Optimize VNF Lifecycle Management using VMware Telco Cloud Automation with VMware Telco Cloud Infrastructure – Cloud Director Edition: Part 2
In part 1 of the series, we discussed the various advantages of integrating VMware Telco Cloud Automation with VMware Telco Cloud Infrastructure – Cloud Director Edition to allow Communication Service Providers (CSPs) to deliver modular, multi-tenant infrastructure that eases the lifecycle management of Virtual Network Functions (VNFs). The validation of this integration was carried out by instantiating a sample VNF via the vApp template method. vApp template method of instantiating a VNF is where each virtual machine (VM) of the VNF corresponds to one vApp. This method is useful in heterogenous environments because the different components that constitute a VNF in those environments are from different vendors or different platforms.
However, some Network Equipment Providers (NEPs) prefer to package all the components of the VNF into one entity, where all the VMs of the VNF belong to one vApp. This homogeneous approach provides much more granular control for NEPs and CSPs to enable consistent interoperability of the network function components. To support this type of deployment method, VMware Telco Cloud Automation instantiates the VNFs via the VNF method. VNF method of deployment in VMware Telco Cloud Automation refers to the deployment of VNFs as a single vApp with all the components or VMs packaged into it.
Furthermore, as part of lifecycle management, it is vital for CSPs to have a process in place to scale the VNFs in a quick, reliable, and agile manner. VMware Telco Cloud Automation integrates with VMware Telco Cloud Infrastructure – Cloud Director Edition to simplify the horizontal scaling of some components of the VNF or the entire VNF.
In this blog, we will walk through the process of instantiating a VNF via the VNF method and then showcase how VMware Telco Cloud Automation simplifies the scaling of the VNFs. For the purpose of this blog, we use a simple 3-tier application as our VNF.
Instantiate the network function via the VNF method
Using vApp templates from the VMware Cloud Director catalog drastically simplifies the process of instantiating a VNF on VMware Telco Cloud Infrastructure – Cloud Director Edition. Hence, the pre-requisite for VNF instantiation is preparing the VMware Cloud Director catalog with the VNF vApp template.
Let us start the process by creating a catalog in the organization VDC by navigating to Libraries -> Catalogs and providing the appropriate details in the organization VDC portal, as illustrated in Figure 1.
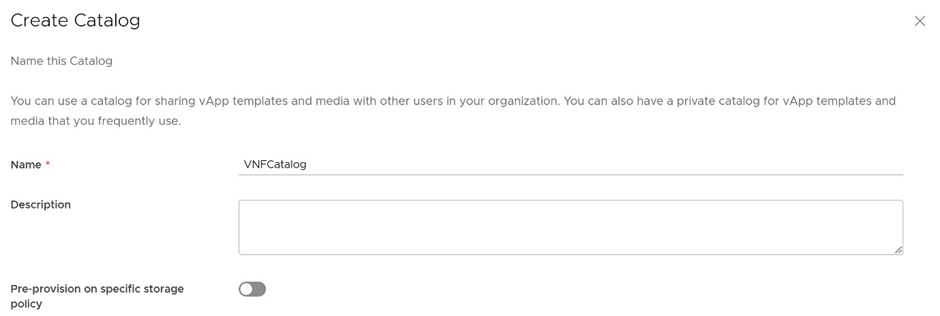
Figure 1: Create Catalog in Organization VDC of VMware Cloud Director
The creation of a vApp template from the OVA file of the VNF while attaching it to the catalog involves navigating to Libraries -> vApp Templates in the organization VDC portal, browsing the OVA file, and then furnishing the name of the vApp template and the catalog. An illustration of this process is depicted in Figure 2.

Figure 2: Create a vApp template
To verify that the vApp template represents the whole VNF with all its components, after the vApp template is successfully created, navigate to Libraries -> vApp Templates and click on the recently uploaded vApp template. In the Virtual Machines tab, you can observe that this vApp template contains all the VMs of our sample 3-tier VNF as illustrated in Figure 3.
