5G’s advent has ushered in an array of new consumer and enterprise use cases that demand high levels of connectivity with low latency. From autonomous driving and remote healthcare to smart energy grids and factories, 5G technology offers novel business opportunities. In the pre-5G era, businesses relied on a single, shared network for their operations that offered limited avenues for revenue growth. Today, however, with consumers and enterprises’ foreseen demand for 5G use cases, CSPs are searching for new ways to fulfill—and monetize—these requests.
The confluence of 5G, network virtualization (NFV), cloud-native deployments, effective automation, management and orchestration has laid the groundwork for a new type of networking technology suited for these emerging use cases—Network Slicing. Network Slicing enables CSPs to create use case-specific logical networks over their common physical infrastructure. By tailoring (or, “slicing”) their physical infrastructure to provide independent, isolated and customized virtual networks, CSPs can address specific connectivity requirements for customers. Network Slicing allows CSPs to create and monetize a new breed of services—like Massive Machine Type Communication (mMTC), Ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communication (uRLLC) or enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB)—through standard frameworks to design, create, and manage network resources that can be packaged and exposed directly to CSPs’ customers.
It comes as no surprise, then, that by 2025, the expected market for slicing-enabled revenues comes to $45B.[1] By 2030, that market size increases to roughly $200B—implying a 36% annual growth rate.[2] What’s more, Network Slicing will, by 2030, comprise roughly 30% of 5G revenues for CSPs.[3]
To capture this burgeoning market, CSPs need to ensure that their networks employ strong orchestration and automation practices that manage the complexity of Network Slicing. Successful Network Slicing orchestration supports lifecycle management for the creation, modification, and termination of individual services, while also promoting the assignment of underlying resources. As such, VMware, through its Telco Cloud Automation, has unveiled a fifth layer of network automation (see Figure 1 below) that delivers 5G Network Slicing capabilities to CSPs. Network Slicing for VMware Telco Cloud Automation provides a standard method of managing and exposing network resources to the end user, while assuring the delivered slice’s purpose and characteristics (i.e., throughput, latency, location, isolation level, etc.).
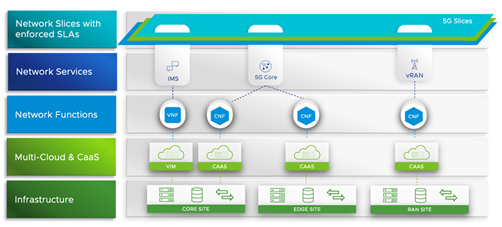
What is Network Slicing for VMware Telco Cloud Automation?
Network Slicing for VMware Telco Cloud Automation plans to support 3GPP standard-compliant Network Slicing management, enabling users to plan, design and instantiate end-to-end network slices across the RAN, edge, core and transport network domains, as depicted in Figure 2 below. Network Slicing for VMware Telco Cloud Automation will enable CSPs to unify these domains and close the gap between the endpoint consumed services and the required network resources, from physical or cloud infrastructure.
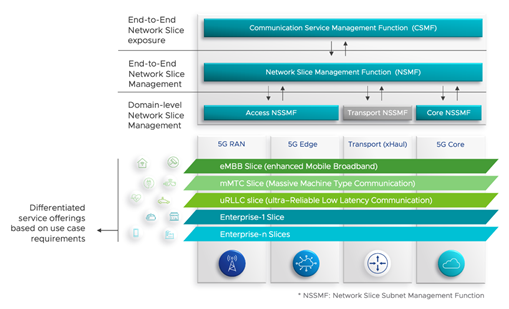
Network Slicing for VMware Telco Cloud Automation, through VMware and in conjunction with customers who also served as solution design partners, propose standard 3GPP network slicing management architecture, illustrated in Figure 3 below, that is comprised of the following components:
- Communication Service Management Function (CSMF), which acts as the interface towards service order management and Operations Support Systems (OSS);
- Network Slice Management Function (NSMF), which manages the lifecycle of the end-to-end slice across the RAN, 5G core and transport network domains; and
- Network Slice Subnet Management Function (NSSMF), which manages the lifecycle of the Network Slice subnets within a network domain and applies the NSMF’s lifecycle management commands (i.e., instantiate, scale, heal, terminate).
