In the first part of this blog series, we took a high level view of all the modes that are available with Migration Coordinator, a fully GSS supported tool built into NSX that enables migrating from NSX from vSphere to NSX (NSX-T).
The second blog in this series, will take a closer look at the available options for in-place migrations, along with the pros and cons of each approach.
NSX for vSphere: Fixed Topology
This mode was the very first mode introduced with migration coordinator in the NSX 2.4 release. This mode supports migrating configuration and workloads to NSX, using the same hosts that are running NSX for vSphere. It only needs extra capacity to run the NSX appliances such as the Managers and Edges.
Locating the mode: Marked in red below.

NSX Prep
- Installation: NSX manager and Edges
- Configuration: None
Pros:
- Workload Migration: Built in
- Bridging: Built in
Cons:
- Customization options: None
- Timing workload migration: No control
- Supported topologies: Only 5
Distributed Firewall, Host and Workload
This mode is useful when the requirement is to migrate only Distributed Firewall configuration.
Locating the mode
This mode is under the “Advanced Migration Modes” marked in red below.

NSX Prep:
- Installation: NSX manager and Edges
- Configuration:
- Configure the N/S network connectivity and
- South bound T0s all the way down to the Segments
Pros:
- Workload Migration: Built in
- Bridging: Built in
- Customization options: North bound of segment can be customized as required
Cons:
- Timing workload migration: No control
- Supported topologies: Any
NSX for vSphere: User Defined Topology – Complete migration
User Defined Topology mode is built to merge the simplicity of “Fixed Topology” mode with flexibility of “Distributed Firewall, Host and Workload” mode. In this mode, users still have the flexibility to configure the N/S connectivity and create the T0s. Rest of the configuration, networking and security, can be migrated with the migration coordinator using the mode.
Locating the mode
This mode is under User Defined Topology mode.
Click on the User Defined Topology Mode highlighted in red below:
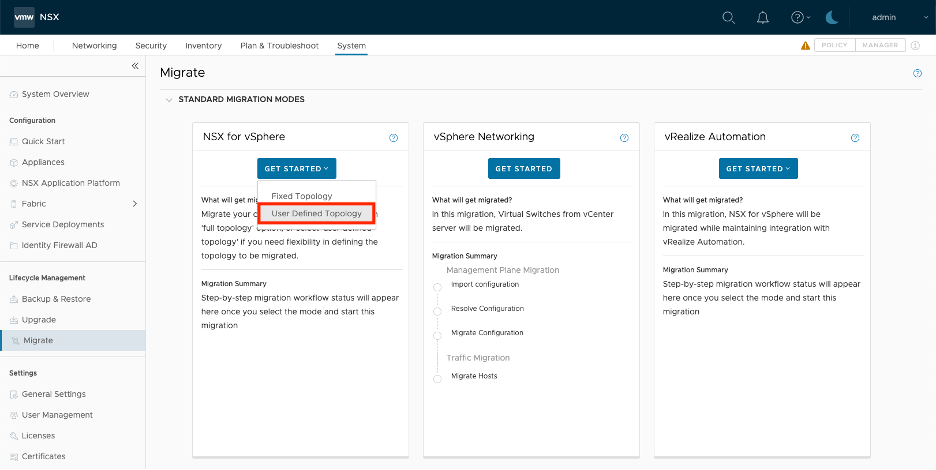
And then select the first option highlighted in red below:

NSX Prep:
- Installation: NSX manager and Edges
- Configuration:
- Configure the N/S network connectivity and
- Create T0s
Pros:
- Workload Migration: Built in
- Bridging: Built in
- Customization options: N/S connectivity and T0 design
- Supported topologies: Any
Cons:
- Timing workload migration: No control
NSX Global Manager: User Defined Topology – Complete migration
For customers with Cross VCenter Deployments, migration coordinator allows migrating their NSX for vSphere into Federation using the “User Defined Topology – Complete Migration” Mode for an in-place migration approach. This mode is only available via the Global Manager.
