Recent studies show that 40% of internet website traffic originates from bot activity. Depending on the purpose of your website, this bot traffic could be good (for example, search engine crawlers) or bad (website scrapers). In the 40% of traffic typically created by bots, approximately 15% delivers welcome functionality – this traffic comes from good bots. However, the other 25% comes from bad bots undertaking activities that most organizations will want to prevent.
VMware NSX Advanced Load Balancer cybersecurity solutions will let you identify the human users and bot traffic to your website and then allow you to decide how any traffic you classify as problematic gets handled. It does this via Bot Detection, Bot Classification, and an Action engine. More detail on the bot protection solution is below, but before we get to that, let’s take a deeper dive into the various types of bots that need to be detected.
Good Bots and Bad Bots
Categorizing bots as good or bad can sometimes be arbitrary depending on what the bot is doing and the purpose of the website it is targeting. However, most people will agree on the bots placed in each group.
Good Bots – Good bots perform jobs on the web that provide a benefit. Examples include:
- Search Engine Crawlers – such as GoogleBot, Bingbot, and DuckDuckBot that continuously index web content to provide it in search results on Google, Bing, DuckDuckGo, and increasingly on smart devices. Not every organization wants their website to be open to web crawlers to index, and they might class these bots as bad. But for the most part, web crawlers are seen as good, but they can be blocked if required.
- Partner Bots – bots that provide automated business services between websites. An everyday use case is between e-commerce applications and payment processors. A partner bot, such as PayPal’s Instant Payment Notification (IPN) bot, automatically passes a transaction status back to an e-commerce site. This makes the customer experience much smoother and boosts customer satisfaction. Many other types of B2B partner bots exist to enhance cooperation and services delivered via the web.
- Site Monitoring Bots – many services exist to monitor the status of websites and web applications to alert site owners when there is a problem. Pingdom is one example. Sophisticated monitoring bots can also report page load times and uptime within specified periods.
- Copyright Checking Bots – using copyright-protected content lifted from the source to pass off as original on another site is a frequent issue on the web. The copied content can be text, music, video, or any other type of content that you can view on websites. Copyright checking bots act similarly to web crawlers but focus on finding materials copied without the originator’s permission. This allows the owner of the copyrighted material to issue takedown notices.
- Backlink Check Bots – by definition, the web contains collections of pages that link to others on the same site or external websites. Pages that link to a particular page are known as backlinks. These play an essential role in how search engines rate and rank web pages and where they get shown in search results. Backlink checking bots are similar to the web crawlers that index pages, but they provide information relevant to SEO professionals looking to optimize websites and individual pages to improve web search results.
- Website Feed Bots – many services provide automated feeds with updates on websites. In effect, they push changes to subscribers without them having to check a particular web page. These services often aim to mimic the functionality provided by RSS or Atom news feeds now that including a news feed via RSS or Atom isn’t as common as it once was. To identify website changes, feed bots grab the current content periodically, compare it to the previous version, and then alert anyone subscribed to that site’s alerts. Many website owners would classify these types of bots as bad, given that they can reduce traffic to their site, which can impact advertising revenue and usage stats.
Bad Bots – these are easier to classify than some good bots, assuming you are not a bad actor looking to do nefarious activities on the web.
- Scraper Bots – automated malicious bots that copy information from a website that will be useful to others. Examples include the wholesale copying of pricing and product information so that a competitor can adjust their pricing and product descriptions to attract customers from the site they scraped.
- Spam Bots – these often target comment sections on websites to promote dubious ideas, post phishing links, or other links to cybercriminal sites. Many website platforms have built-in protection against the sort of content these spam bots post, but the bad actors continually evolve them, and it makes sense to block them before they try to post on websites.
- Click Fraud Bots – many websites rely on web advertising to fund the site or even as a generator of income for the site owners beyond the day-to-day running costs. Click fraud bots get used to artificially inflate interactions with ads and other website controls to raise the number of clicks reported back to advertisers or others monitoring web traffic. The online fraud bots aim to simulate the behaviors of real people on a site to evade bot protections.
