The cloud is now a way of life for all businesses. Getting to the cloud for many has been a challenge, the recent pandemic has put more pressure than ever before on remote working and hence cloud computing. The statistics below are just a snapshot but clearly speak for themselves – with demand on-premises decreasing, expanding to cloud a top IT spending driver, and customers expecting more cloud usage than ever before – now is the time to focus on capturing workloads to cloud.

The good news, VMware just made it a lot easier for Cloud Providers! It is with great pleasure VMware announces VMware Cloud Director Availability 4.2 General Availability!
Cloud Director Availability 4.2 comes with two significant new features to help you capture workloads and keep them in your cloud:
- Self-service migrations from a customer on-premises, or from your VMware Cloud Director cloud data center to VMware Cloud Director service in VMware Cloud on AWS (note: on-premise to VMware Cloud on AWS is one way only, VMware Cloud Director to VMware Cloud on AWS is bi-directional)
- Minimize risk and speed up customer migrations to your cloud with new Layer 2 network stretch services from an on-premises to the Provider VMware Cloud Director cloud, all configured and managed by VMware Cloud Director Availability
Migrations to Cloud Director service
VMware Cloud Director Availability uses vSphere scheduled block replication; this uses the classic data engine (HBR) on each ESXi host. VMware Cloud Director Availability 4.2 introduces a new data engine (VMC) that enables support for VMware Cloud on AWS despite its design specifics which limit access to administrative ESXi APIs. For this reason, we have created a new replication service called H4DM Service. This service is auto-selected based on your choice of target to migrate to, but it should be noted that for migration to on-premises to VMware Cloud on AWS, the current capability only supports one-way migration.
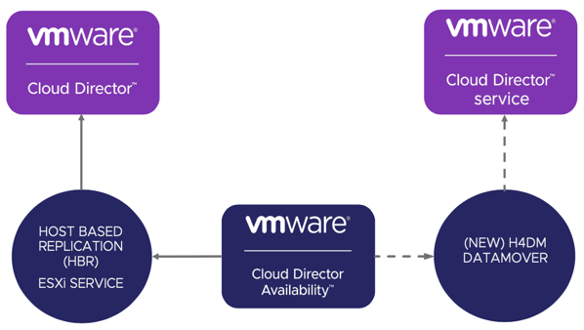
The result is tenants now have a choice of viable migration targets by adding a straightforward option for migrating workloads from on-premises or private VMware Cloud Director cloud sources to VMware Cloud Director service targets. It guarantees a smooth customer experience by using an already known UI and following a sequence of steps that both providers and tenants are familiar with. All this is achieved in full compliance with the high security principles set by VMC and without any design modifications that may lead to infrastructure changes on the provider side.

Getting Started
To enable migrating workloads to VMware Cloud on AWS, Service Providers first need to deploy VMware Cloud Director Availability 4.2 in their Compute Domain of the SDDC linked to the Cloud Director service.
Apart from choosing which data engine to be activated during the Site Details step of the Initial Setup Wizard, the deployment process and the configuration steps are the same as in the previous VMware Cloud Director Availability releases.
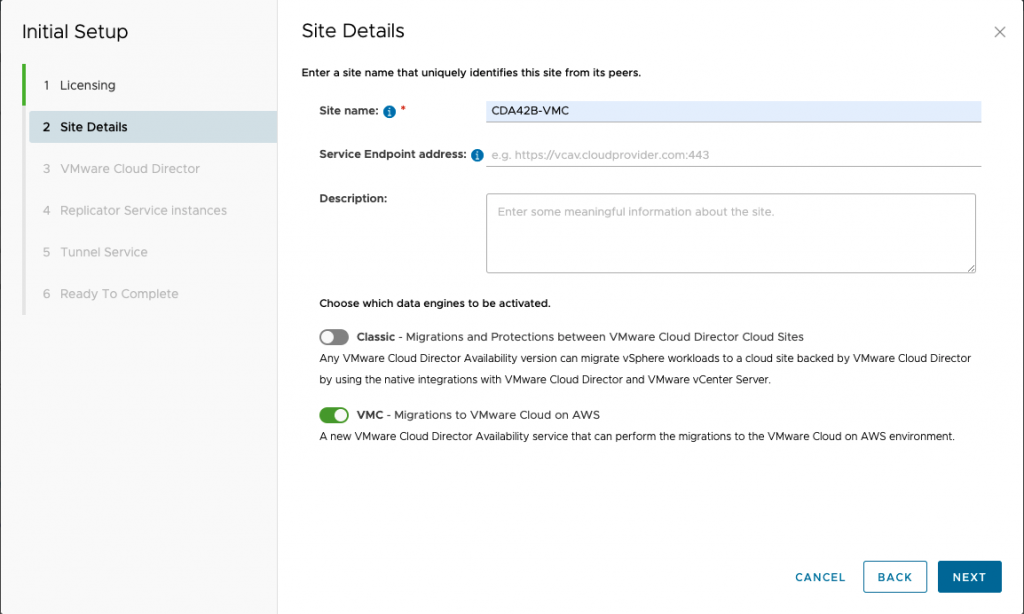
The appliances that a provider needs to run are also the same – Cloud Replication Manager, Cloud Replicator, and Cloud Tunnel, these need to be deployed in the Compute domain. After all the necessary firewall rules are applied and the Service Endpoint is accessible, the setup is completed.
You can find the detailed steps in the Migrations to VMware Cloud Director service using VMware Cloud Director Availability whitepaper or in this video.
For any additional reference, you can review the full VMware Cloud Director Availability documentation
Stretching Layer 2 Networks On-Premises
Stretching on-premises networks to the cloud reduces the downtimes and makes the process more fluid while migrating applications. The available ways for achieving it were pretty complex and involved serious effort from a provider. VMware Cloud Director Availability 4.2 comes with new functionality that enables managing the network stretching directly from its UI to facilitate the process.

However, at this moment, only VMware NSX-TTM Data Center backed clouds are supported as a target.
In the UI, you can find a new menu called L2 VPN Sessions that will navigate you to the configuration interface.

Getting started
Stretching an on-premises network to the cloud involves the VMware® NSX Edge™, also known as ‘NSX Autonomous Edge’, and includes four steps that need to be completed.

With the Layer 2 network stretch in place, the complex applications that consist of multiple workloads can be appropriately migrated from an on-premises data center to your cloud. There is no need for tenants to change anything in the application configuration after the migration, negating IP and network changes. This way, the risk of problems caused by such changes is removed, and the proper application operation is guaranteed. The layer 2 VPN will remain active for as long as required but can only be used by VMware Cloud Director Availability for replication traffic.
You can see the whole configuration process in this video. For more details, please refer to the official VMware Cloud Director Availability documentation.
To wrap up VMware Cloud Director Availability 4.2 is now much more focused on making migrations simpler and providing migration to Cloud Director service in VMware Cloud on AWS. We hope you find this useful and look forward to feedback regarding these features.
Remember, to get the latest updates check this blog regularly, you also can find us on Slack, Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn as well as many demo videos and enablement YouTube, especially our Feature Fridays series!