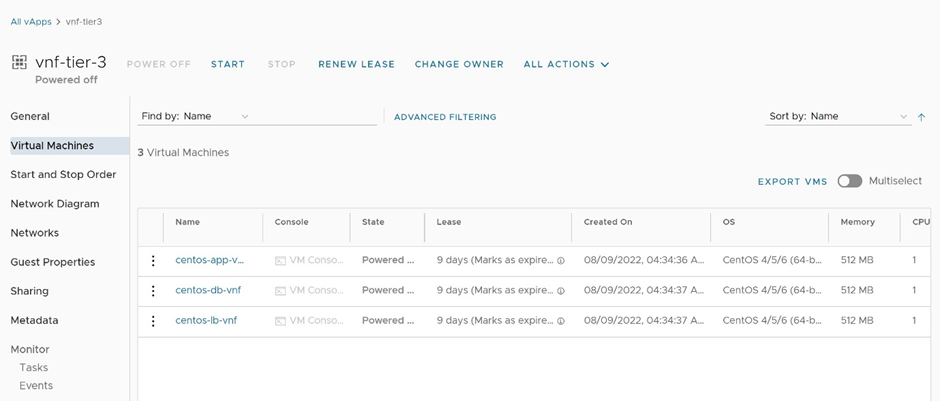
Figure 3: Verify vApp template has all the network function components
Once the catalog in VMware Cloud Director is prepared with appropriate VNF vApp template, we can leverage VMware Telco Cloud Automation to make the onboarding and instantiation of VNFs much easier. Onboarding a VNF in the VMware Telco Cloud Automation portal is a one-step operation of navigating to Network Functions in the Catalog section, and clicking Onboard Network Function. Then type in a name for the network function package, browse the CSAR file of the VNF and click Upload, as shown in Figure 4.
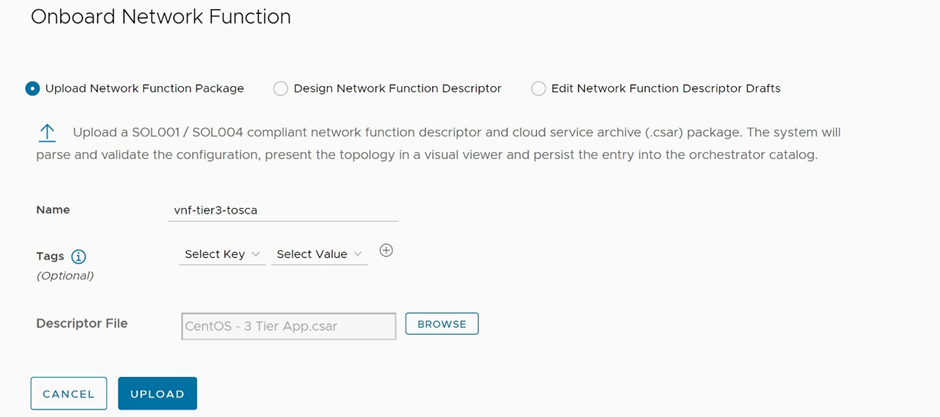
Figure 4: Onboard network function
This will onboard the CSAR file of the VNF to VMware Telco Cloud Automation as depicted in Figure 5.
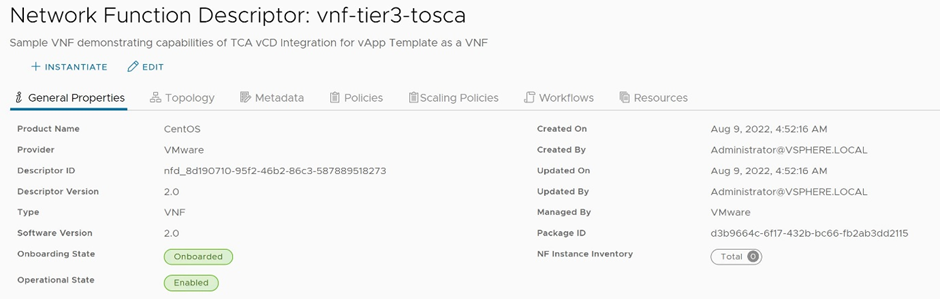
Figure 5: Onboarded VNF details
The most important step of the process is to instantiate the VNF, which involves the deployment of the VNF as a vApp on VMware Telco Cloud Infrastructure – Cloud Director Edition. To do that, click on Instantiate in the corresponding network function catalog details in VMware Telco Cloud Automation portal, provide a name for this instance, select the VMware Cloud Director VIM, select the compute profile pointing to the respective organization VDC, and an appropriate storage profile. Then choose the VNF template method, select the VMware Cloud Director catalog containing the template, and then select the vApp template which represents the whole VNF as illustrated in Figure 6 below.
