Since its inception, VMware Cloud on AWS has depended upon our hyper-converged solution, vSAN. Using vSAN allows our customers to expand or contract their SDDC clusters as needed. This capability dramatically simplifies operations and infrastructure complexity. Furthermore, it is generally the most economical way to operate within the AWS Cloud, but there are exceptions to that rule.
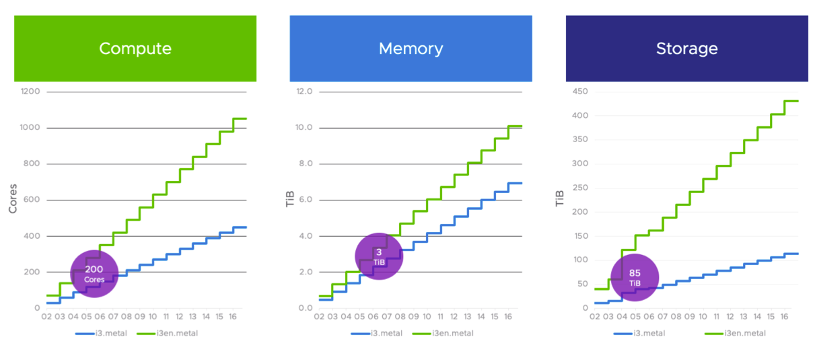
While the number of hosts required to support a given workload is driven by CPU, memory, or storage, the difference is typically within a few hosts, and for the most part, it works out. This is not the case when storage requirements dramatically exceed the hosts needed for compute and memory.

Introducing NFS Datastore support for VMware Cloud on AWS
To resolve this tension, we have added support for NFS Datastores on VMware Cloud on AWS. NFS Datastore support allows independent scaling of compute and storage, enabling organizations to right-size their deployment to control costs. This also makes VMware Cloud on AWS more suitable for storage intensive workloads. NFS datastores supplement vSAN and can be used to store Virtual Machines, Virtual Disks, Content Libraries, ISO, etc. While built upon the long-standing NFS support used on-premises, there are some changes of note.
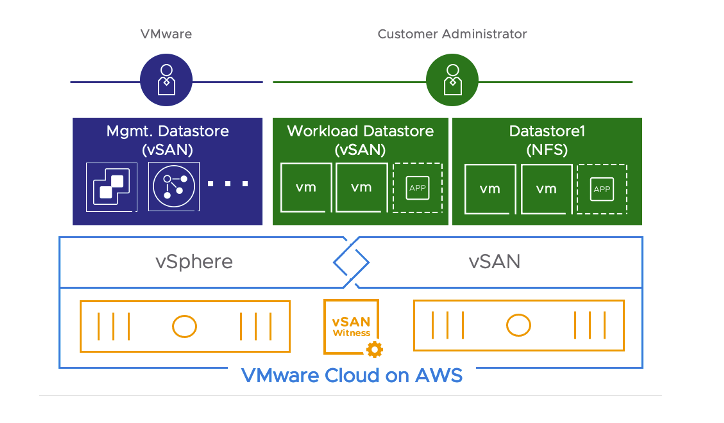
VMware Cloud on AWS Certified NFS Storage
We have created a new NFS certification process to ensure a consistent experience and help you integrate external storage into your cloud SDDC. VMware will require any datastore target to maintain a VMware Cloud on AWS NFS Storage certification.
VMware Cloud on AWS SDDC Integration
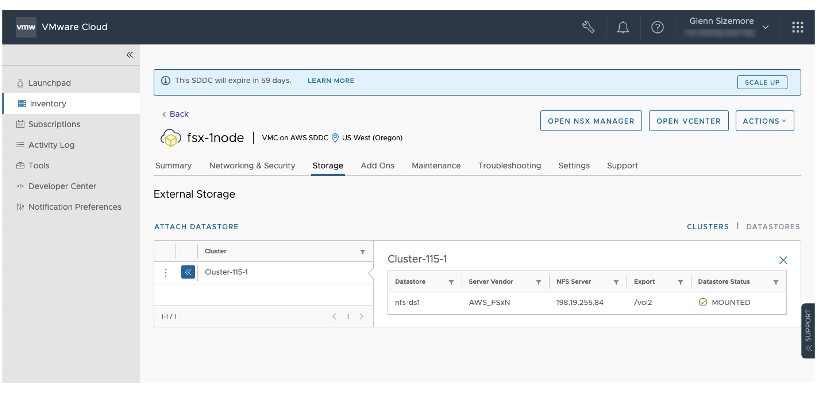
NFS Datastore management is integrated into the VMware Cloud on AWS Console and API to simplify SDDC administration. As a customer, you declaratively add a datastore to one or more clusters. From that point on, the service will manage and monitor that datastore as part of the cluster. The service supports up to four datastores per cluster, and any datastore can be attached to every cluster in the SDDC. We recently announced VMware Cloud on AWS integration with Amazon FSx for NetApp ONTAP as an external NFS datastore supported by this integration. When using FSx for NetApp ONTAP as a datastore, Amazon Web Services (AWS) provides lifecycle management of the FSx for NetApp ONTAP file system (security updates, upgrades, and patches), VMware is responsible for the SDDC lifecycle management and the customer is responsible for establishing the network connectivity, creating, and attaching the external NFS datastore to the SDDC. In this case, customer owns and manages the storage configuration.
