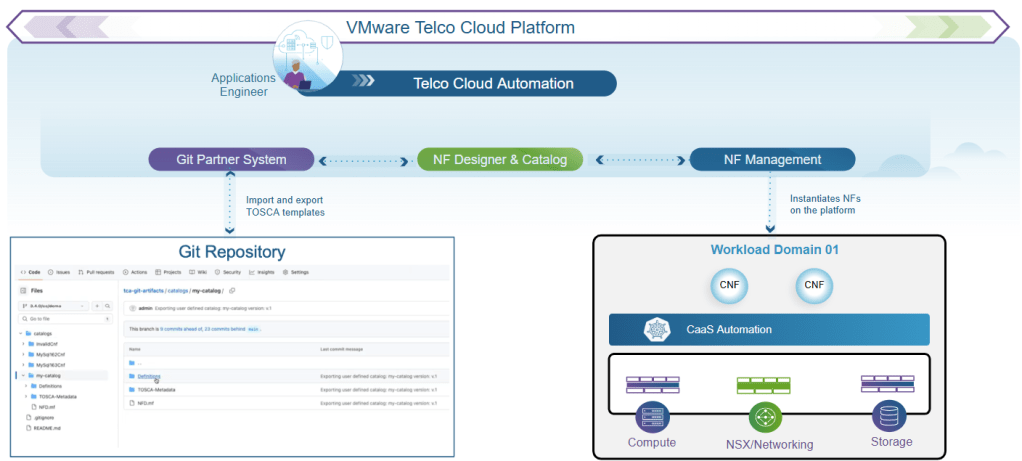
In the rapidly evolving telecommunications landscape, embracing virtual network functions (VNFs) and cloud-native network functions (CNFs) necessitates highly agile and accelerated development and deployment methodologies. The existing methodologies defined by European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) standards use the Topology and Orchestration Specification for Cloud Applications (TOSCA) templates to define the network functions. TOSCA templates include references to virtual and container resources, infrastructure requirements, lifecycle management workflows, and all the necessary information/scripts that orchestrators need to deploy, manage, and scale the VNFs or CNFs. These TOSCA templates are packaged and distributed as Cloud Service Archive (CSAR) files. However, relying on traditional, often manual, approaches for managing these templates can lead to inefficiencies, significant versioning challenges, and a lack of transparency throughout the network function lifecycle. This would, more often than not, force Communication Service Providers (CSPs) to choose either to adhere to the ETSI standards with comprehensive definition of xNFs or adopt modern, agile, and robust methodologies such as Git. As telecommunication networks become progressively more dynamic and software-defined, establishing robust and agile management practices for these artifacts, while adhering to the comprehensive definition as per the standards, is paramount to ensure consistency, drive innovation, and reduce operational overhead.
To simplify the lifecycle management of xNFs and bridge the gap between adherence to ETSI standards and adoption of modern agile practices, in VMware Telco Cloud Platform 5.1, Broadcom introduces the capability to manage the TOSCA artifacts that make up the network functions via Git. Leveraging Git to manage the TOSCA artifacts offers various key advantages, such as:
- Comprehensive version tracking: Git allows for detailed tracking of all changes made to the artifacts, providing greater visibility and making it easy for audits, modifications, rollbacks, etc.
- Faster and secure development: The branching capability of Git facilitates parallel development, enabling multiple individuals and teams to collaborate on the network function artifacts simultaneously. All the artifact updates are auditable, traceable, and approved via an approval process, making the development process faster and secure in nature.
- Faster problem resolution and restoration of service: Detailed tracking of changes with historical data assists administrators and support engineers to identify the point of introduction of the problem and revert to a working version of the network functions.
- Easily scalable across sites: Git allows the users to consume the same artifacts and scale the network function deployments to multiple sites, synchronizing the configuration across sites with minimal efforts.
