VMware Cloud on AWS provides a stable, consistent and globally available infrastructure solution. There are circumstances in which users will need to deploy the vSphere hosts containing VM data in one data center while maintaining a dedicated witness host in an offsite location. In this how-to article, we walk you through deploying a two-node VMware vSAN cluster on-premises with an offsite witness deployed in VMware Cloud on AWS.
VMware vSAN and VMware Cloud on AWS
VMware vSAN aggregates disks that are locally attached to vSphere hosts into a robust, resilient virtual SAN. Workloads placed on the vSAN benefit from per-VM flexible storage policies including failures-to-tolerate, space reservation, disk striping and more.
vSAN redundancy is normally achieved via deployment of three or more physical ESXi servers. Each object stored on vSAN will have a minimum of two data components mirrored across two of the hosts, plus a witness component located on the third host.
There are circumstances in which it may be desirable to deploy the vSphere hosts containing VM data in one data center and to maintain a dedicated witness host in an offsite location. This can apply in a vSAN stretched cluster scenario or in a two-node vSAN cluster. Caveats for each of these can be found in the hyperlinks.
Practical examples for an offsite witness might include a large grocery or department store chain with 2-node clusters on-premises at each store and a consolidated set of witness appliances in the cloud. Organizations with two data center locations may choose to deploy a stretched cluster for resiliency and then leverage the cloud as a geographically separate witness location.
VMware Cloud on AWS is a cloud solution jointly developed by VMware and Amazon Web Services that allows VMware vSphere workloads to be deployed on bare-metal ESXi hosts located in AWS data centers worldwide.
As of version 6.7, vSAN supports the use of a vSAN Witness Appliance to act as a dedicated witness node. VMware customers leveraging VMware Cloud on AWS who require an offsite location for a vSAN witness node can deploy the Witness Appliance in their VMware Cloud on AWS software-defined data center (SDDC). An excellent summary article on this configuration was written by Glenn Sizemore in a separate VMware Blog.