- Web Crawler impersonators – many websites are configured to allow the web crawler bots from search engines to access particular areas on the site via the characteristics of the incoming crawler request. Cyber attackers have realized this, and they create bots that impersonate good bots such as GoogleBot, Bingbot, and DuckDuckBot to get access to web pages blocked to other attack methods. Once they are granted access by impersonation, these bad bots can scrape sites, post spam, and use other cyberattack methods.
- Botnets – automated attacks against websites via overwhelming traffic sent from compromised devices on the internet are known as botnet attacks. They are frequently used to mount DDoS attacks to take a website offline, send massive amounts of spam, and allow for stealth attacks of other types while a botnet attack is happening.
What is Bot Management?
Protecting a site against bot attacks requires a solution that can identify bots of all kinds, separate them from humans, and then allow website administrators to decide what should happen to bot traffic.
NSX Advanced Load Balancer includes a management solution to deal with bot traffic. It uses an engine that has three core components. Figure 1 illustrates them:
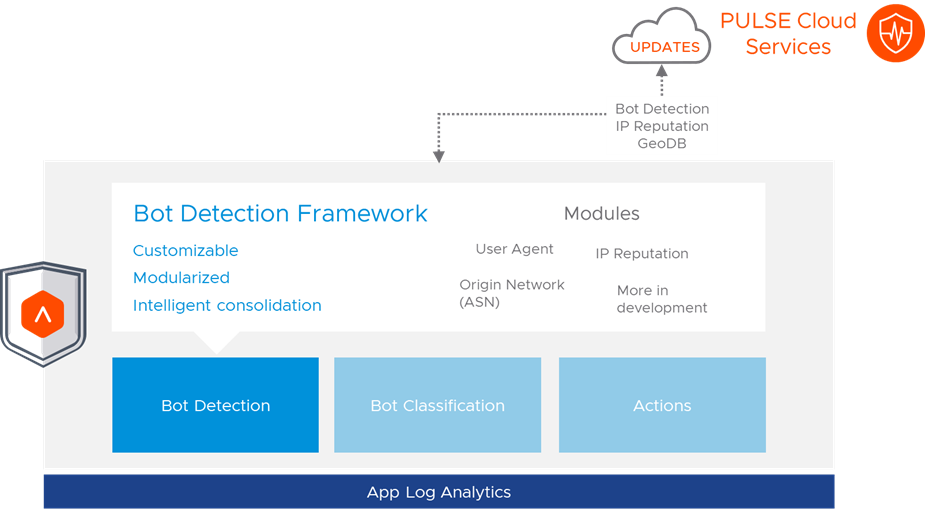
The bot protection builds on the solid core of the WAF pipeline, which delivers web cybersecurity. The core components provide:
Bot Detection – the primary and most important step in the bot protection process. Various checks such as IP reputation, IP location, User-Agent ID, Origin Network (ASN), and more are used. TLS fingerprinting that compares TLS information against that expected from a particular user agent is currently rolling out via the NSX Advanced Load BalancerTech Preview process. Note that IP reputation and other data used in detection get updates via the PULSE Cloud services and that a subscription to this is required to use bot protection.
Bot Classification – the engine uses the information gathered and decision algorithms to determine if a particular connection is coming from a bot or a human. If a connection is from a bot, the engine classifies the bot type using a bot mapping policy. The classification types are Human, Good Bot, Bad Bot, Dangerous Bot, User Defined, and Unknown Client.
Actions – business logic is used for each type of classification using HTTP policies, DataScript, or WAF rules. The choices available are: Allow, Close Connection, Rate Limit, and Send Custom Response.
You can read more about the bot protection engine on the documentation Bot Management page.
The NSX Advanced Load Balancer Bot Protection Philosophy
The primary focus of the bot protection and management solution is to provide effective differentiation between bots of all kinds and humans. After this classification gets made to the highest level of accuracy, we feel that the actions that follow should be defined by each organization based on their business needs and goals.
Our solutions provide the platform for website and web application bot protection based on your rules and provide additional cybersecurity protections via a WAF and more. See the Platform Overview page for a deep dive into the NSX Advanced Load Balancer solutions.








