When deploying virtual machines (VMs), where they land matters — not just for performance, but for efficiency, compliance, and cost. That’s where Workload Placement in VMware Cloud Foundation (VCF) comes in. It finds the ideal cluster or host for each VM by evaluating real-time capacity, performance data, and your organization’s business or operational intent.
In short, it helps ensure every workload lands exactly where it should — without the manual guesswork.
Why Workload Placement Matters
If you’ve ever had to manually decide where to deploy a new workload, you know how easy it is to create resource hotspots or imbalance within your clusters. Workload Placement eliminates that uncertainty.
By continuously analyzing real-time capacity and performance metrics, VCF automatically recommends — or even performs — optimal VM placements. This ensures your workloads meet performance, compliance, and cost objectives while freeing your teams to focus on innovation instead of firefighting.
How It Works: The “Smart Room Planner” Analogy
Think of Workload Placement as a smart room planner for your data center.
Each VM is a piece of furniture — some large, some small, all with specific needs. The clusters and hosts are rooms with varying space, lighting, and features. Workload Placement evaluates the “furniture” and the “rooms” to find the perfect fit for its intended use.
![]()

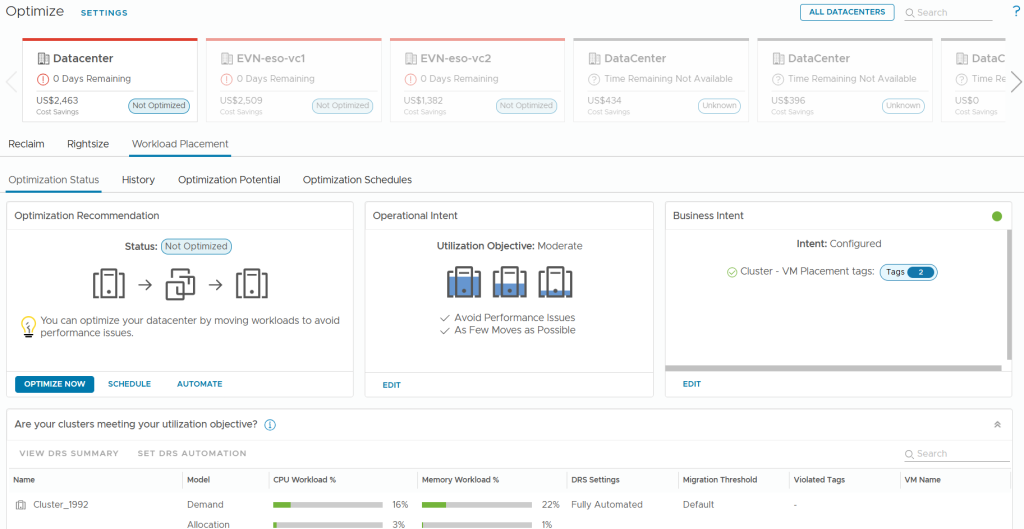
Business and Operational Intent