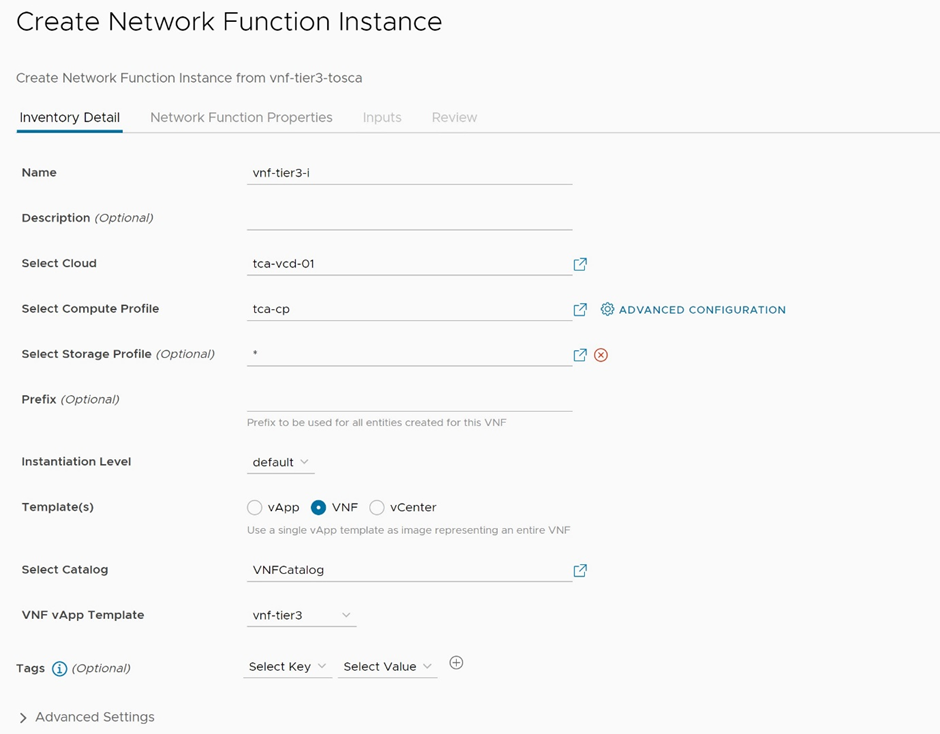
Figure 6: Instantiate the network function – select the infrastructure and template
In the Network Function Properties tab, select the overlay network segment for the load balancer VM’s external network connection point lb-external as shown in Figure 7. This network segment represents the network of the load balancer VM which has access to external segments outside the organization VDC.

Figure 7: Instantiate the network function – select organization VDC network
In the workflows tab, fill in the load balancer external IP. An example of this configuration is portrayed in Figure 8.
Note: In our case, we used an overlay segment as the external network for the load balancer VM and for this reason, the traffic entering or leaving the environment will need to be NAT’ed. If you are using a similar configuration, configure the DNAT IP here.
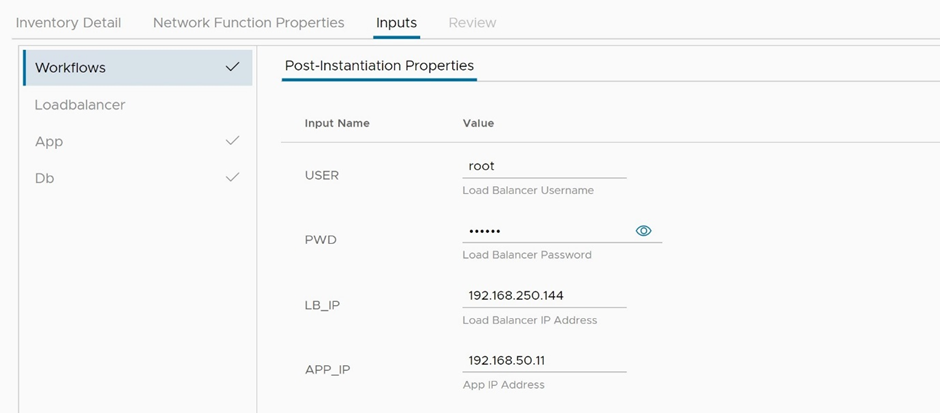
Figure 8: Instantiate the network function – post-instantiation properties
In the Load Balancer VM tab, enter the IP address, prefix, and gateway to be assigned to VM NIC attached to the overlay network segment, as depicted in Figure 9.
