
It’s official: the Internet of Things (IoT) is beyond the hype phase. For about 43 percent of enterprises, IoT is now a strategic business initiative either already in place or in the works, according to a 2016 Gartner survey.
Just how are huge organizations using connected “things” and the resulting Big Data generated to solve their most complex business problems? Here are five examples of enterprise IoT projects.
- BT uses location intelligence to more efficiently deploy engineers and roll out communications services to the field. UK-based communications services company BT uses Pitney Bowes location intelligence mapping applications to make the most efficient use of their employees and resources. Location intelligence technology helps the company analyze and visualize real-time sensor data from plant equipment. This information allows BT to more accurately pinpoint the location of their network, down to individual cables, in relation to customer properties. The company is then able to respond faster to outages and use that combined location and customer data to make more informed decisions when rolling out new services.
- Siemens turns wind farms into smart, distributed machines. Siemens, the largest engineering company in Europe, is one of the world’s leading suppliers of wind power solutions. To ensure they maximize the use of expensive wind farms in unpredictable weather, the company uses RTI messaging software to remotely monitor hundreds of wind turbines for predictive maintenance and adjust them to balance periods of high wind.
-
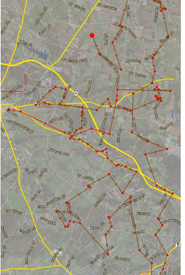 UPS delivers operational cost savings tracking drivers’ routes. UPS installed GPS tracking technology and vehicle sensors to delivery trucks in 2008 to identify the shortest and most cost-efficient route combinations. UPS’s On-Road Integrated Optimization and Navigation (ORION) data-crunching technology has already helped the company save an estimated 1.5 million gallons of fuel on 10,000 routes alone. The package delivery company plans to use ORION technology to optimize every North American route (55,000 total) by 2017.
UPS delivers operational cost savings tracking drivers’ routes. UPS installed GPS tracking technology and vehicle sensors to delivery trucks in 2008 to identify the shortest and most cost-efficient route combinations. UPS’s On-Road Integrated Optimization and Navigation (ORION) data-crunching technology has already helped the company save an estimated 1.5 million gallons of fuel on 10,000 routes alone. The package delivery company plans to use ORION technology to optimize every North American route (55,000 total) by 2017. - Ochsner integrates IoT medical devices and data with electronic medical records. New Orleans-based Ochsner Health System integrated their electronic health record (EHR) system, Epic, with wearable and IoT technology to improve patient engagement and outcomes. Real-time patient health data, from IoT endpoints like wireless scales and blood pressure monitors, feeds directly into the patients’ Epic medical record so that doctors can remotely monitor patients and more accurately analyze their health.
-
 AT&T container tracking builds efficiencies into shipping operations. Shipping companies leveraging AT&T’s intelligent container fleets can gain greater visibility into their container or trailer fleet. With this real-time data, companies can better prevent theft, more accurately track inventory and more efficiently manage the distribution process.
AT&T container tracking builds efficiencies into shipping operations. Shipping companies leveraging AT&T’s intelligent container fleets can gain greater visibility into their container or trailer fleet. With this real-time data, companies can better prevent theft, more accurately track inventory and more efficiently manage the distribution process.
The Role of IoT in End-User Computing

IoT-generated data and IoT devices need to be secured and managed from a central place, right alongside all of the other technology and endpoints in the enterprise. And data will need to be connected to existing business systems so that employees can access IoT intelligence within business-critical applications. Essentially, IoT brings distributed enterprise resources into the EUC environment, which makes them more visible, accessible and, as a result, valuable.
The growth of enterprise IoT will have a profound impact on the future of EUC. Read more about VMware’s approach to IoT.