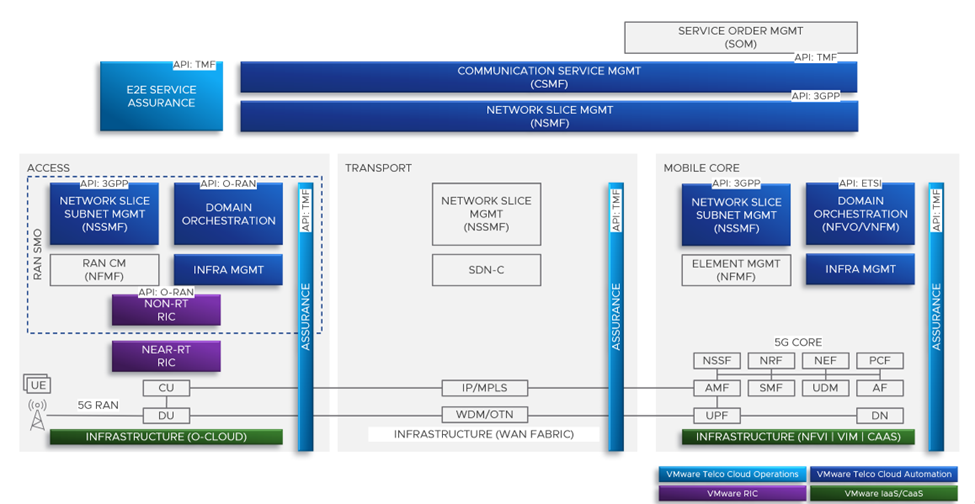
The foundational framework for Telco Cloud Automation’s Network Slicing capabilities also leverage integration with Transport domain orchestration. Network Slicing for VMware Telco Cloud Automation will support the key network slicing use cases including design/onboarding, instantiation, monitoring and other day 1 and 2 operations. Figure 4 below presents some examples of slice design and instantiation.
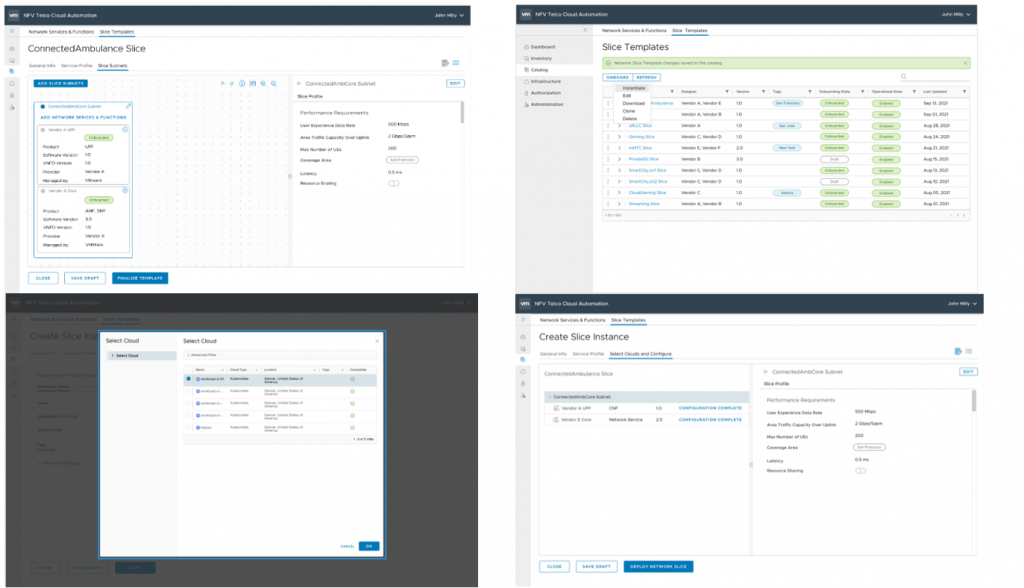
VMware’s Approach
VMware is uniquely positioned to offer an unparalleled Network Slicing service. Working with customers to construct a Network Slicing architecture grounded in industry standards, with key integrations into VMware Telco Cloud and using automation from slice down to the infrastructure, VMware’s Network Slicing is designed with CSPs’ requirements top-of-mind. VMware, through its Telco Cloud Automation orchestrator, unifies its Network Slicing capabilities with other layers of Telco Cloud Automation (see Figure 5 below) and can, therefore, streamline the slice instantiation process and the configuration of underlying network resources.