Leveraging VMware Cloud on AWS provides a stable, consistent and globally available infrastructure solution. Adding a witness to a VMware Cloud on AWS SDDC in Frankfurt, Paris or Dublin for EMEA operations will use the same process and result in the identical look and feel as adding a witness to a VMware Cloud on AWS SDDC in Oregon or California for operations in the United States.
This “How To” article covers the steps to deploy a two-node VMware vSAN on-premises with an offsite witness deployed in VMware Cloud on AWS. It assumes hands-on familiarity with vSphere hosts, vCenter, and VMware Cloud on AWS administration.
On-premises Configuration
Nested ESXi hosts were deployed for the on-premises environment:
- 2 x ESXi 6.7 hosts (nested). Each host has:
- CPU: 2 CPUs
- Memory: 8 GB RAM
- Network: 2 NICs
- Disk:
- 8 GB – vSphere installation
- 5 GB – vSAN Cache
- 20 GB – vSAN Capacity
- 20 GB – vSAN Capacity
- All vSAN disks marked as “Flash”
Nested ESXi hosts and their vCenter VM were deployed on physical ESXi hosts:
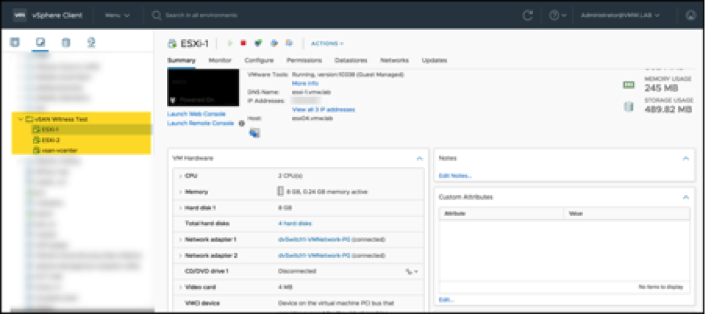
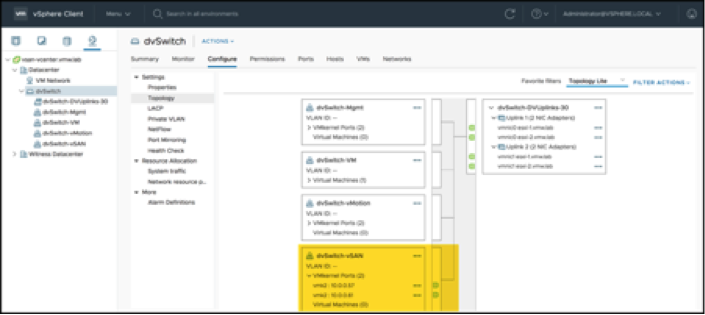
Within the nested hosts, each has a vSAN VMkernel NIC on a virtual distributed switch:
VMware Cloud on AWS
A single-node VMware Cloud on AWS SDDC was created for the vSAN Witness Test:
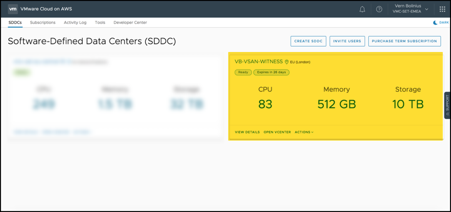
A dedicated network segment was created for the vSAN Witness Appliance:
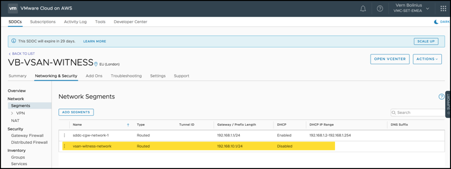
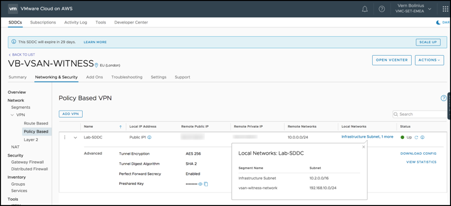
A Policy-Based VPN from on-premises to the SDDC was created to allow:
- vSAN Witness Appliance management network to communicate with the on-premises vCenter
- vSAN Witness Appliance vSAN network to communicate with the on-premises vSAN network
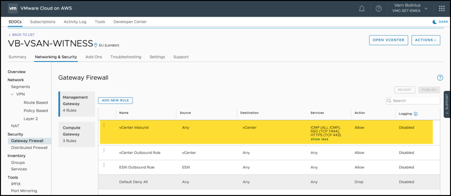
VMware Cloud on AWS Firewall Rules
A few firewall rules are required:
- Management Gateway rule to allow traffic from the Internet to reach the VMware Cloud on AWS vCenter (vCenter Inbound). You’ll need this to deploy the Witness Appliance from the source laptop/desktop to which you downloaded it. Note that this may be further secured by only allowing access to the cloud vCenter via the VPN, and not via the Internet.
