
In computer systems, a snapshot is the state of a system at a particular point in time. To avoid downtime, high-availability systems may instead perform the backup on a snapshot—a read-only copy of the data set frozen at a point in time—and allow applications to continue writing to their data. [ Wikipedia ]
This blog addresses how one can take VM level snapshot of Oracle Single Instance / RAC workloads using VMware snapshot technology, keep certain caveats in mind.
VMware Snapshots
Snapshots capture the entire state of the virtual machine at the time you take the snapshot. You can take a snapshot when a virtual machine is powered on, powered off, or suspended. To take a snapshot of a suspended virtual machine, wait until the suspend operation finishes before you take a snapshot.
When you create a memory snapshot, the snapshot captures the state of the virtual machine’s memory and the virtual machine power settings. When you capture the virtual machine’s memory state, snapshots that capture the memory state of a virtual machine take longer to complete. You might also see a momentary lapse in response over the network.
When you quiesce a virtual machine, VMware Tools quiesces the file system in the virtual machine. The quiesce operation pauses or alters the state of running processes on the virtual machine, especially processes that might modify information stores on the disk during a restore operation.
More information on VMware Snapshots can be found here.
Considerations with VMware Snapshot and Oracle workloads
An important consideration needs to be kept in mind with regards to VMware snapshots. When a snapshot removal (consolidation) is in progress, you cannot perform other VM tasks, such as power operations, or vMotion migration, in the virtual machine. You must remove the snapshot without any interruption to ensure data integrity. Based on the amount of snapshot delta to be committed, the amount of time varies.
For busy virtual machines, the volume of activity may consume system resources for longer than a usual amount of time. The Virtual Machines are stunned for the duration of the consolidate. In typical circumstances, this process is completed almost immediately. VM with considerable amounts of delta gathered in the temporary snapshot are stunned for a noticeable or disruptive amount of time. This can have adverse effects on guest applications or services
This may affect Oracle database operations, so the recommendation is to delete or coalesce the VM snapshots during outside business processing times, during a quiet period when we do not have any heavy database activities.
More information on this can be found in the KB ‘Snapshot removal stops a virtual machine for long time (1002836)’
VMware vmdk Multi-writer flag (MWF)
By default, the simultaneous multi-writer “protection” is enabled for all. vmdk files ie all VM’s have exclusive access to their vmdk files. So in order for all of the VM’s to access the shared vmdk’s simultaneously, the multi-writer protection needs to be disabled.
The below table describes the various Virtual Machine Disk Modes:

As we all are aware of , Oracle RAC requires shared disks to be accessed by all nodes of the RAC cluster.
KB 1034165 provides more details on how to set the multi-writer option to allow VM’s to share vmdk’s.. As per this KB, Requirement for shared disks with the multi-writer flag setting for a RAC environment is that the shared disk is
- has to set to Eager Zero Thick provisioned
- need not be set to Independent persistent
While Independent-Persistent disk mode is not a hard requirement to enable Multi-writer option, the default Dependent disk mode would cause the “cannot snapshot shared disk” error when a VM snapshot is taken.
Use of Independent-Persistent disk mode would allow taking a snapshot of the OS disk while the shared disk would need to be backed up separately by a third-party vendor software
Supported and Unsupported Actions or Features with Multi-Writer Flag

**** Important ***
- SCSI bus sharing is left at default and not touched at all in case of using shared vmdk’s. – Leave it alone for RAC with shared vmdk’s!!!
- It’s only used for RAC’s with RDM (Raw Device Mappings) as shared disks.
VMware recommends using shared VMDK (s) with Multi-writer setting for provisioning shared storage for ALL Oracle RAC environments (KB 1034165)
The Oracle on VMware Hybrid Cloud High availability guide can be found here
High Level Summary of the exercise below
- VMware recommends using shared VMDK (s) with Multi-writer setting for provisioning shared storage for ALL Oracle RAC environments (KB 1034165)
- Trying to take VM level Snapshot’s of the online OR offline RAC VM’s with both non-shared vmdk’s and shared vmdk’s , all vmdk’s et disk mode as ‘Dependent’ will error out
- For non-shared vmdk’s, Oracle RAC VM’s Snapshot can be taken, to backup OS and Oracle binaries , by setting the RAC shared vmdk’s to disk mode ‘Independent-Persistent’
- Setting disk mode of shared vmdk’s as Independent-Persistent would allow taking a snapshot of the non-shared vmdk’s (OS and Oracle binaries)
- Shared vmdk’s/ disks would need to be backed up separately either using Oracle RMAN, a Third-party vendor Agent based software or Storage based backup
- Storage based backup of shared vmdk’s could include
- In case of VMFS based FC datastores, backup of vmdk’s datastore ensures datastore / lun level backup , we do not get vmdk level granularity
- In case of vmdks backed up Virtual Volumes, storage based vVOL level backup ensures vmdk level granularity
- In case of RDM’s are used, storage based backup of RDM luns
- ensures datastore / lun level backup , we do not get vmdk level granularity
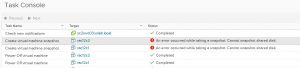
Trying to take VM level Snapshot’s of the online OR offline RAC VM’s with both non-shared vmdk’s and shared vmdk’s , all vmdk’s et disk mode as ‘Dependent’ will error out.