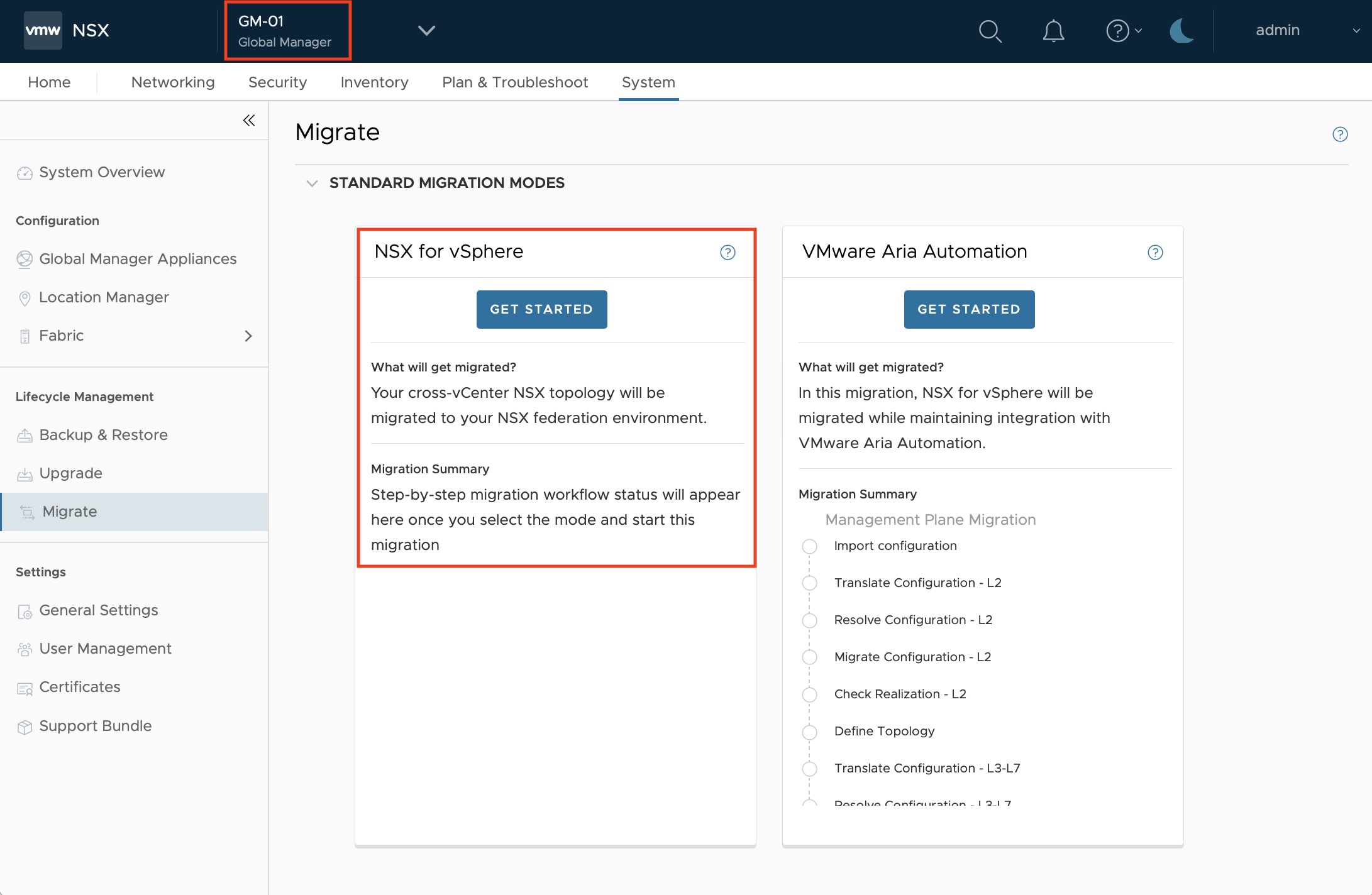
Locating the mode
On the Global Manager under System -> Migrate, select the NSX for vSphere mode, highlighted in red below:
Select the “Complete migration”, highlighted in red below:
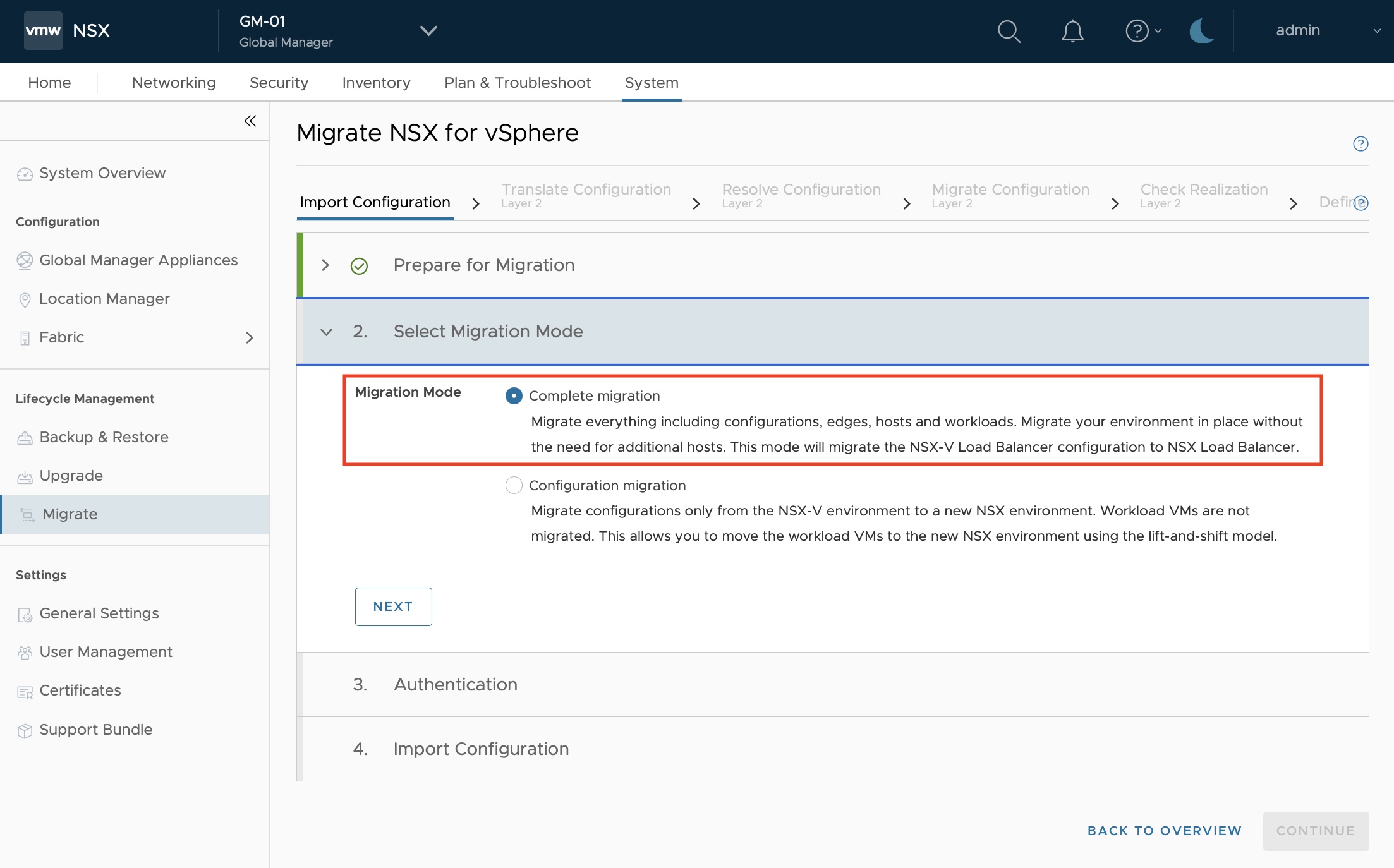
NSX Prep:
- Installation: NSX global and local manager, Edges
- Configuration:
- Configure the N/S network connectivity and
- Create T0s
Pros:
- Workload Migration: Built in
- Bridging: Built in
- Customization options: N/S connectivity and T0 design
- Supported topologies: Any
Cons:
- Timing workload migration: No control
Conclusion
In the second part of this blog series, we took a closer look at the in-place migration options available using the Migration Coordaintor. In-place migration modes are designed for cases where preference is to use the existing hardware and letting Migration Coordaintor take care of all the details of the workload migration. Some of these modes also allow flexibility in defining the north / south connectivity.
In the third part of this series, we will take a look at the lift and shift migration modes.
Resources
Want to learn more? Check out the following resources:
- Migration Coordinator Documentation:
- Design Guide
- Try out NSX


Comments
0 Comments have been added so far