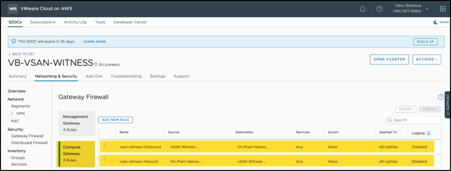
- Compute Gateway rule (vsan-witness Outbound) to allow traffic from the Witness Appliance to reach:
- The on-premises vCenter Server
- The on-premises vSAN network
- Compute Gateway rule (vsan-witness Inbound) to allow traffic from on-premises to reach
- The vSAN Witness management NIC
- The vSAN Witness vSAN network NIC
vCenter Inbound:
vSAN Witness Traffic:
Deploying the Witness Appliance
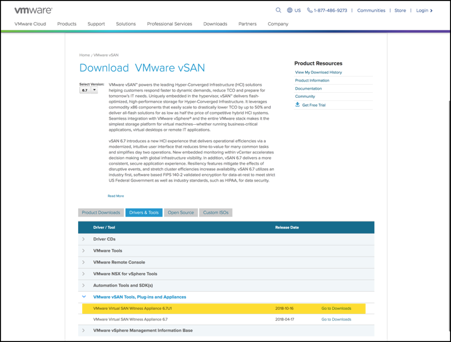
Download the VMware vSAN Witness Appliance
Download the VMware vSAN Witness Appliance from vmware.com. The version of the appliance should match your on-premises version of vCenter:
Deploy the Witness Appliance on VMware Cloud on AWS
Change the extension of the downloaded Witness Appliance from *.OVF to *.OVA
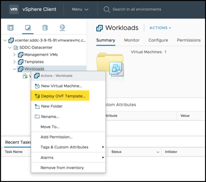
Sign in to the VMware Cloud on AWS vCenter and navigate to the Workloads folder to deploy the OVF template:
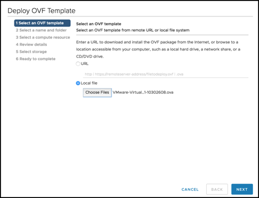
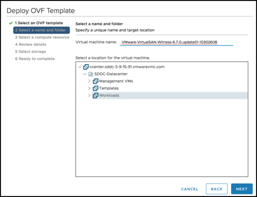
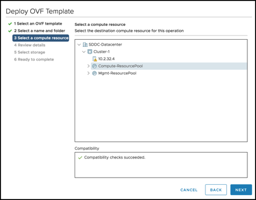
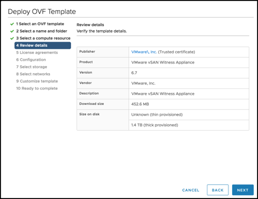
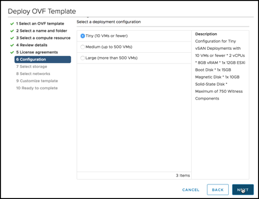
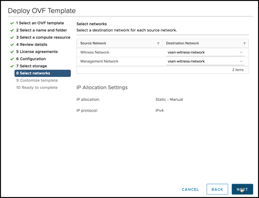
Note that both the Witness Network and the Management Network have been mapped to the same “vsan-witness-network”. These could be separated if desired and placed on distinct VMware Cloud on AWS network segments.
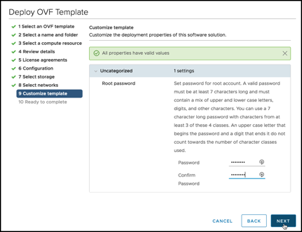
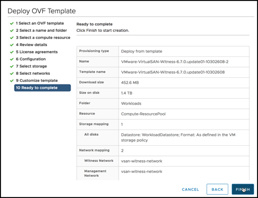
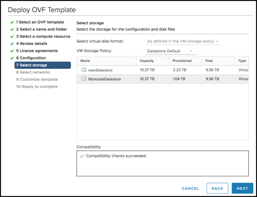
When complete, you will have a vSAN Witness Template deployed into the Workloads folder in VMware Cloud on AWS, ready to be configured:
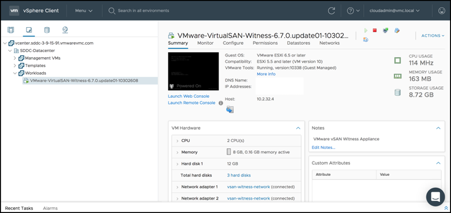
Configure the Witness Appliance
Once the appliance has been deployed on the VMware Cloud on AWS SDDC, it needs to be configured.
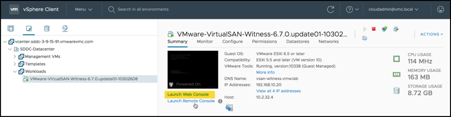
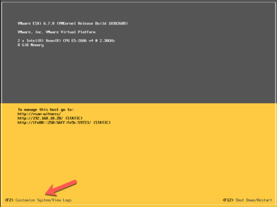
First, set the Management interface values from the appliance’s console. Remember, this is an ESXi host, and can be configured as such.
