VMware is pleased to announce the general availability of VMware Telco Cloud Automation 2.2. This latest version of VMware Telco Cloud Automation—announced on January 12th, 2023—focuses on key feature upgrades and new capabilities for Communication Service Providers (CSPs). The new features central to Telco Cloud Automation 2.2 fall under several broad themes: multi-cloud management, improvements to CaaS automation, enhanced platform security and operability, and the general availability of Network Slicing for VMware Telco Cloud Automation. The confluence of these features will further support your drive towards network modernization, monetization and programmability.
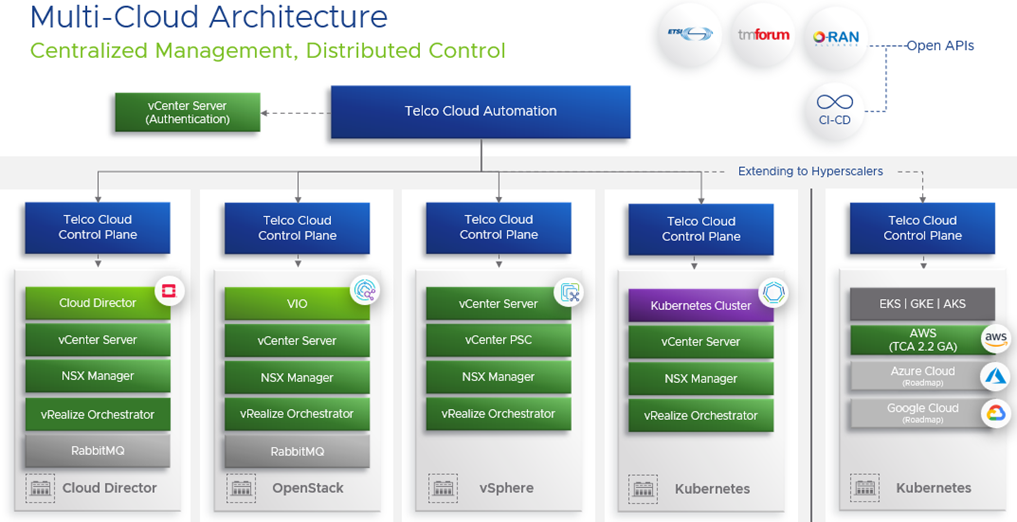
Importantly, VMware Telco Cloud Automation 2.2’s improvements continue to serve as an integral, differentiating aspect of the VMware Telco Cloud Platform stack—offering a comprehensive, end-to-end solution for CSPs seeking to automate network operations (see Figure 1 below). VMware Telco Cloud Automation—in conjunction with other VMware Telco Cloud Platform products like VMware Bare Metal Automation (beta – initial bare metal server provisioning and bootstrapping), VMware Telco Cloud Service Assurance (network monitoring, analytics and diagnostics) and Tanzu Kubernetes Grid (Kubernetes orchestration)—enable streamlined network management, visibility and performance. The improvements to VMware Telco Cloud Automation in this release, coupled with the holistic benefits of the VMware Telco Cloud Platform, are also crucial to reducing operational costs and developing innovative paths to revenue for your network.

Centralized Multi-Cloud Management with Public Cloud and On-Prem Environments
Driven by the need for business agility, acceleration in innovation and scale of operations, CSPs are undertaking the task of constructing distributed, multi-cloud networks. Telco Cloud Automation enables CSPs to take full advantage of their multi-cloud ecosystem by providing a centralized management plane (see Figure 2 below). As part of Telco Cloud Automation 2.2, you can now deploy VMware Telco Cloud Automation natively on Amazon’s AWS and/or EKS. More specifically, with Telco Cloud Automation 2.2, you can provision cloud-native network functions directly on native Amazon EKS, bringing unified management of workloads on-premises and on public cloud infrastructures. As such, Telco Cloud Automation 2.2 allows CSPs to leverage Telco Cloud Automation functionality over a public cloud—improving flexibility, scalability, and reliability with the choice for workload deployments on-prem and over AWS. What’s more, this multi-cloud functionality allows for ease of workload onboarding, instantiation and lifecycle management while promoting mobility from the network core to edge to RAN.