Performance considerations
VMware Cloud on AWS uses ‘Partition Placement Groups’ to attempt to place every host in each cluster in different AWS logical partitions. Logical partitions do not share the same underlying hardware. While this increases the resiliency of the service by limiting the impact of an underlying infrastructure failure, it also has an impact on NFS performance. Each host currently maintains a single TCP/IP session for each datastore mount. Those sessions are throttled at 5Gbps by the AWS backend. In practice, this means that each datastore mount on each host can expect ~450MB/s throughput.
Putting this together, each datastore can drive up to 450MB/s of throughput on each host. Hence, if a single datastore were mounted on five hosts, theoretically, the cluster would have access to 2GB/s of throughput. We expect these limitations to be temporary and should not impact most workloads. However, depending on your specific scenario, you may consider them in your storage requirements.
Restrictions
External storage may not be used with any VMware Cloud on AWS Stretched SDDC. Any attach requests submitted to a Stretched Cluster will be blocked at the platform layer until this restriction is lifted.
VMware Site Recovery does not support configuring an NFS datastore as the replication source or target within VMware Cloud on AWS. VMware Site Recovery can be activated on an SDDC/Cluster using external storage but will not allow an external datastore to be selected when configuring protection.
VMware Cloud Disaster Recovery does not support external storage.
Support and SLA considerations
VMware provides SLA coverage for any NFS Storage that VMware manages. Customers who connect storage not directly controlled by VMware are responsible for the availability of any data stored.
When deploying external NFS datastores, customer is responsible for the following:
- Configuring and maintaining the storage target for use as a datastore.
- Configuring and maintaining network connectivity between the storage target and every host within the SDDC.
- Maintaining free capacity within the datastore.
In the event of an issue, VMware Support remains the first point of contact and will make its best effort to resolve the problem. Should support verify that the problem is not anywhere in the VMware SDDC and the storage is managed by the customer, VMware will guide the customer through pulling in the appropriate support resources. In the case of FSx for ONTAP, VMware will guide the customer through engaging AWS support to troubleshoot FSx.
Summary
If you have previously assessed VMware Cloud on AWS and found your storage requirements were too large for the service, now is an ideal time to reassess. With the addition of external storage, we have rewritten the rules around what workloads “fit” within the cloud. We look forward to sharing more details as we continue to enhance this integration.
For more information on VMware Cloud on AWS integration with Amazon FSx for NetApp, read the announcement blog by Hitendar Sethi, Product Marketing, VMware cloud on AWS
Additional resources:
- FAQs: Integration with Amazon FSx for NetApp ONTAP
- Demo: Integration with Amazon FSx for NetApp ONTAP
- Deployment Guide
- TCO Calculator for Amazon FSx for NetApp ONTAP
For more information related to VMware Cloud on AWS, here are some key resources you can use:
- Visit VMware Cloud on AWS website or watch VMware Cloud on AWS: Overview.
- Follow us on Twitter @vmwarecloudaws and give us a shout with #VMWonAWS.
- Leverage the new VMware Cloud on AWS Techzone for curated technical documentation.
- Watch informative demos, overview videos, webinars and hear from customers on our YouTube channel: VMware Cloud on AWS on YouTube.
- Try the VMware Cloud on AWS Lightening Lab for a first-hand immersive experience.
- Read Technical Guides on Operations, Applications, and Performance.
- Listen to latest episodes of VMware Cloud on AWS Unplugged Podcast.
- Check out the Cloud Customer Success Community, engage with your peers and get your questions answered.
Disclaimer: VMware makes no guarantee that services announced in preview will become available at a future date. The information in this blog is for informational purposes only and may not be incorporated into any contract. This article may contain hyperlinks to non-VMware websites that are created and maintained by third parties who are solely responsible for the content on such websites.
Discover more from VMware Cloud Foundation (VCF) Blog
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.