Powering off the RAC Cluster VM and taking a VM snapshot fails as shown below.
Oracle single Instance database and VMware Snapshot
From a VM perspective, steps to take a VM level snapshot, whether the underlying storage is VMFS or NFS or vSAN or even vVOL, is the same.
The “Oracle Database 12c on VMware vSAN — Day 2 Operations and Management” guide covers the day 2 operation of VM’s running an Oracle workload on a VMware vSAN environment.
Example of an Oracle Single Instance Setup with VMware Snapshot
Setup bellow shows a VM ‘Oracle19c-BM’ hosting 19c Grid Infrastructure and RDBMS on OS OEL 7.6. An Oracle Single instance database ‘dbprod’is created on this VM.
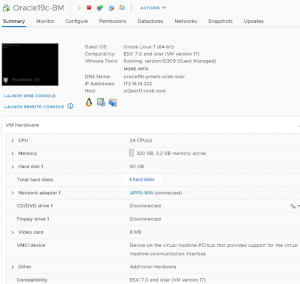
The VM ‘Oracle19c-BM’ has 4 vmdk’s and the vmdk’s are backed up a Pure X50 AFA storage array
- Hard disk 1 (60 G) is on SCSI0:0 and is for root volume (/)
- Hard disk 2 (60 G) is on SCSI0:1 and is for oracle binaries (/u01 for Grid and RDBMS binaries)
- Hard disk 3 (2 TB) is on SCSI1:0 and is for oracle database files
- Hard disk 4 (100 G) is on SCSI2:0 and is for oracle redo logs files
All vmdk’s including the database vmdk were set to
- Sharing set to ‘No Sharing’
- Disk mode is set to ‘Dependent’
Details of the database vmdk is shown below:
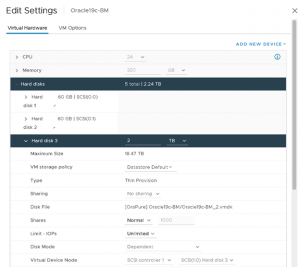
As mentioned above, While Independent-Persistent disk mode is not a hard requirement to enable Multi-writer option, the default Dependent disk mode would cause the “cannot snapshot shared disk” error when a VM snapshot is taken.
Use of Independent-Persistent disk mode would allow taking a snapshot of the OS disk while the shared disk would need to be backed up separately by a third-party vendor software
To take a snapshot of the Oracle VM hosting the single instance database, we can either
- Set the single instance database in a Begin backup mode, take the VM snapshot, and End the backup mode
- Take a database crash consistent snapshot
We decided to go with the database crash consistent snapshot.
The steps to take a VM level snapshot of an single instance database in a crash consistent mode are the same as the case of a regular VM.
Click VM ‘Edit Settings’, then click ‘Take Snapshot’
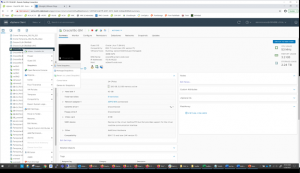
We decided not to take the snapshot with VM memory, as explained, when you capture the virtual machine’s memory state, snapshots that capture the memory state of a virtual machine take longer to complete.
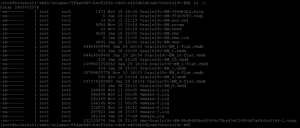
After the successful completion of the VM Snapshot, login to the ESXi server via ssh and check the VM ‘Oracle19c-BM’ folder on the datastore.
Before the snapshot, we can see ‘*-flat.vmdk’
After the VM snapshot is taken – we can see the Snapshot vmdk’s as well, ‘*-000001.vmdk’ and ‘*-000001-sesparse.vmdk’.
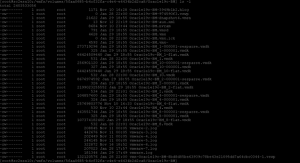
We can now use Third party backup vendor software to create backups from the VM snapshots
Example of an Oracle RAC Setup with VMware Snapshot
Setup bellow shows an Oracle RAC with 2 VM’s ‘rac19c1’ and ‘rac19c2’. hosting 19c RAC Grid Infrastructure and RDBMS on OS OEL 7.6 with Oracle RAC database ‘rac19c’.
