IP Spaces Refresher
IP Spaces in VMware Cloud Director (VCD) is an improved IP address management solution to enable Service Providers and Tenants to manage IP address allocations in VCD securely and independently for various purposes. The feature empowers the Provider to construct public (shared) or private IP address ranges and blocks for the Tenants, allowing greater control and management of IP address distribution and usage. By exploiting IP Spaces, Organizations can have individual IP schema available for their virtual data centers while ensuring that IP conflicts are avoided. This provides Tenants or businesses with a more secure and scalable networking environment.
VCD 10.5 introduced significant new IP Spaces capabilities, which I will deep-dive in two consequent blog posts – starting with the IP Space’ Network Topology enchantments for Default NAT and Firewall rules auto-configuration.
Provider Gateway Uplink Association
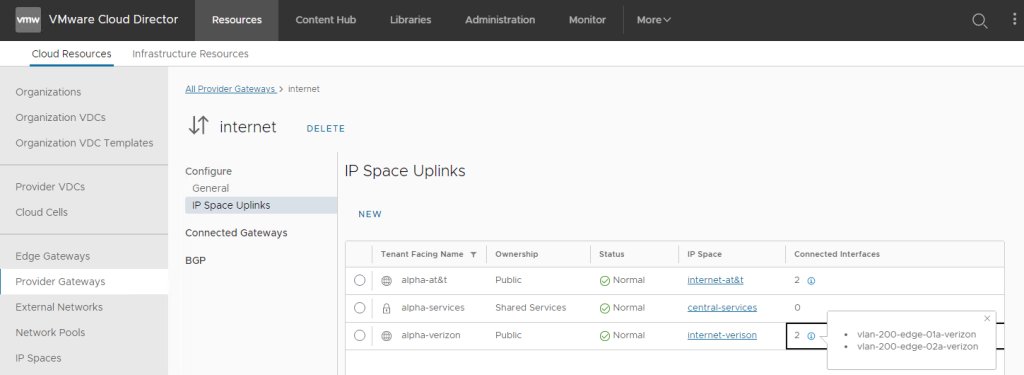
VCD 10.5 provides a more granular Provider Gateway IP Space Uplink association. The service providers can associate actual NSX Tier-0 Gateway interfaces with the IP Spaces Uplink.
Understanding the underlying Tier-0 Gateway interfaces and having those mapped to specific IP Spaces provides a simple configuration of NAT and Firewall rules that require interface awareness. This allows a more flexible way to configure the IP Space mapping and enable the north-south traffic with autogenerated default NAT and Firewall rules (described below) per Tier-0 interface/s. The Tier-0 Gateway interface/s can be used in multiple IP Spaces Uplinks definitions. Providers can also choose not to select any interface, in which case the NAT and Firewall rules get applied to all.
IP Space’ Network Topology Defaults
In addition to the previously existing “Route Advertisement” enablement in the Network Topology section of an IP Space, VCD 10.5 supports default SNAT, NO SNAT, and NAT matching Firewall rules auto-generation. This feature helps the provider to set up tenants’ communication paths quickly and securely by intelligently utilizing the IP address data from the IP Spaces.
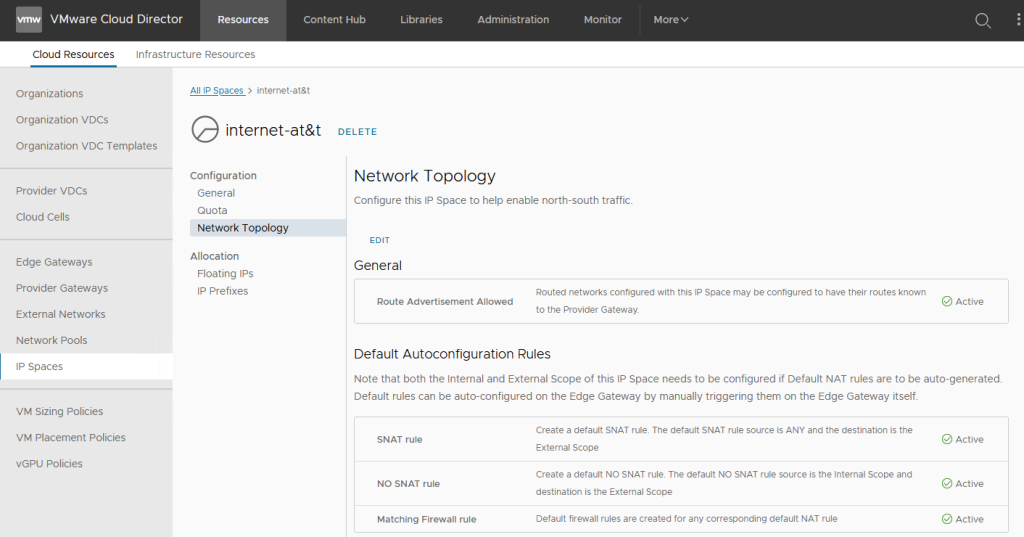
To create these rules, the provider must manually initiate an workflow. This can be done on either an Edge Gateway or a dedicated Provider Gateway that is backed by an Active/Standby Tier-0/VRF.