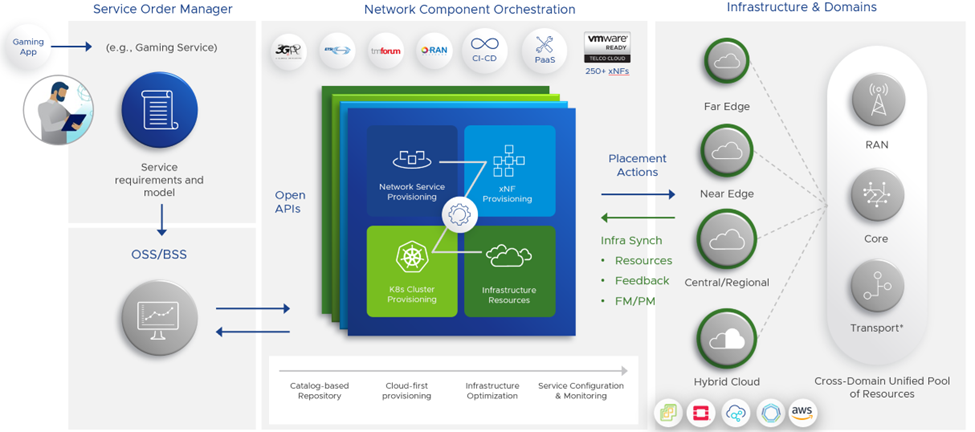
What’s more, VMware’s Telco Cloud Automation offers a single abstraction across all domains and clouds—a crucial value proposition for CSPs working with distributed, multi-cloud networks. Finally, VMware offers a robust multi-vendor ecosystem[4] of network functions which can be extended to support Network Slicing.
Benefits for CSPs
5G Network Slicing enables Service Providers to create on-demand, isolated, end-to-end logical networks running on a shared and common infrastructure. These programmable overlay networks are associated with specific business purposes and follow a set of predefined SLAs with Quality-of-Service (QoS) indicators and security requirements. Take, for example, the benefits that Network Slicing can offer to autonomous vehicle operations, remote healthcare, smart energy grids and manufacturing. Isolated network traffic through slices can satisfy stringent regulatory requirements, guarantees necessary QoS for tailored performance, reliability and scale, ensures end-to-end SLAs and enables CSPs to address customer-specific security demands. Network Slicing, moreover, allows CSPs to configure for high availability—guaranteeing a level of performance and reliability for customers.
Network Slicing addresses a pressing question for CSPs: how to provide the technological framework to support, enable and scale 5G-related use cases. CSPs seeking to empower their customers with use case-specific network slices will require an automated Network Slicing solution grounded in effective management and orchestration. Through Network Slicing for VMware Telco Cloud Automation, CSPs will easily segment their networks, provision network resources on-demand and help their customers unlock additional revenues through new 5G use cases. This is more than building a modern network; rather, it is creating the network of the possible.
For additional information on
Network Slicing and how VMware plans to offer this next-gen service for CSPs,
check out VMware’s “Network of the Possible” presentation at VMworld 2021 here.
[1] “Network Slicing: A Go-to-Market Guide to Capture the High Revenue Potential,” Ericsson and Arthur D. Little, May 2021: p. 7.
[2] “Network Slicing: A Go-to-Market Guide,” p. 7.
[3] “Network Slicing: A Go-to-Market Guide,” p. 7.
[4] See here for VMware’s Telco Cloud vendor marketplace. Currently, VMware’ Telco Cloud supports 250+ network function vendors.
Discover more from VMware Telco Cloud Blog
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.








