure and independent network environments.
- Enhanced Security: Application owners gain the ability to create DFW rules for their applications only and enforce strict security by implementing micro-segmentation policies.
- Operational Efficiency: Administrators provide networking and security guardrails and monitor all VPCs from a centralized view. They also control networking resources via quotas for various projects or teams.
VMware NSX VPC is essential for enterprises looking to modernize their private cloud infrastructure. It enables faster deployment, more consistent networking policies, and reduced operational complexity.
What’s New in VMware Cloud Foundation 5.2.1?
The latest release of VCF 5.2.1 brings enhanced features that further improve the operational management of NSX VPCs in private clouds. One of the most notable features is the integration of NSX Projects and VPCs directly into vCenter, allowing for seamless visibility and management of these network resources.
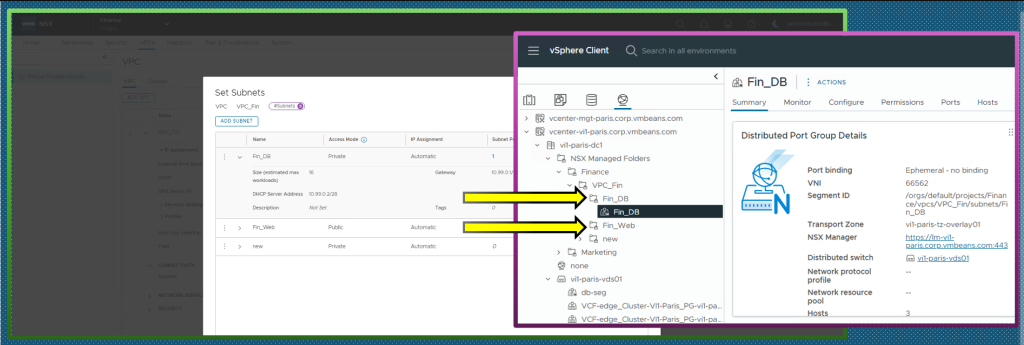
NSX VPC in vCenter
VCF 5.2.1 introduces a significant enhancement to network management: NSX VPCs are now visible with in vCenter! This means vCenter now displays NSX Projects and VPCs in an organized tree structure directly within the vCenter Network tab. This streamlines multi-tenancy management and makes it easier for administrators to manage isolated networking environments. You’ll gain better visibility and control over network segments, enabling quicker and more efficient network configuration for individual projects or tenants.
Key Benefits:
- Simplified Management: Application owners can now manage their VPC subnets directly in vCenter with an intuitive tree structure for easy navigation and organization. No need for them to access NSX Manager to assign Virtual Machine to the VPC Subnet!
- Enhanced Isolation: Control user visibility to enhance environment isolation. Each vCenter user can be restricted within vCenter to see only their own VPC networks (port groups) within the shared private cloud infrastructure.
- Automation and Efficiency: Automate VPC deployment through VMware Cloud Foundation Automation and streamline network segmentation for tenants, projects, or departments. Create and manage isolated environments with ease.
This integration provides a centralized view of all VPC-related networking operations, reducing the need to manage separate tools for network configuration and simplifying private cloud operations.