So how do you define what the “perfect fit” is within VMware Cloud Foundation when it comes to VMs, Hosts, and Clusters?
This is accomplished by setting Operational and Business intent, which is, essentially, you defining to what ‘optimized’ means for your business.
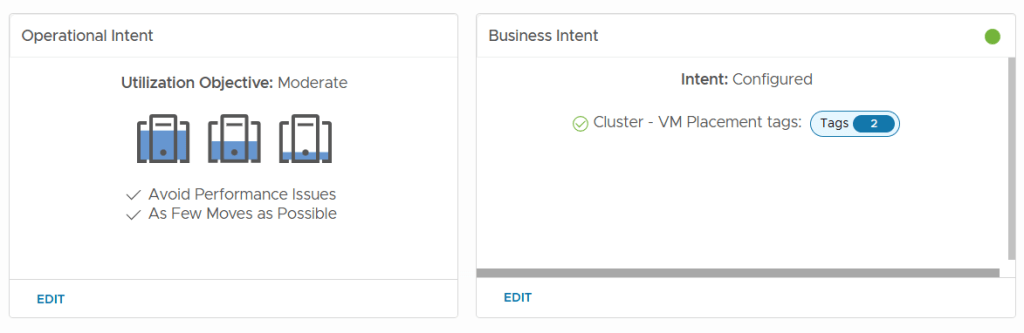
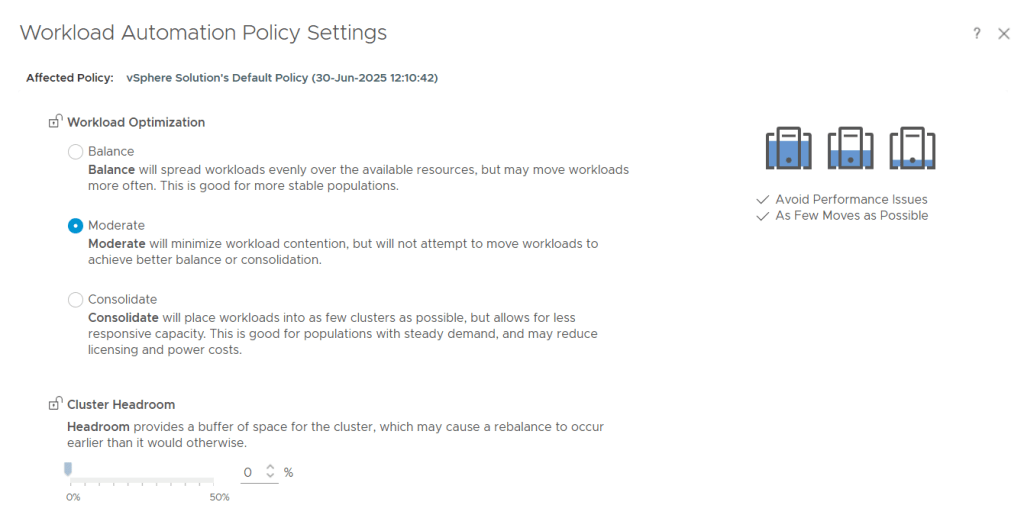
On the Operational side, you might be focused on performance. You want to reduce risk from demand spikes. You’d set a Balance objective.
If minimizing workload contention is your intent, Moderate workloads would be the ideal choice.
Conversely, you might want to Consolidate workloads to maximize utilization, which lets you power off unneeded hosts and save costs.”
On the Business side, it’s all about rules. This is how you enforce compliance—like PCI. It’s how you manage software licensing—this is a huge one. Grouping all your Microsoft or Oracle VMs on specific licensed hosts to avoid massive license creep.
It’s also how you deliver SLA tiers—making sure your ‘Gold’ apps are always running on your ‘Gold’ hardware.”
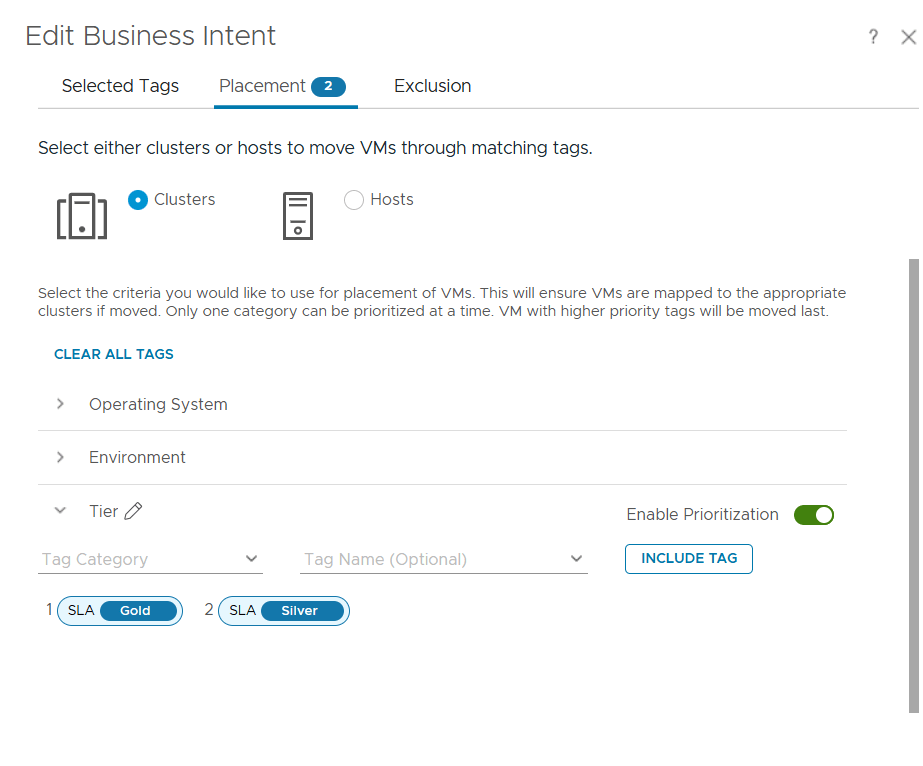
Expressing Intent with Tags
So how do exactly you enforce Intent? Workload Placement doesn’t assume how you intend to use your VMs — but Tags can make that intent explicit.
Continuing our smart room analogy, you wouldn’t put a bed in the kitchen. Similarly, tags ensure VMs are only placed in clusters meant for their purpose.
