Customers worldwide are using modern technologies such as AI / ML at retail stores, factories, and other edge sites to improve efficiency, increase security, lower costs, and delight their customers. Deploying workloads at the edge, close to where data is produced, cuts costs and speeds up decision-making. But scale, inconsistent network connectivity, and limited IT availability make it challenging to manage and secure edge locations.
Understanding the security challenges at the edge
Several security challenges at the edge include physical security, patching, and network isolation. While manufacturing is the top industry affected by ransomware (Source: 2023 Ransomware Analysis, Guidepoint, Jan 2024), the security challenges remain the same for every vertical:
- Privacy and security: At the edge, data and apps need to be protected from not only cybersecurity risks but also local risks. Edge locations may not have the same physical security protection level of a data center. They need to protect against local threats such a USB insertion or theft of a server. Edge hardware is often in unsecure locations such as under a retail counter or in a back room, exposing it to tampering or theft risks.
- Increased exposure to threats: Edge sites are typically characterized by a mix of industrial (e.g. industrial robots) and consumer IoT devices(e.g. security cameras). Because they are exposed to both internal and external personnel, these devices expand the security threat vector greatly. The average cost of a successful attack on an IoT device exceeds $330,000 according to research by PSA Certified.
- Inconsistent patch management and updates: As customers scale to thousands of locations, the challenge of maintaining edge components are significant. Security vulnerabilities, compliance concerns, and operational inefficiencies become hard to manage. Manual updates and user errors often result in downtime and increased maintenance costs, while outdated software exposes devices to cyber threats and hampers performance.
Zero-trust access is required to ensure a robust Industrial Control System (ICS) and OT security enabling IEC-62443 compliance. The IEC-62443 standard offers comprehensive guidelines and requirements helping organizations protect critical infrastructure and processes.
Overcoming security challenges to deliver edge-native applications
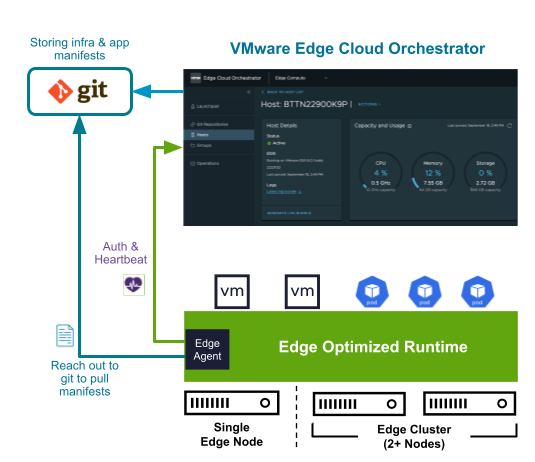
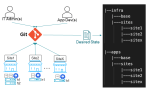
Figure 1: Edge Optimized Orchestration for Edge Compute Stack
VMware Edge Compute Stack is a purpose-built, integrated virtual machine and container-based stack that enables organizations to modernize and secure edge-native apps at the far edge. VMware Edge Compute Stack platform enables built-in security measures to address potential lack of physical security at edge locations. This edge-optimized platform features zero-touch provisioning and lifecycle management of apps and infrastructure, simplifying operations and reducing the need to dispatch IT personnel to edge locations.
Let’s learn how VMware Edge Compute Stack helps simplify the edge while minimizing security risks, so you can focus on your business goals:
- Secure app management at edge locations: Maintaining industrial computers (IPCs) on the shop floor is cumbersome and often results in significant delay in security updates and vulnerability remediation. The most common way of updating software is with a USB drive during production breaks, and it often happens that IPC fails after a bad security patch causes the production line to stop. With VMware Edge Compute Stack, system administrators can manage infrastructure, application lifecycle, and updates through desired-state configuration. Operations can be quickly restored to a previously known good state, allowing production to continue. Additionally, the Kubernetes (K8s) distribution included with VMware Edge Compute Stack allows teams to adopt modern agile practices that can greatly improve security remediation times. Simple GitOps-based infrastructure, along with VM and container-based apps, means teams will always be able to maintain rapid and consistent release of updates and security patches, enabling compliance and operational efficiency.
Figure 2: Secure app management with VMware Edge Compute Stack
- Pull-based architecture: By leveraging a pull-based orchestration model and decoupling the control plane from the management plane, VMware Edge Cloud Orchestrator (VECO) provides a single management plane capable of scaling to tens of thousands of hosts/locations. VMware Edge Compute Stack hosts always initiate the network connections to the management plane to upload telemetry, device health/heartbeats, and check for changes to their desired state configuration. Due to this design, VMware Edge Compute Stack hosts can be placed behind firewall, NAT, or proxy devices without the requirement for inbound firewall rules or reachability. Pull-based model also scales patch management and updates of applications and infrastructure so these can be tested and applied faster with VMware Edge Cloud Orchestrator. The pull-based architecture also works well with security updates for edge systems that have intermittent connectivity such as ships, aircraft, or military transports. As soon as they connect, they will sync their desired state to take on new patches or updates.
Additionally, VMware Edge Compute Stack hosts can be shipped with no sensitive data on board. The hosts will pull their desired state and software at first boot, which limits data loss exposure when compared to shipping fully provisioned systems to remote locations.
Figure 3: Pull Mode Approach with VMware Edge Compute Stack
- Physical security: VMware Edge Compute Stack host lockdown mode prevents console access to host at the remote site. The secure bootstrapping/zero-touch provisioning methodology is designed specifically for edge sites where physical security can’t be assumed. It allows administrators to explicitly define pertinent identifying information (device make/model/serial# or a unique activation key) into VMware Edge Cloud Orchestrator to prevent the activation of unknown hosts.
- Data encryption: The management plane traffic between the host and VMware Edge Cloud Orchestrator is TLS encrypted for authentication and encryption of that data in motion. The customer gets the data security and encryption of data at rest on the k8s i.e when encryption is configured, data is encrypted while stored in etcd, and is only decrypted when the resource is requested via a Kubernetes API request.
- Authentication: VMware Edge Compute Stack provides a token-based stateless authentication mechanism instead of simple user/password for host management.
- Visibility across IT, IoT and OT: The integrated VMware Edge Intelligence component provides 360-degree visibility into network flows and applies AI/ML observability techniques to gain insight and provide device profiling/behavioral baselining. This can provide valuable insight into anomaly detection related to security events.
Conclusion
In addition to the other benefits discussed in our first post, VMware Edge Compute Stack addresses edge security at multiple levels:
- VMware Edge Compute Stack implements a bootstrapping process that caters to highly untrusted locations such as the back room of a retailer. Encryption mitigates risks with hardware in unsecure physical locations.
- Security updates to applications are simple and quick to deploy with VMware Edge Cloud Orchestrator.
- From a network access standpoint, the Edge Agent opens an ephemeral connection to VMware Edge Cloud Orchestrator, thereby negating the need to keep long-lived open inbound access to the edge.
- Integrated Edge Intelligence provides 360-degree visibility into network flows and applies AI/ML techniques to detect anomalies of potential security threats.
Try VMware Edge Compute Stack for free
- Try VMware Edge Compute Stack for free at support.broadcom.com/group/ecx/trials-program
- Questions? Email us at sde-edgecomputestack.pdl@broadcom.com
Learn more
This blog is part of a series exploring the real challenges of deploying and managing applications at the edge, and how VMware Edge Compute Stack helps companies overcome those obstacles to meet their business goals.
- The five biggest challenges in edge computing
- How to properly scale edge computing deployment and management
- Solve for limited or unreliable network connectivity
- Tackle the problem of limited onsite personnel (coming soon)