CaaS Automation Improvements for Better Management of Cloud-Native Workloads
VMware Telco Cloud Automation 2.2 introduces numerous improvements to our Container-as-a-Service (CaaS) automation module. In this latest release, you have more control and resiliency over container-based workloads with features that allow you to maintain consistent performance and scale—even if your network experiences operational issues and downtime.
Worker Nodes Anti-Affinity
Data-intensive, container-based applications require redundancy and high availability to guarantee their continued operation in the event of a physical host’s failure. Telco Cloud Automation 2.2 supports high availability of applications by allowing you to run TKG (Tanzu Kubernetes Grid) nodes on different hosts—diversifying the application’s location in case a single physical host fails. With Telco Cloud Automation 2.2, you can define “anti-affinity” specifications for the nodes (i.e., which nodes cannot run on the same hosts) so you can run the application in a distributed method on several physical hosts—ensuring it continues to run should one host fail.
Tanzu Kubernetes Grid (TKG) Clusters Backup, Restore and Self-Healing
Similar to the benefits of worker node anti-affinity, when operating TKG management and worker clusters, a CSP needs to ensure proper backup of the workloads in the event of a failure. With Telco Cloud Automation 2.2, you can restore the cluster data to a new cluster should the existing one fail. This feature is particularly important for VMware Telco Cloud Automation because infrastructure and cluster customization (through our “Dynamic Infrastructure Policies”) to fit specific network requirements allows you to enable customized 5G-based use cases, and it is crucial that these customizations are seamlessly backed up and restored.
Telco Cloud Automation 2.2 can, moreover, enable TKG’s “Machine Health Check” feature in the event of a physical host or management cluster failure to create a new node. If the cluster fails, TKG will create a new node that Telco Cloud Automation will then manage—guaranteeing minimal downtime and continued CaaS operations to maintain critical applications and services.
CaaS Cluster Node Auto-Scale
Certain telco applications that support high-performance workloads require different network resources at different times to support their functionality. In other words, these applications necessitate the CSP’s underlying resources in certain periods of time and, at other times, do not require the requisite level of resources. As such, it is important to scale up and down the Kubernetes layer that runs the application in response to the application’s demands in specific time periods. When an application demands increased resources, VMware Telco Cloud Automation will enable TKG to create new nodes that support the application’s increased requirements. VMware Telco Cloud Automation will then manage those new nodes accordingly and TKG will terminate those additional nodes when they are no longer required. This dynamic autoscaling with VMware Telco Cloud Automation 2.2 and TKG saves time and efficiently manages your resources—ensuring top application performance and saving resources when they are not needed.
Platform Operability and Security
VMware Telco Cloud Automation 2.2 offers a broad range of platform operability and security enhancements. With this latest update, you can restrict the permission and access level of their network function vendors operating in your network and find additional support for IPv6 and air-gapped environments. Below we highlight the latest important platform operability and security enhancements in Telco Cloud Automation 2.2.
Airgap Server Improvements
To enable CaaS automation operations and CNF customization when not connected to the internet, VMware Telco Cloud Automation offers functionality over air-gapped servers. Telco Cloud Automation 2.2 can support incremental upgrades of the air-gapped servers themselves (i.e., the packages that the air-gapped server stores). These incremental upgrades to air-gapped servers importantly present VMware Telco Cloud Automation 2.2 as a product for you to continue to run your air-gapped workloads seamlessly and without downtime.
IPv6 Support
As a security necessity and due to the shortage in IPv4 addresses, you might require IPv6 for VM and cloud-native use of Telco Cloud Automation. In other words, CSPs cannot use their networks without additional IP addresses. Accordingly, IPv4 lacked the necessary scale that IPv6 now offers. VMware Telco Cloud Automation 2.2 represents an important step in the evolution of offering IPv6 to support various external interfaces that require new IP addresses. With VMware Telco Cloud Automation 2.2, you can find full dual-stack support by keeping certain interfaces on IPv4 and migrating others to IPv6. This newfound ability to scale and expand new networks and services with IPv6 allows you to deploy VMware Telco Cloud Automation 2.2 in an IPv6-only (IPv6 dual-stack) network and, correspondingly, manage IPv6 infrastructure, CaaS, and xNFs—improving security and scale of operations. VMware Telco Cloud Automation 2.2 supports, specifically, IPv6 dual stack, CaaS Automation, PaaS extensions and Harbor, and CNF LCM.
