by: VMware Director, Solutions Engineering and Design Swapnil Hendre and VMware Director, IT App Ops Mukund Yadav
To learn more about how VMware IT’s NSX micro-segmentation strategy, read the blog, “Applying NSX Data Center Micro-Segmentation Across Applications in VMware IT’s Global Environment.”
Applications are rapidly evolving to meet the constant demand from business to deliver new functionality. Classic data center designs assume that all east-west (server-to-server) traffic is allowed, and any device inside the data center is generally authorized to communicate with any other device in the data center. Because all devices exist inside a hardened security perimeter, everything should be safe from external attack. Recent data breaches have shown that this assumption is not always correct.
In this blog, we will discuss how we implemented NSX Data Center micro-segmentation internally as part of our ERP (SAP) migration to control east-west communications and improve our security posture. Each module was micro-segmented before it was rolled out to production. Due to the sheer volume of workflows involved, this was one of the more complex micro-segmentation projects VMware IT has undertaken to date.
From start to finish, the process took about three months. The policy creation process only took a few days; most of the time was spent in discovery due to the high volume of traffic and testing to ensure the connections were as clean as possible before SAP was launched into production.

SAP Micro-Segmentation Overview
Without NSX Data Center micro-segmentation, SAP landscapes have few or no lateral controls inside the perimeter. If one virtual machine (VM) is compromised, the threat can move laterally and put the entire SAP landscape at risk.
The VMware NSX Data Center product natively enables micro-segmentation and the ability for us to implement a Zero-Trust architecture in which security services specify the traffic that is permitted and everything else is blocked. Zero-Trust centers on the belief that an organization should not trust anything inside or outside its perimeters and instead should verify anything connecting to its systems before granting access.
NSX Data Center micro-segmentation was implemented using a well-defined process that starts with application discovery (the process of identifying unique data flows), followed by dynamic security group creation, security policy creation, reporting / alerting, and finally security policy enforcement (blocking unauthorized traffic).
Here are the steps we followed for the micro-segmentation of each SAP module:
- Identified the servers in the app and organized them into different functional groups. We worked with the migration team to capture server names and created dynamic groups according to their functionality, such as application servers and database servers.
- Defined a security policy for each group. Next, we wrote separate firewall rules for each group, then mapped the security policies to each group. Applying firewall rules to a group instead of individual VMs simplified and centralized management.
- Enabled the discovery, capture, and analysis of traffic in and out of the application. vRealize Log Insight was used to identify the traffic flows in and out of each SAP module. (We switched to using vRealize Network Insight for subsequent micro-segmentation projects). Because of the complexity of our SAP landscape and the sheer volume of data, global security policies were implemented for core services such as NTP, DNS, backups, SMTP, etc. By disabling logging for these services, we could better handle the remaining workflow data.
- Defined, enabled, and tested the firewall rules that restrict east to west traffic. We reviewed the firewall rules for each SAP module with the development teams, including the usual traffic between load balancer, application servers, and databases, and the traffic from middleware and management tools. These rules were reviewed against corporate policies with the Information Security (InfoSec) team, then implemented in a pre-production environment.
- Tested to ensure that each module was working as expected. When any issues were reported during pre-production testing, we reviewed the relevant source-target IPs and port numbers and modified them as necessary. We followed the same process to implement the rules in production.
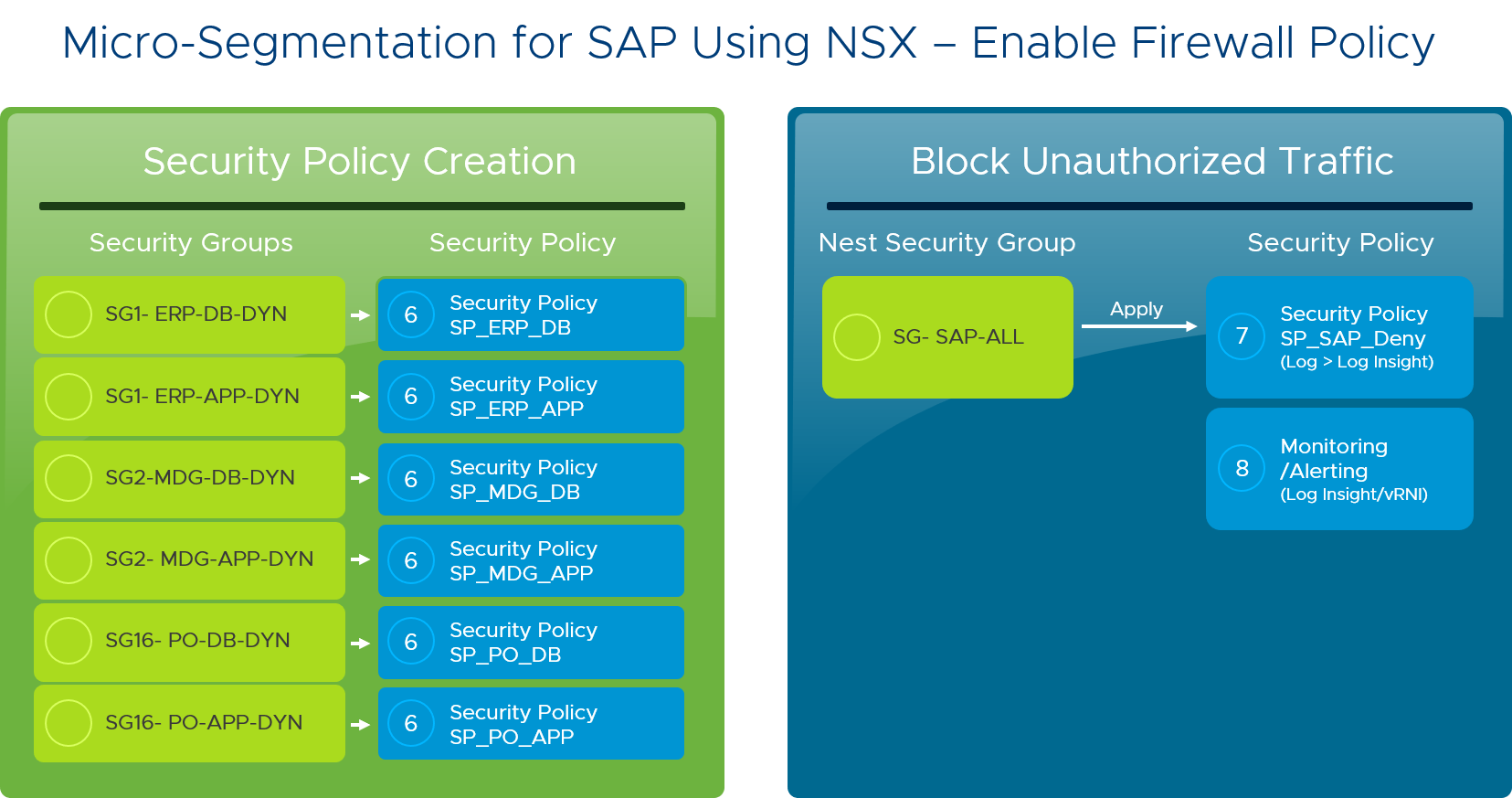
Now, each SAP application is secured using the NSX Data Center distributed firewalls, which essentially means each VM now has its own network perimeter. In addition, security policies are aligned with logical groups, and unauthorized traffic is blocked. The security blast radius is dramatically minimized.

