Edge computing, along with AI and cybersecurity, is fast making its way into CIO agendas and boardroom discussions. Companies in all verticals are using edge compute to see real business benefits from enterprise data. Manufacturers are seeing positive impacts such as better security, product quality, and worker safety. VMware Edge Compute Stack, a purpose-built edge compute solution, can provide a number of benefits to manufacturers.
Importance of the edge for industry
Edge can be categorized as a distributed entity in between where the process takes place and an IT environment, like a data center or cloud infrastructure, where data resides centrally and is analyzed for business inferences. There is tremendous value in moving this computing and analytical power close to where data is being created or transacted to enable decisions to be made at a much faster pace (sometimes even averting major hazards). This edge transformation leads to tangible business outcomes such as increased efficiency and profitability. Deploying a reliable, distributed, and secure edge platform allows users to deploy AI applications to help multiply the benefits by many folds.
The latest IDC Worldwide Edge Spending Guide confirms the growing interest in edge computing strategy. According to the report, $232 billion will be spent alone in 2024—an increase of 15.4% from 2023. This figure is expected to grow to $350 billion by 2027. On a similar note, Gartner reports also reveal how the bulk of applications and data will be located outside of clouds and data centers by 2027, reiterating the importance of edge strategy.
Enterprises are acknowledging this paradigm shift and actively carving out an edge management and orchestration strategy for their businesses.
Industry 4.0 trends and technologies
With the advent of omni-present and faster connectivity, data is being generated from all corners of the manufacturing plant and at a much faster pace compared to a few years ago. Technologies like LoRa WAN, private 5G, NB-IoT and embedded systems are disrupting the way plant managers run their factory operations. This McKinsey article lists four key areas where disruptive technologies add immense value in the manufacturing vertical marking Industry 4.0 transformation:
- Connectivity, data and computational power
- Machine learning and artificial intelligence
- Human-machine interactions, like robotics
- Advanced engineering
Edge computing for Industry 4.0
Edge computing is at the forefront of helping customers realize their Industry 4.0 aspirations. As mentioned earlier, as systems become more connected, data becomes ubiquitous and can be leveraged in multiple applications.
Connectivity for predictive monitoring
For a plant manager, unplanned downtime at a factory floor can be a nightmare and it continues to be a challenge for the majority of them. Unplanned downtime is an event where a machine or system is unavailable. This adversely affects operational efficiency and supply chain predictability, and adds to unforeseen operational costs.
Overall equipment effectiveness (OEE) is a well-established key performance indicator (KPI) for all manufacturers. Such breakdowns also impact OEE negatively.
With the help of edge computing and embedded sensors, machines can be monitored proactively to ensure optimal performance. The machine diagnostics can be analyzed and any deviations from prescribed behavior can alert the factory manager to take pre-emptive action and turn an unplanned event into a planned one. This way they can ensure predictive maintenance and better uptime on their floor, meet their OEE targets, and smooth supply chain operations.
Artificial intelligence for quality and safety
AI is another key trend of Industry 4.0 where data analytics can be leveraged widely on a factory floor for a variety of use cases. Computer vision is one such area where camera feeds coupled with AI applications can be used to identify defective finished products, monitor machine conditions, alert for hazards like fire or intrusion, and monitor workers for their whereabouts in risky zones. Ensuring safety gear is ON for workers before stepping into hazardous zones is another key focus area for plant managers.
For a large-scale plant, centralizing and analyzing these camera feeds can lead to massive cabling and power cost. More importantly, delayed action on a critical alert can lead to a life-threatening hazard or defective finished products being shipped out.
With the help of distributed deployment, Edge Compute Stack running AI apps can circumvent these delays, ensuring faster decisions. This also eliminates the need for extra staff to analyze vision inputs 24×7, reducing operational overhead.
Advanced engineering for sustainability
CxOs are taking up bold environmental, social and governance (ESG) goals as investors question major industry players about their carbon footprint. There is growing demand to reduce energy consumed, turn to cleaner energy alternatives, and deploy energy saving methods. Legacy, proprietary systems have long dictated the use of dedicated appliances each time a new application needs to be run. This results in multiple systems to be managed, adding server/ industrial PC sprawl, which then adds to power consumption.
Edge computing directly aids in containing hardware/industrial PC sprawl by allowing you to run multiple industrial applications on a commercial off the shelf hardware (COTS) machine, leading to aggressive compute optimization. With this optimization, cybersecurity posture can be improved drastically with better visibility into vulnerability upgrades and patching.
VMware Edge Compute Stack
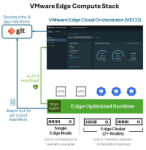
VMware Edge Compute Stack is an industry-leading solution for the manufacturing vertical that is helping customers in their Industry 4.0 journey. It is a secure, enterprise-grade, scalable solution purpose-built for the edge. The solution has two major components:
- Runtime stack software is deployed on the node/host that sits at the customer site.
- VMware Edge Cloud Orchestrator (VECO) centrally manages all these nodes deployed in a distributed manner in customer remote sites.
VMware Edge Compute Stack provides end-to-end lifecycle management of applications deployed both as virtual machines and containers. This is also tested to run real-time applications, which is often the requirement given the deterministic nature of a manufacturing process. In addition to the normal servers seen in IT environments or factory server rooms, the solution is also validated to run on ruggedized hardware (e.g. Siemens BX-39) that can be deployed in hostile environments. At the same time, the solution is tested to comply with major OT protocols like Modbus.
VMware Edge Compute Stack ver 3.7 is the latest release in the family, helping customers in the manufacturing domain quickly deploy apps in their remote sites and gain real time insights that can help in streamlined factory operations, improved worker safety and better productivity. See the release notes here.
While edge computing and IoT are set to positively impact many industries, verticals like manufacturing, retail, transportation and utilities are well positioned to benefit at a much larger scale from these technologies.
For more details about how VMware Edge Compute Stack works, please visit our blog post Redefining Edge Operations with VMware Edge Compute Stack 3.5.