Official General Availability of Network Slicing for VMware Telco Cloud Automation: End-to-End Orchestration with Network Slicing
As demands from customers to offer new, differentiated services increases, CSPs are searching for new ways to fulfill—and monetize—these requests. Network Slicing allows you to create and monetize a new breed of services—from Massive Machine Type Communication (mMTC) or Ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communication (uRLLC) to enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB)—through standard frameworks to design, create, and manage network resources that can be packaged and exposed directly to the end users.
5G Network Slicing enables you to create on-demand, isolated, end-to-end logical networks running on a shared and common infrastructure. These programmable overlay networks are associated with specific business purposes and follow a set of predefined SLAs with Quality-of-Service indicators (QoS) and security requirements. Network Slicing for VMware Telco Cloud Automation provides a standard way of managing and exposing network resources to the end user, while assuring the delivered slice’s purpose and characteristics (i.e., throughput, latency, geographical location, isolation level, etc.)
Network Slicing for VMware Telco Cloud Automation—in general availability with VMware Telco Cloud Automation 2.2—supports 3GPP standard-compliant Network Slicing management, enabling users to plan, design and instantiate end-to-end network slices across the RAN, edge, and core network domains (see Figure 3 below).
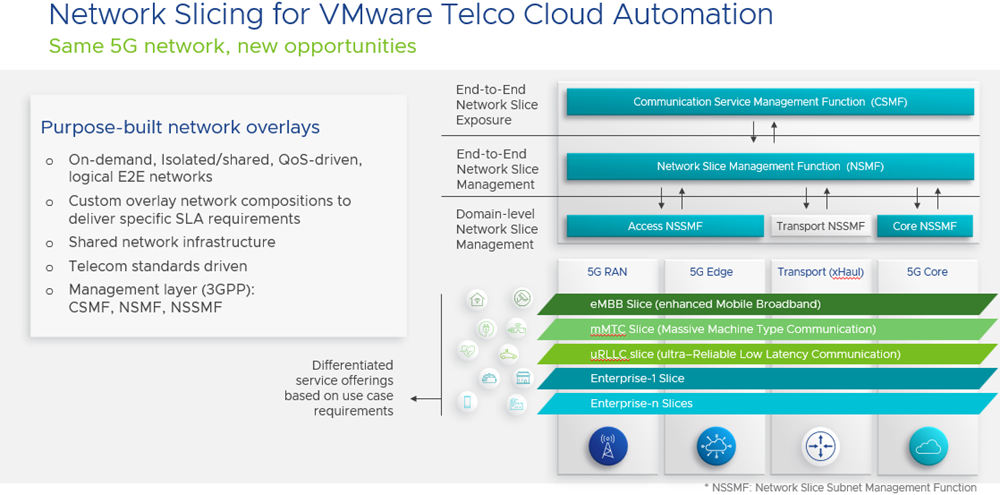
Network Slicing for VMware Telco Cloud Automation enables you to unify these domains and close the gap between the endpoint consumed services and the required network resources, from physical or cloud infrastructure. Importantly, network slicing enables you to create use case-specific logical networks over their shared physical infrastructure. By tailoring (or slicing) your physical infrastructure, you can provide independent, isolated, programmable and customizable virtual networks, that address specific connectivity requirements for your customers—enabling you to meet, exceed SLAs and charge for new, innovative services. For more information on Network Slicing for VMware Telco Cloud Automation, see the datasheet here.
Network Function Partner Ecosystem
A fundamental aspect of any orchestration solution is its ability to evolve in a multi-cloud, multi-vendor ecosystem. As an infrastructure provider for many years, VMware has a robust group of network function partners certified on its technology (300+ network functions certified from 50+ vendors and all major equipment providers). Recently, Ericsson, Mavenir, Nokia, NEC, and Samsung all published 5G core certifications on the marketplace. As part of VMware Telco Cloud Automation’s efforts, many of these partners now integrate their VNFs and CNFs to both automation and infrastructure layers of the Telco Cloud (see Figure 4 below).