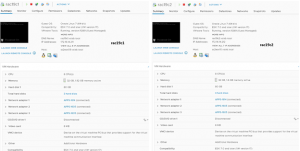
Both VM’s ‘rac19c1’ and ‘rac19c2’ have has 3 vmdk’s and the vmdk’s are backed up a VMware vSAN storage
- Hard disk 1 (880 G) is on SCSI0:0 and is for root volume (/)
- Hard disk 2 (80 G) is on SCSI0:1 and is for oracle binaries (/u01 for Grid and RDBMS binaries)
- Hard disk 3 (1 TB) is on SCSI1:0 and is for RAC cluster data
The OS and Oracle Binaries vmdk’s were set to
- Sharing set to ‘No Sharing’
- Disk mode is set to ‘Dependent’
The RAC cluster shared vmdk was set to
- Sharing set to ‘Multi-writer’
- Disk mode is set to ‘Independent-Persistent’
Details of the shared database vmdk is shown below:
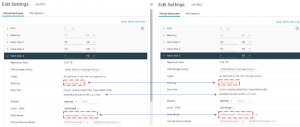
As mentioned above, While Independent-Persistent disk mode is not a hard requirement to enable Multi-writer option, the default Dependent disk mode would cause the “cannot snapshot shared disk” error when a VM snapshot is taken. Use of Independent-Persistent disk mode would allow taking a snapshot of the OS disk while the shared disk would need to be backed up separately by a third-party vendor software
To take a snapshot of the RAC VM hosting the RAC database, we can either
- Set the RAC database in a Begin backup mode, take the VM snapshot, and End the backup mode
- Take a database crash consistent snapshot
We decided to go with the database crash consistent snapshot.
The steps to take a RAC VM level snapshot of an RAC database in a crash consistent mode are the same as the case of a Single instance Oracle VM.
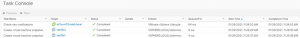
VM level snapshot’s of RAC VM’s ‘rac19c1’ and ‘rac19c2’ is taken.
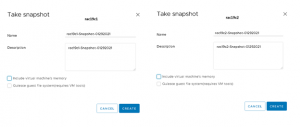
Details of RAC VM snapshot are shown as below.
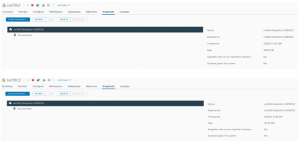
RAC VM snapshot have been successfully taken.
.
After the successful completion of the RAC VM Snapshots, login to the ESXi server via ssh and check the RAC VM ‘rac19c1’ and ‘rac19c2’ folders on the vSAN datastore.
After the RAC VM’s were snapshotted, we can see we have snapshot for all vmdk’s except the shared vmdk’s for the RAC cluster.

We can now use Third party backup vendor software to create backups from the RAC VM snapshot which comprises of the OS and Oracle binaries. The RAC database can be backed up via Oracle RMAN utility.
Summary
- VMware recommends using shared VMDK (s) with Multi-writer setting for provisioning shared storage for ALL Oracle RAC environments (KB 1034165)
- Trying to take VM level Snapshot’s of the online OR offline RAC VM’s with both non-shared vmdk’s and shared vmdk’s , all vmdk’s et disk mode as ‘Dependent’ will error out
- For non-shared vmdk’s, Oracle RAC VM’s Snapshot can be taken, to backup OS and Oracle binaries , by setting the RAC shared vmdk’s to disk mode ‘Independent-Persistent’
- Setting disk mode of shared vmdk’s as Independent-Persistent would allow taking a snapshot of the non-shared vmdk’s (OS and Oracle binaries)
- Shared vmdk’s/ disks would need to be backed up separately either using Oracle RMAN, a Third-party vendor Agent based software or Storage based backup
- Storage based backup of shared vmdk’s could include
- In case of VMFS based FC datastores, backup of vmdk’s datastore ensures datastore / lun level backup , we do not get vmdk level granularity
- In case of vmdks backed up Virtual Volumes, storage based vVOL level backup ensures vmdk level granularity
- In case of RDM’s are used, storage based backup of RDM luns
- ensures datastore / lun level backup , we do not get vmdk level granularity
- All Oracle on vSphere white papers including Oracle licensing on vSphere/vSAN, Oracle best practices, RAC deployment guides, workload characterization guide can be found at the “Oracle on VMware Collateral – One Stop Shop“
Discover more from VMware Cloud Foundation (VCF) Blog
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.





