By Brady Kachapuram, VMware Senior Product Marketing Manager, and Anthony Sivesind, VMware Edge Solution Architect
Power outages are becoming more frequent
Extreme weather events such as prolonged heatwaves and winter storms are increasingly impacting electric grids in their present state. Over the past 20 years, there has been a 67% increase in power outages from weather-related events, according to analysis by Climate Central. The aging grid, mostly built in the 1950s, is a major contributor to these outages.
Current substation architecture is outdated and inflexible
Distributed Energy Resources (DERs), which could make the grid more resilient to these impacts, cannot be orchestrated using existing technology. The vast amounts of data that can be generated by the grid is not easily collected and shared across the landscape. This limits centralized management systems, and makes it challenging for operators to accurately estimate and react to the changes in electricity demand as well as to minimize disruption during extreme weather events.
Legacy substation technology is built on thousands of fixed-function devices that cannot easily protect and control two-way flows of electricity within substations. They also will not provide value to leverage for future grid solutions such as blockchain transacted energy and packetized energy management. Installing, servicing, and upgrading these fixed-function devices is also very expensive and time consuming. And meeting NERC CIP compliance standards is still a painstaking and error-prone manual process.
Substation virtualization will make the grid more resilient
Utilities have taken a step towards a smarter grid by virtualizing critical grid management applications within the control center, using VMware Cloud Foundation and North American Electric Reliability Corporation Critical Infrastructure Protection (NERC CIP) compliant VMware Validated Designs. It has never been a better time to extend that capability into modernizing substations with the availability of IEC-61850-3 certified servers built for substations and VMware vSphere supporting latency-sensitive workloads in the substation.
Modern substations require standardized, flexible, scalable, and secure systems to build a data-driven power grid to improve the local decisions being made in real time (RT) and manage instabilities caused by fluctuating demand and generation imbalances over a wide area — all while remaining secure, resilient, and easy to manage. Modernizing the legacy command-and-control infrastructure within power substations, switchyards, and generation facilities today is a massive undertaking. But virtualization can initially reduce labor and downtime while building a platform with enormous return-on-investment potential.
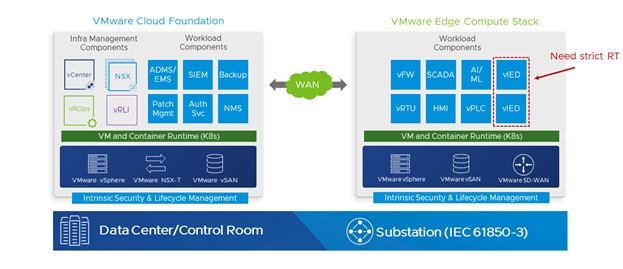
Utilities are beginning to recognize the need for optimizing and modernizing substations by building more intelligence at the edge. As an increasing number of sensors generate more data, greater processing power at the edge (substation) is the key needed to unlock the ability to continually analyze and act upon this overwhelming volume of information with minimal latency. The journey to modern substation architecture starts with leveraging standardized, commercial, IEC-61850-3 certified commercial-off-the-shelf (COTS) ruggedized server hardware for the substations, and implementing software-defined automation and control systems. Multiple substation workloads can be virtualized and consolidated onto a single platform, making management of these workloads easier.
VMware, the trusted digital foundation to accelerate innovation, provides a purpose-built platform that meets the security, performance, and manageability requirements for running substation workloads. The VMware Edge Compute Stack offers a single platform for running VM and container-based workloads and supports real-time workloads (such as protection relays or other critical components).
In addition to a more resilient grid, utilities gain the following benefits from virtualized edge compute:
- Connect their control center(s) to their edge substations, switchyards, and generation facilities and manage them with a common set of tools
- Reduce CAPEX due to labor reductions with hardware consolidation, and reduce OPEX due to labor reductions and lower maintenance overhead
- Simplify installation, maintenance, and future upgrading of utility workloads while making work environments safer by minimizing the number of dangerous touchpoints
- Streamline NERC-CIP compliance with increased access to data and smaller physical networks
Learn more at DISTRIBUTECH
Join VMware at DISTRIBUTECH, the leading transmission and distribution event, in Dallas from May 23-25, 2022. We will showcase our joint solutions with multiple ecosystem partners including Intel, Dell, Crystal, Advantec, and ABB that enable utilities to build modern substations.
About the authors
Brady Kachapuram works as a Senior Product Marketing Manager on the VMware SASE team, where he focuses on vertical solutions for VMware SASE and Edge. Prior to joining VMware, Brady held a variety of product and engineering roles at Pure Storage, Ruckus Networks and Cisco focusing on the enterprise and commercial business. Brady has an MBA from USC and an engineering degree from Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati. In his spare time, Brady enjoys visiting the National Parks and going out for a run. Brady also likes to read nonfiction books. “Thinking Fast and Slow” by Daniel Kahneman continues to be his favorite. Brady lives in the Bay Area with his wife and toddler son.
Anthony Sivesind received his B.S. degree, as well as his M.S. degree, in electrical engineering from Arizona State University, with an emphasis in mechatronics and alternative energy. He has 18 years of overall experience in the utility industry and worked in a variety of roles during his tenure at Salt River Project, including designer, engineer, and project manager of major substation construction and transmission jobs, new protection and control initiatives, as well as standards development and implementation. He exited as an executive engineer working within the Protection, Automation, and Control Strategy department, focusing on research and development initiatives to efficiently protect and control the grid, in support of SRP grid modernization. He recently joined VMware as an Edge Solutions Architect to extend his learning and to lend his experience within their utility vertical. He is a member of IEEE, and a licensed electrical engineer in the state of Arizona.