You Wouldn’t Try to Combine Self-Driving Technology and a Manual Shift Car
Many people see Tesla as the future of driving. Tesla cars come standard with software-enabled autopilot features and full self-driving (FSD) capabilities in beta that continue to improve through over-the-air software updates. However, no manual shift hardware is found among their fleet, as FSD and stick shifts are two technologies that fundamentally mismatch.
Automation and programmability are key to realizing the full potential of FSD. In the same way, modern, advanced load balancing is essential to full network automation via VMware NSX.
The Future of Load Balancing: Aligning with VMware’s Multi-Cloud Strategy
Analogous to Tesla, NSX Advanced Load Balancer (Avi) is the future of load balancing. Built on a software-defined architecture, Avi comes standard with features and capabilities designed to meet your load balancing needs today and into the future — regardless of where your applications are deployed. No load balancing hardware is required.
Avi offers the industry’s only complete L4-L7 application services for VMware environments. VMware acquired Avi two years ago to enter the load balancing and WAF space. Since then, VMware has successful replaced 12,000+ hardware load balancers, with more than 5,000 load balancers replaced in 2021 alone. We are continuing this journey with NSX in terms of tighter and more seamless integration. And, as our capabilities evolve, the platform and its app services will be continuously upgraded through over-the-air software updates.
What’s New?
Scaling up and migrating to a cloud environment — whether public or private — requires simplified load balancing deployment, configuration, and management; end-to-end app performance visibility and control; and the ability to rapidly add new environments and capabilities to an existing environment. Avi can do all of this and more!
With the NSX-T 3.2 release, we’ve further simplified installation and deployment of NSX Advanced Load Balancer (ALB) through tighter integration with NSX Manager.
Simply put, Avi is able to install and deploy the Avi Controller from the NSX-T Manager. Thanks to API integrations between the two platforms, customers can configure load balancing services using the NSX-T Policy UI and APIs.
As seen in Figure 1 below, you can directly cross launch the Avi UI from the NSX UI instead of having to log into the Avi console separately.
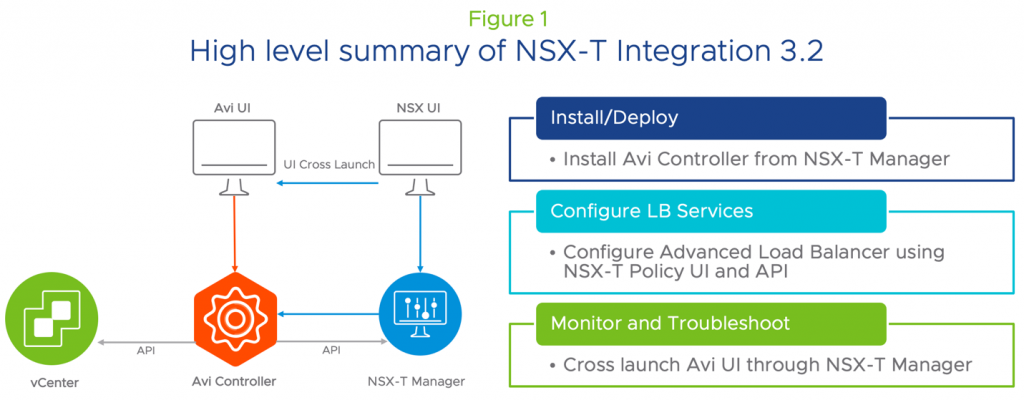
You now have two ways to consume Avi. After seamlessly deploying the Avi Controller through NSX-T Manager, you can consume basic load balancing use cases through the NSX-T UI and API.
Avi is VMware’s load balancing choice going forward. That means that, for all VMware products, you will see increasingly tighter integrations, and not just with NSX. The recommendation for all customers is that whenever you are doing a new deployment, go ahead and start consuming Avi. For any existing deployment, migrate to Avi.
For advanced use cases, our recommendation is to consume Avi directly using automation (e.g., vRA, vRO, Ansible, Terraform) or the Avi UI/API. Furthermore, NSX customers can migrate their load balancing solution from NSX-v to the VMware NSX Advanced Load Balancer using the Migration Coordinator or via NSX-T with a standalone tool.
For more details, read the recent blog on migration and watch the webinar Deploying Elastic, Self-Service Load Balancing for VMware NSX-T.
Avi has a Single API End Point for All Integrations
Because Avi is an API-first, API-driven architecture, you can integrate with different ecosystems, not only at the infrastructure level but also at the operational and orchestration levels. This clearly differentiates Avi from legacy load balancers, and it’s all possible because of Avi’s 100% REST API model. See Figure 2 below.
The Avi Controller can be deployed using your orchestration tools — for example, vRO/vRA, Ansible, or Terraform. You can even use NSX-T Policy APIs or the NSX-T UI to deploy the Avi Controller for the initial install itself, or you can use any of the SDKs like Go or Python to deploy them.
Once you deploy your orchestration tools, you can integrate new or existing environments/ infrastructures with Avi Controller’s automation. What does that mean for you? It means that load balancing functionality is available wherever you require it, be it bare metal or a virtualized environment, on-prem, or a cloud-native container environment.
Each cloud has its own implementation of a load balancer. You don’t have the same look and feel, or the same operational capabilities, when you’re using multiple clouds in your deployments. With Avi, you can easily integrate today’s most widely used IaaS automation platforms (NSX-T, VMware, Kubernetes, OpenShift, AWS, Azure, Google Cloud Platform, etc.). For those of you familiar with the VMC on AWS offering, when deployed, Avi has a no access solution. We have expanded this offering to the other public clouds like Azure and Google Cloud.
Once you achieve complete infrastructure automation, you can move to operationalize or automate your operations. We integrate with many operational automation tools, such as Grafana, Prometheus, Splunk, Zabbix, Infoblox, Slack, VENAFI, AppViewX, PageDuty, and Route53. Leveraging your preferred tools, Avi knows when to create new service engines and when to scale. Together, Avi works with your tools to determine when you need to scale out and in, utilizing metrics to make your provisioning much more intelligent.
Why is this important to you? Your workflows will have the same look and feel across all environments, from the same controller.
Install, Deploy and Consume Avi Today!
Resources:
- Check out our NSX-T Integration Guide
- Visit our Migrate to Advanced Load Balancing webpage
- Review our on-demand webinars: Deploying Elastic, Self-Service Load Balancing for VMware NSX-T and What’s New in VMware’s Multi-Cloud Load Balancing and Application Services.
- Keep current on all things Avi: VMware Load Balancing and WAF blog.


Comments
0 Comments have been added so far