When a service provider wants to utilize both natively routed and NAT-ed topologies (Route Advertisement and SNAT are selected), they can specify that they would also like a default NO SNAT rule. This selection will allow for a configuration that prevents the IP Space Internal Scope subnets from being NATed, while all the rest of the traffic will be subject to the default SNAT rule.
A detailed demo of configuring these capabilities, including tests and verifications for the implemented default NAT and Firewall auto-configurations, is available here:
Default Service Configuration Details
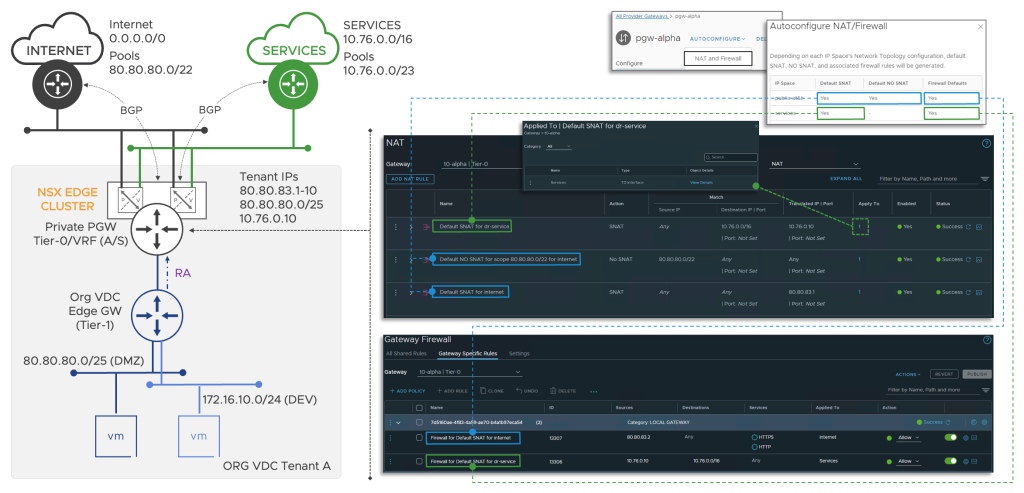
The provider can create default NAT and Firewall rules on the Provider Gateway if it meets two conditions:
- The Provider Gateway is Private (tenant dedicated)
- An Active/Standby Tier-0/VRF backs the Provider Gateway
The NAT and FW rules on the Provider Gateway are not currently exposed in the VCD UI, but can be viewed and managed from the NSX Manager. This functionality will be provided in a feature VCD release.
In case the Provider Gateway’s requirements are not fulfilled, or such configuration is not desired, default NAT and Firewall rules can be auto-created on the Edge Gateway (if required). The default services auto-configuration on the Edge Gateway works for any IP Spaces enabled Provider Gateway deployment models (Public, Private, A/A, and A/S Tier0).
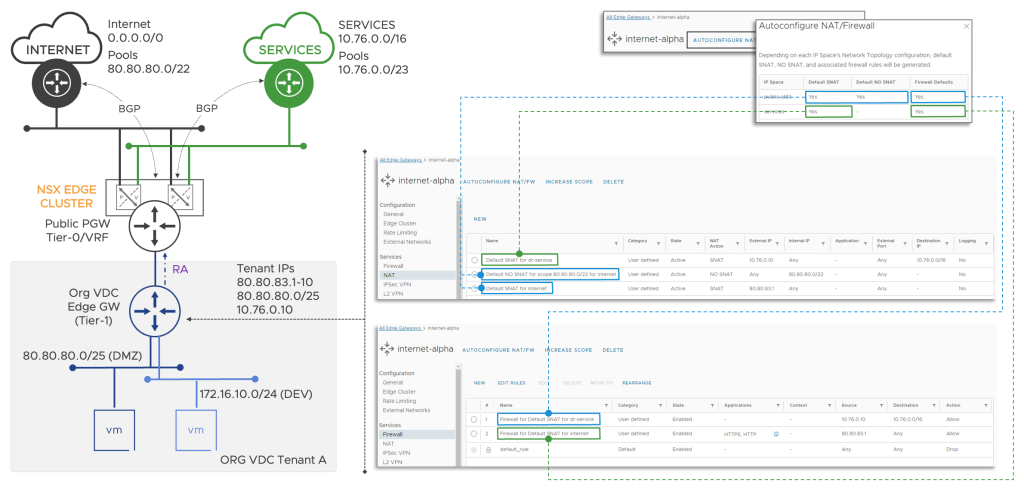
The current default NAT rules workflow assumes greenfield Edge or Provider Gateways (existing NAT rules are not supported). VCD also does not currently track Edge Gateway or Provider Gateway changes (for example, a new Tier-0 GW interface) to update the already deployed default NAT and Firewall rules. In the case of such, the service provider has to navigate to each Gateway and re-apply the defaults. In future releases, this experience will be enhanced.