Launch the Web Console for the VM and log into the ESXi console:
Navigate to Configure Management Network and set networking values:

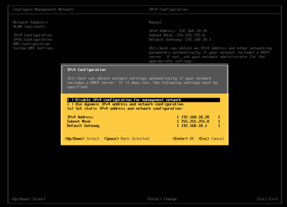
Similarly, set the DNS Configuration and DNS Suffixes.
When complete, log into the ESXi host from a browser on-premises:

Under Networking, set the address for the vSAN VMkernel NIC. Note that this NIC has vSAN Services enabled by default:
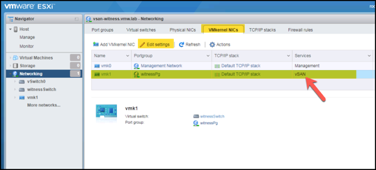
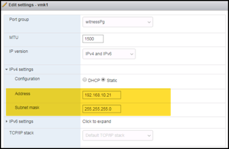
Add the Witness Appliance to the On-premises vCenter
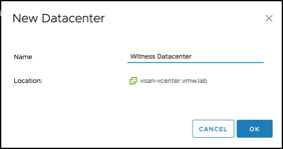
Create a new data center called “Witness Data center”
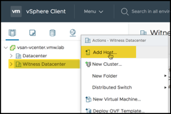
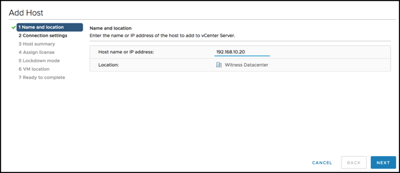
Add the Witness Appliance to the Witness Data center using “Add Host…”
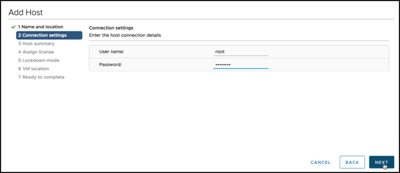
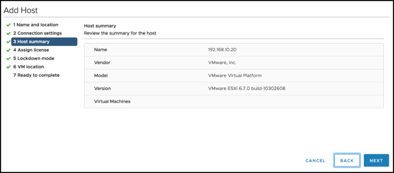
Note that the vSAN Witness Appliance has its own license. It is not necessary to assign one.
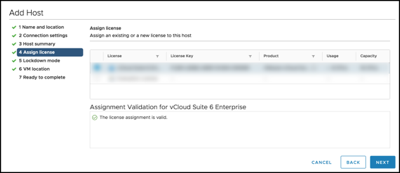

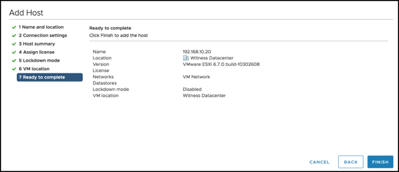
Create the vSAN
In your on-premises cluster, create the vSAN.