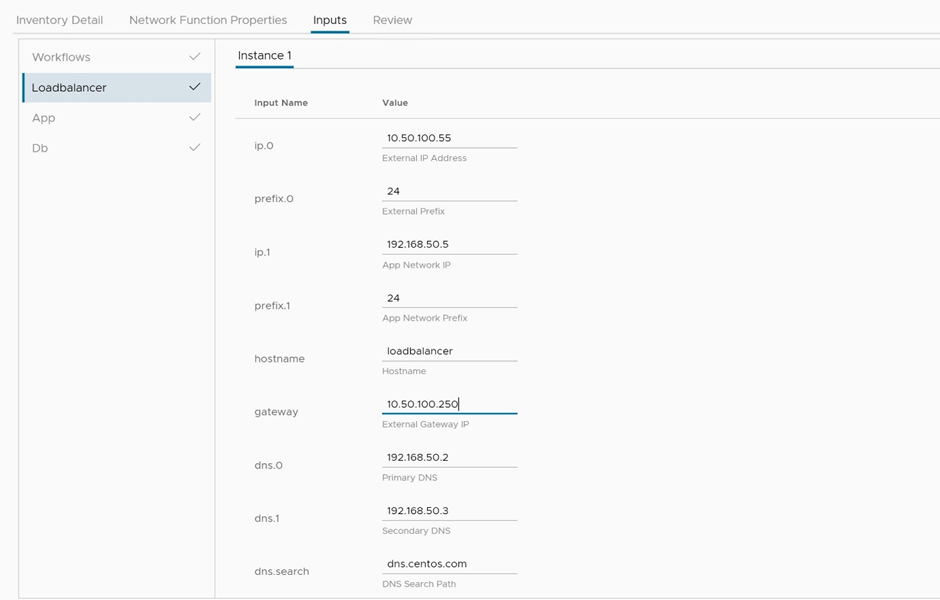
Figure 9: Instantiate the network function – load balancer properties
Review the whole configuration and instantiate the VNF. This instantiation of the sample 3-tier VNF via the VNF method takes around 15-20 minutes to create and configure all the VMs, an illustration of this process is shown in Figure 10.
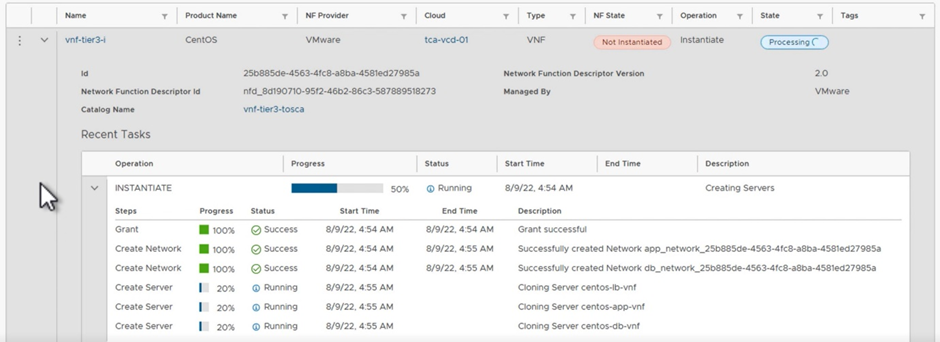
Figure 10: Process of network function instantiation
Once the instantiation process is completed, we can browse the application using the load balancer’s external IP and see that it is rendering the expected service as depicted in Figure 11.

Figure 11: Network function output
Scale the network function
Let us consider a scenario where the traffic to our 3-tier VNF has increased. This increased traffic must be processed by the front-end app tier of the application which can be overwhelmed with the increase in the load. To mitigate this overwhelming affect, we need to scale the app tier and load balance the traffic using load balancer VM to multiple VMs in the app tier.
The process of scaling a VNF is automated and simplified to a large extent with the integration of VMware Telco Cloud Automation and VMware Cloud Director. VNFs can be scaled with a couple of steps in the VMware Telco Cloud Automation portal by navigating to the VNF instance in the Network Function tab of the Inventory section and clicking on Scale button. Then select the scale level to specify how many additional VMs are to be added as depicted in Figure 12.

Figure 12: Scale the network function – scale parameters
Next, in the Inputs tab, provide the appropriate IPs for App and DB networks, and choose a different hostname for the new app VM as shown in Figure 13.
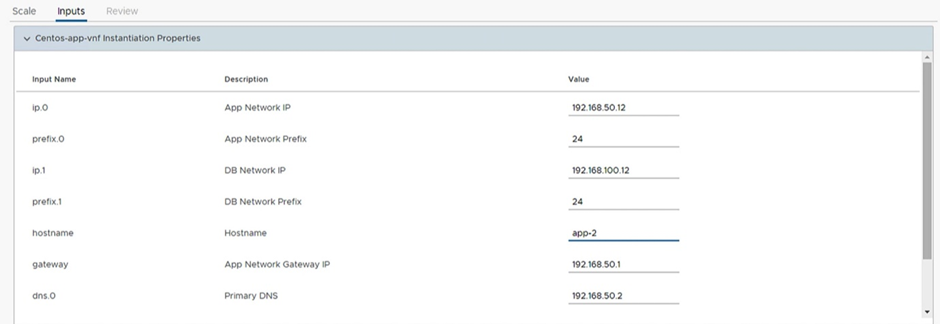
Figure 13: Scale the network function – VM properties
Once you furnish all the details, review the information and then click Finish, as illustrated in Figure 14. It takes a few minutes to create and configure the new app VM. The progress of the scale task can be observed by expanding the corresponding VNF instance.