The SAP project was a business-critical greenfield deployment with a high level of complexity and visibility. As a result, we needed to carefully consider our approach during the migration. We worked with multiple teams (Development, QA, Security, Cloud, Application Operations) to ensure the integrity of each module’s micro-segmentation policy in the rapidly changing environment.
Micro-Segmentation Rules
Our SAP micro-segmentation project involved both custom and standard rules. In the following table is a sample rule set we used. vRealize Network Insight (recommended) or vRealize Log Insight simplify the process of planning the rule set.
Sample Rule Set

What We Learned
During the SAP micro-segmentation process IT learned several lessons that can be applied to future projects:
- We implemented comprehensive, automated alerting so that the Operations teams could quickly identify the root causes of issues before any impact on users.
- We did extensive testing in a non-production environment to ensure that SAP behaved normally. This helped us sort out many issues before they could impact users in production.
- Prior to the SAP deployment, we made sure the Operations and Application Support teams connected to servers via secure VDI, not from the local system.
Securing against external and internal threats is one of VMware IT’s highest priorities. The investment of time and resources to micro-segment all SAP modules provided the granular level of security IT needed to isolate and protect all parts of the application from any type of compromise. Watch this space as we post additional blogs about deploying NSX Data Center micro-segmentation for our other applications.
VMware on VMware blogs are written by IT subject matter experts sharing stories about our digital transformation using VMware products and services in a global production environment. Contact your sales rep or vmwonvmw@vmware.com to schedule a briefing on this topic. Visit the VMware on VMware microsite and follow us on Twitter.