- Eliminates the need for packaging TOSCA artifacts: Leveraging Git eliminates the need to package the TOSCA templates into CSAR files. It allows the application engineers to onboard and deploy the network functions by directly integrating the Git repository with the catalog and instantiation engine.
You can design the TOSCA artifacts using VMware Telco Cloud Platform, export it to Git and manage further development via Git. Or you could design the artifacts directly in Git and import it into Telco Cloud Platform. The TOSCA artifacts in the Git repository should be in an unzipped format and adhere to the folder structure below:
NF-Descriptor-Name/
|- TOSCA-Metadata/
| – TOSCA.meta
|- Definitions/
| – NFD.yaml
|- NFD.mf
Let’s now run through the process of importing and exporting the TOSCA artifacts via Git. In this example, we will design a TOSCA template using the network function designer capability of Telco Cloud Platform and export it to Git. We will manage further modifications to the artifacts via Git and import it back. You can repeatedly import from the same Git source; subsequent imports will only process changes in the network function descriptors since the previous import. We will also quickly touch base on the process of onboarding the network functions using the TOSCA template draft, managed by Git.
- First, we need to register the Git repository as the Partner System in VMware Telco Cloud Automation. Log into VMware Telco Cloud Automation UI, navigate to the Partner Systems sub-section under the Infrastructure section and click Register.
- Provide the name, URL, and credentials of the Git repository and click Next.
- In the next window, select any CaaS workload clusters with which you would like to associate the Git repository. Click Finish.
- The next step is to add the Git repository as a Git source in the network function catalog. Navigate to the Git sources tab in the Network Function sub-section under the Catalog section, and click New Git Source.
- Provide the name, select the Git repository partner system, folder name, and revision details. Click Add.
- We will design the network function descriptor now. Navigate to the Catalogs tab in the Network Function sub-section under the Catalog section and click Onboard Network Function.
- Select Design Network Function Descriptor radio button. Provide a name for the draft and select the type as Cloud Native Network Function. Click Design.
- Furnish the provider and product information in the General Properties tab.
- Click the Topology tab, drag and drop the helm object, and provide the details of the helm chart. Click Update, Save Draft, and close the draft.
- Navigate to the Drafts tab in the Network Function sub-section under the Catalog section, verify that the network function draft is saved. Note that the source of the draft is “Designer”.
- Click on the Ellipsis and click Push to Git.
- Select the Git source and click Push.
- Open the Git repository and verify the TOSCA artifacts have been pushed to Git.
- Observe in VMware Telco Cloud Automation UI that the source of the network function draft has changed to “Git”.
- The application engineers can now collaborate on these artifacts to design and develop the TOSCA artifacts for the network functions in an agile manner. Once the artifacts are ready to ship and are pushed to Git, we can import them back into VMware Telco Cloud Automation.
- To do that, navigate to the Drafts tab in the Network Function sub-section under the Catalog section, and click on Import From Git.
- Select the Git source to import from and click Import.
- The network function modified in Git repository by the application engineers is imported as a draft.
- Click on the ellipsis next to the imported draft, click Onboard, and confirm to onboard the draft as a catalog.
- It can now be instantiated by application engineers when required. The same Git repository can be added to another Telco Cloud Platform environment and the network function TOSCA artifacts can be imported and deployed, enabling seamless scalability.
Through this exercise, we have showcased the ease of importing and exporting the TOSCA artifacts to and from Telco Cloud Platform and Git repository to simplify the lifecycle of the network functions. Leveraging the capabilities of Git to manage the TOSCA artifacts provides a reliable, scalable, agile, and secure process to develop, deliver, deploy, and operate the network functions across various networks. This bridges the gap between process adherence to the ETSI standards and modernization of the operational principles, promoting the best of both worlds for CSPs to manage their networks efficiently.
To know more about VMware Telco Cloud Platform and its integration with Git and GitOps, refer to the documentation here.
Discover more from VMware Telco Cloud Blog
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.