Start by right-clicking on the Cluster and select “Settings”:
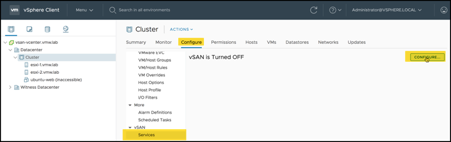
Under vSAN, select “Services” and click “Configure…”
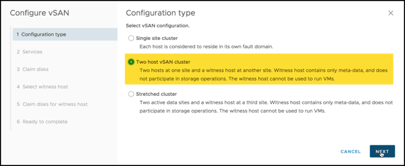
Note that I am choosing to configure a 2-node vSAN cluster with a remote witness. The same screen would be used to enable a Stretched Cluster:
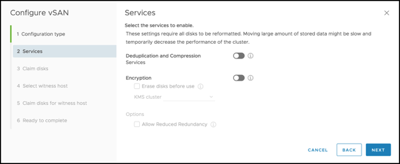
I am choosing to not enable deduplication, compression, or encryption in the demo environment:
I am claiming the 5 GB disks (1 per host) for the Cache tier and the 20 GB disks (2 per host) for the vSAN:
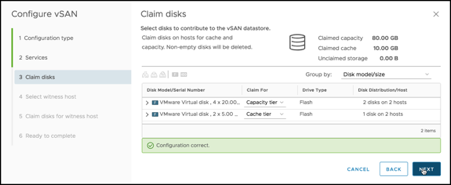
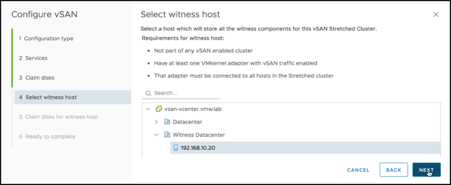
For the Witness Host, specify the Witness Appliance you installed in VMware Cloud on AWS:
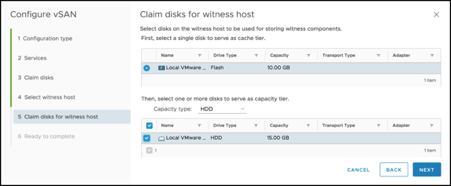
The vSAN configuration displays the disks on the witness virtual appliance:
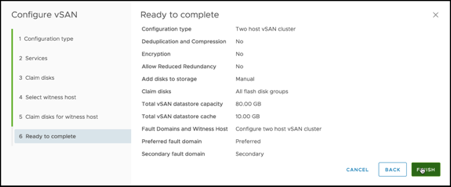
When the configuration finishes, we have a 2-node vSAN cluster on-premises with a remote witness on VMware Cloud on AWS!
Deploy a VM
Deploying a VM will show us that the workload components are distributed to the vSAN data nodes and to the witness node, as expected.
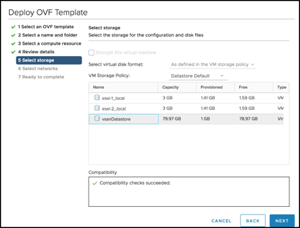
Deploy a workload – in this case an OVF Template of a small Ubuntu Linux VM – onto the vsanDatastore:
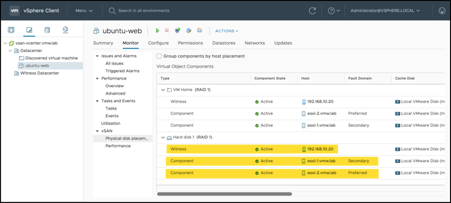
With the VM fully deployed, go to the VM in your on-premises vCenter and click on Monitor. In the vSAN drop-down for the VM, under Physical disk placement, you can see that the VM’s data components are distributed between the two on-premises ESXi hosts and the witness components are on the remote witness appliance:
Congratulations, you’ve successfully deployed a 2-node vSAN stretched cluster on-premises with a witness on VMware Cloud on AWS.
Resources
- You can learn more about our VMware Cloud on AWS service at the VMware Cloud on AWS website or by viewing the VMware Cloud on AWS: Overview video
- Learn about the features and capabilities of VMware Cloud on AWS in this Evaluation Guide
- Follow us on Twitter @vmwarecloudaws and give us a shout with #VMWonAWS
- Watch informative demos, overview videos, webinars and hear from our customers: VMware Cloud on AWS on YouTube
- Try the VMware Cloud on AWS Hands-on Lab for a first-hand immersive experience
- Read our latest VMware Cloud on AWS blogs
- Obtain the VMware Cloud on AWS Solution Brief and VMware Cloud on AWS TCO 1-pager
- Follow the VMware Cloud on AWS release notes on continuing updates
Discover more from VMware Cloud Foundation (VCF) Blog
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.