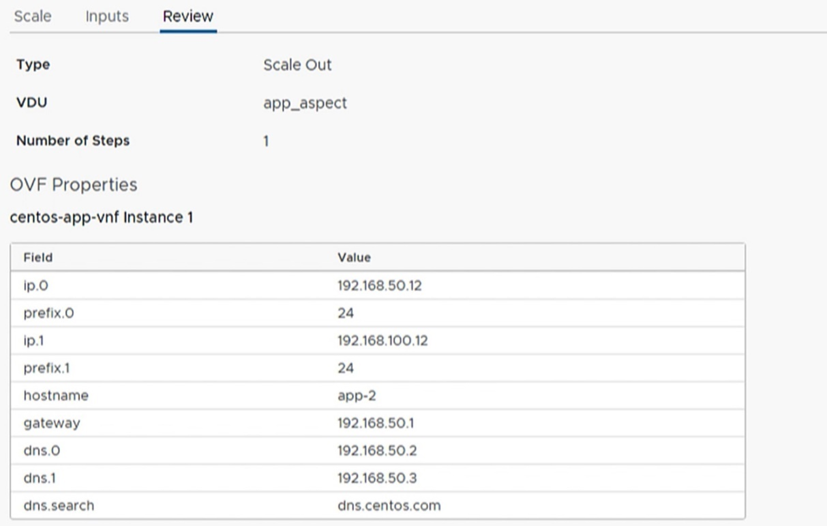
Figure 14: Scale the network function – review details
For these scaling operations, CSPs are usually required to modify some configuration on the VNF components to ensure the scale operation renders expected results. And in this regard, VMware Telco Cloud Automation comes with the ability to allow certain pre-defined workflows to be run on the VNFs without any hassle, in conjunction with VMware Aria Automation Orchestrator (previously VMware vRealize Orchestrator). These workflows can be related to adding, removing, or modifying the configurations of the VNF and are defined in the onboarded CSAR file of the VNF.
For the sample 3-tier VNF we considered, it requires app-2 IP to be attached to the load balancer after the scaling task is completed. This task can be achieved by running a workflow add-app-to-lb defined in the CSAR file of the VNF. To run this workflow, navigate to the appropriate VNF in the Network Function tab of the Inventory section, and click Run Workflow. Choose the add-app-to-lb workflow in the Select a Workflow tab, and then enter the external IP of the load balancer VM and the App network IP of the app-2 VM in the Run Workflow tab, as depicted in Figure 15.
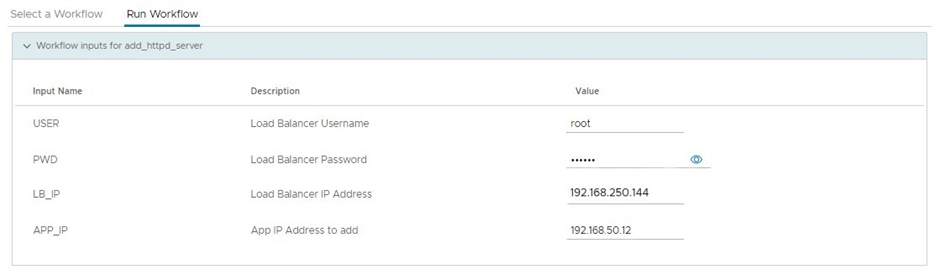
Figure 15: Scale the network function – run add-app-to-lb workflow
Once the workflow is successfully executed, we can browse the external IP of the load balancer VM multiple times and observe that the VNF is rendering the expected service by load balancing the traffic between both app-1 and app-2 VMs as shown below in Figures 16 and 17.

Figure 16: Scale network function result – app-1

Figure 17: Scale network function result – app-2
Conclusion
In this post, we have detailed the process of onboarding and instantiating a VNF on VMware Telco Cloud Infrastructure – Cloud Director Edition using VMware Telco Cloud Automation via the VNF method (where one vApp represents the whole VNF). Furthermore, we have demonstrated how easy it is to scale the VNFs horizontally using VMware Telco Cloud Automation.
Throughout this activity, we have emphasized how VMware Telco Cloud Automation integrated with VMware Telco Cloud Infrastructure – Cloud Director Edition simplifies the lifecycle management of VNFs.
Discover more from VMware Telco Cloud Blog
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.