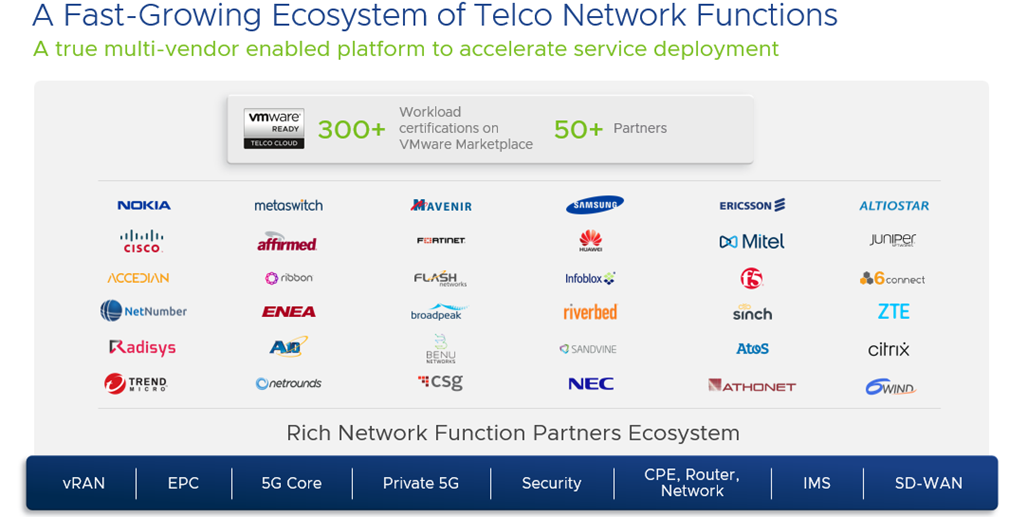
Seamless certification of network functions can prove difficult. Typically, without an automated certification and onboarding process like the one that Telco Cloud Automation facilitates, there is a steep learning curve for network function providers—one needs to learn, for instance, how to write TOSCA templates, plans, and to create workflows—all of which require robust technical knowledge. Telco Cloud Automation 2.2 automates many of these otherwise complex, manual onboarding and certification processes through a simple workflow editor GUI and debuggers—all of which streamline difficult, manual processes and accelerate the onboarding and certification of network functions. The certification process via VMware Telco Cloud Automation and the VMware Ready for Telco Cloud Program validates the partner network function CSAR package conformity and the crucial steps of onboarding and lifecycle management over the Telco Cloud platform. This important process allows you to accelerate the deployment of their network functions and limits the risks associated with interoperability.
Note: the VMware Ready for Telco Cloud program also allows network function partners to certify NFs to produce NFs and packages on VMware Telco Cloud Infrastructure and Telco Cloud Platform.
Improved Interoperability with Industry Standards
VMware Telco Cloud Automation supports fundamental ETSI-MANO, TMF, 3GPP for network slicing and O-RAN guidelines for telco component interoperability and leverages native integration with VIM and upstream Kubernetes for northbound interfaces (e.g., placement, KPI collection, etc.). This architecture provides a streamlined and flexible approach for orchestrating telco standards-compliant workloads on a quickly changing, multi-cloud ecosystem. You can interact with telco standards and allow VMware Telco Cloud Automation to translate the requirements in cloud capabilities. Telco standardized interfaces facilitate VMware Telco Cloud Automation deployment and interactions within a multi-vendor architecture. Telco Cloud Automation 2.2 also supports O-RAN (pre-standard) O2 functionality—an important interface that further enables infrastructure and application lifecycle management (i.e., infrastructure and CaaS automation) and network function and network service lifecycle management for O-RAN.
VMware Telco Cloud Automation 2.2 focuses on several important themes for the CSP: network modernization, monetization and programmability. VMware Telco Cloud Automation 2.2, specifically, allows you to extend workloads to public cloud environments and manage them seamlessly, enables more secure and agile network operations, offers improved CaaS automation capabilities and supports the promises and potentials of network slicing. VMware Telco Cloud Automation 2.2, in conjunction with the VMware Telco Cloud Platform stack, creates opportunities for you to streamline and automate complex network operations—reducing operating and capital costs and opening new avenues revenue growth.
For a complete list and detailed description of features, capabilities and enhancements related to this release, see the VMware Telco Cloud Automation Release Notes here.
Discover more from VMware Telco Cloud Blog
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.