Default NAT Rules
Along with the IP Space Internal Scope definition, which is a mandatory parameter, the successful default NAT rules auto-generation requires:
- IP Space External Scope definition
- IP Space IP Ranges for service configuration
- The default SNAT and/or default NO SNAT features have to be enabled for the IP Space Network Topology
In the case of a Provider Gateway workflow, VCD looks at the associated Tier-0/VRF interfaces to determine which IP Spaces need to be considered when generating the default rules. VCD will ignore any IP Space which does not comply with the above prerequisites.
NAT Rules Priority
The default NAT rules definition is based on an IP Space’s Internal and External scope. The rules’ priority (order) depends on whether they are a SNAT rule or a NO SNAT rule and whether or not the external scope is the “default” route (0.0.0.0/0).
The following table provides an example summary of VCD auto-generated default NAT rules and their priorities.
Note: A lower Rule Priority value means a higher inspection priority (first to consider).
| Rule Description | IP Space Internal Scope | IP Space External Scope | Rule Priority |
| Default NO SNAT for WAN | 172.30.0.0/20 | 172.16.0.0/12 | 0 |
| User-created NAT Rule | 50 | ||
| Default SNAT for WAN | 10.76.0.0/16 | 10.0.0.0/8 | 100 |
| Default SNAT for Services | 10.76.0.0/23 | 10.76.0.0/16 | 100 |
| Default NO SNAT for Internet | 80.80.80.0/22 | 0.0.0.0/0 | 1000 |
| Default SNAT for Internet | 80.80.80.0/22 | 0.0.0.0/0 | 1001 |
Matching Firewall Rules
In conjunction with the default SNAT and NO SNAT rules configuration, VCD 10.5 allows the auto-creation of the associated Firewall rules on either the Edge or Provider Gateway. These are only created if NAT or NO NAT rules are generated.
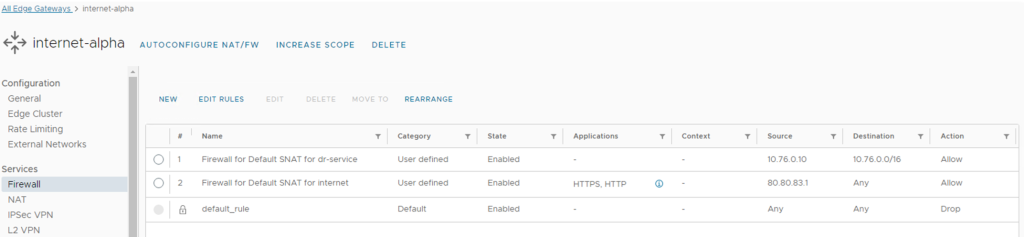
No firewall rule is generated for default NO SNAT rules when the IP Space External Scope is the default route (0.0.0.0/0). For all other default NO SNAT rules, the firewall rule is set using the IP Space Internal and External scopes for the rule source and destination, respectively.
Final Thoughts
VMware Cloud Director 10.5 has brought important new features for IP Spaces to improve the Providers’ and Tenants’ experience with the IP address management service provided.
The goal is to provide rapid, error-prone, and secure solutions so that cloud service providers and enterprises receive streamlined network provisioning and enhance protection in VCD environments.
Check out my second blog from this series if you want to explore another new VCD 10.5 feature – IP Spaces Migration.
Remain up-to-date by regularly checking this blog for the latest updates. You can also connect with us on Slack, Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn.
Stay tuned for new demo videos and enablement on YouTube, especially our Feature Fridays series.



