Since its introduction in vSphere 7.0.GA, vSphere Lifecycle Manager (VLCM) User Interface for vSphere Client (HTML-based) was gradually improved through subsequent update releases. Let’s see some of the features that have been added since it was released.
Importing image from a host while creating a cluster, you can now choose an ESXi host to extract the vLCM image, add it to the VLCM depot and set it as a cluster’s desired state – all this done for you automatically.
This is useful for example for air-gap environments where you do not have access to internet (and to resp. VMware online image depot).
In order to do this, you have to choose “Import image from an existing host in the vCenter inventory” or “Import image from a new host” option:

After choosing one of these options, a list of hosts is presented for extracting the image from:

Importing image from a host while adding it to a cluster – you can choose an option to extract one of hosts being added’ image and set it as a cluster desired state:

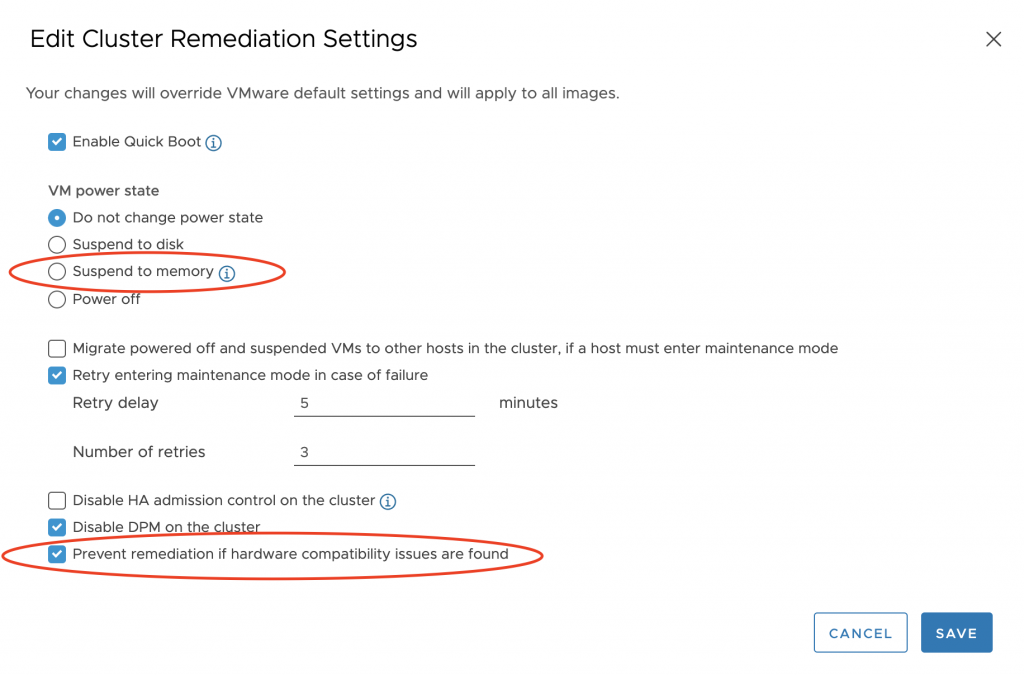
There are two new remediation settings added:
- Suspend to memory – suspends the VM into host’s memory during remediation, thus reducing the time for upgrade and the downtime of system and services. Works only when QuickBoot is enabled.
- Prevent remediation if hardware compatibility issues are found – hardware compatibility checks are performed as part of the remediation pre-check and the remediation tasks for VSAN-enabled clusters. By default, if hardware compatibility issues are found, they are reported as warnings, which does not prevent remediation. With this option turned on, such issues are reported as errors, which prevents the remediation process.
Checking hardware compatibility for disk drives – so far such checks were performed for PCI devices only. In the newly added tab, you can see disks compliance statuses and the affected hosts. You can also manually override the compliance status if needed.

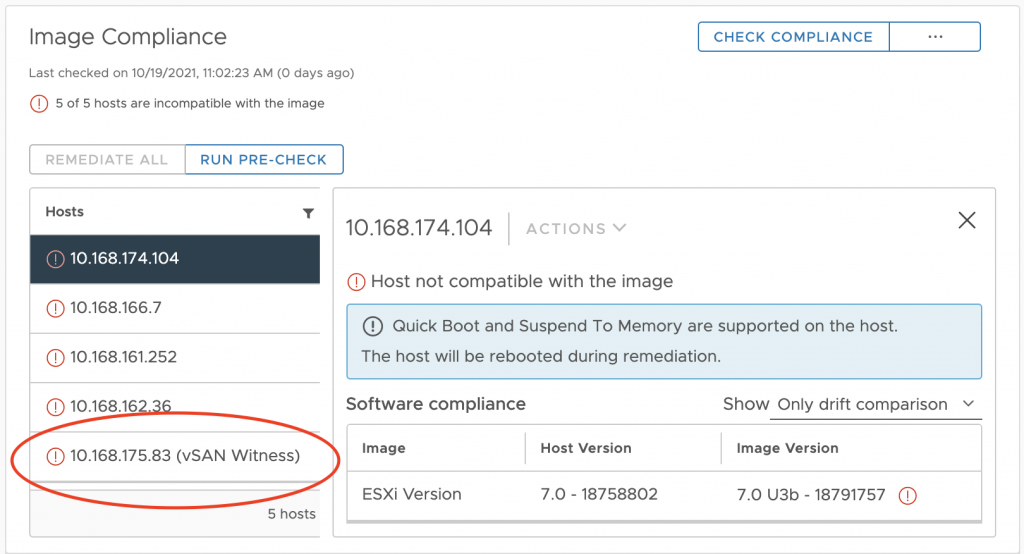
Managing VSAN Witness host – until recently, such hosts could be updated/upgraded through baselines. This was in part because vLCM could only manage hosts within a cluster, and witness host resides outside a cluster. Now vLCM can also manage such hosts and shows their compliance status together with the other hosts from vSAN stretched cluster or two nodes cluster.
Error messages were also improved a lot to become more understandable and actionable.
This is not a comprehensive list – a lot more fixes and small improvements were done, so be sure to check out the latest vSphere Update release!