For example:
- Tag a VM as SLA|Gold.
- Only clusters or hosts with the same tag (i.e. SLA|Gold) will be considered during placement.
This simple system ensures that business intent guides every placement decision.
A Real-World Example
Imagine you’re deploying a critical business application tagged as SLA Gold.

Workload Placement analyzes these options and may recommend Cluster B — balancing capacity and performance for optimal results.
Key Considerations
- Tag workloads with clear intent – Tier (i.e. Gold, Silver, etc.), Environment (i.e. Dev, Prod, etc.), Operating System (i.e. Windows, Linux, etc.)
- Prioritize clusters with balanced compute and storage performance — not just lowest utilization.
- Review recommendations to validate results before enabling automation.
Workload Placement vs. DRS
Workload Placement sounds a lot like Distributed Resources Scheduling (DRS). What’s the difference?
It’s easy to confuse the two, but here’s the distinction.
DRS works WITHIN a cluster. Its job is to balance the hosts inside one cluster.
But what happens when the entire cluster is full? DRS is, essentially, “stuck.” It has nowhere to move the VMs.
And this is where Workload Placement comes in. It works BETWEEN clusters. It looks at the entire datacenter. It will move VMs from a hot cluster to a cool cluster, all while honoring your business intent.
So, think of it this way:
- DRS handles the micro-optimizations.
- Workload Placement handles the macro-optimizations.
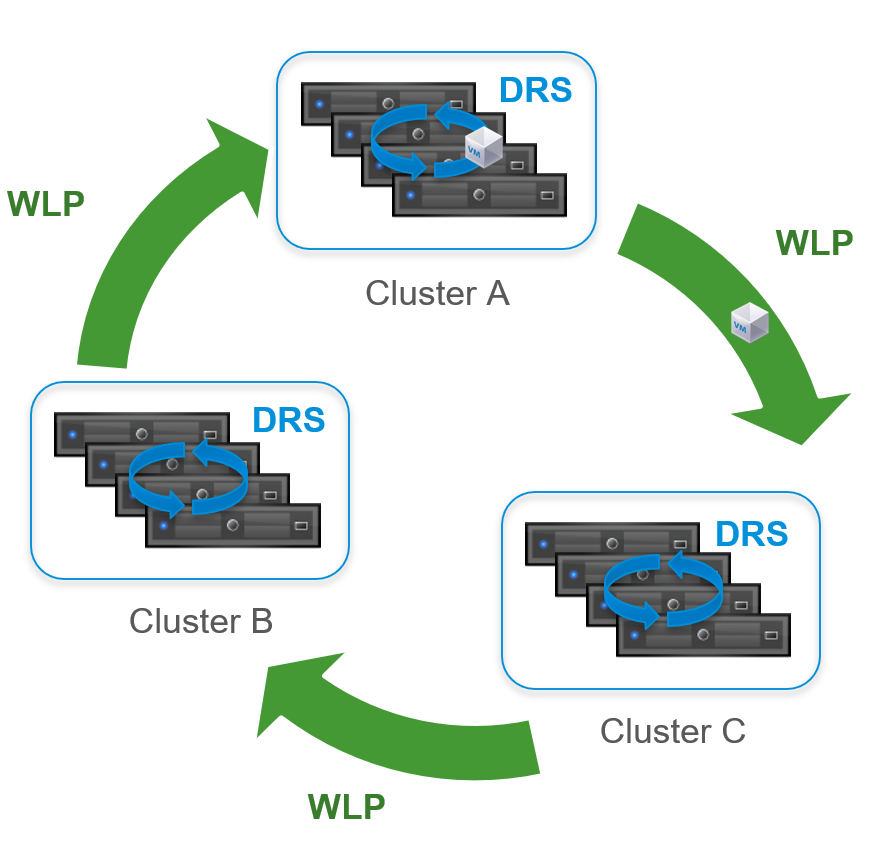
Together, they deliver end-to-end workload optimization — from intelligent initial placement to continuous balancing.
Final Thoughts
Workload Placement in VMware Cloud Foundation is like having a smart room planner for your virtual machines. It examines every “room” in your data center and decides where each workload fits best — keeping performance high, deployments fast, and compliance intact.
When properly implemented, organizations can expect:
- Higher performance and stability — fewer hotspots and smarter matching of compute, memory, and storage.
- Faster deployments — recommendations remove trial-and-error guesswork.
- Improved compliance — tagging ensures workloads follow business intent.
- Better cost control — balanced utilization reduces overprovisioning and unnecessary hardware spend.
Ready to see Workload Placement in action?
Click here to learn more about VMware Cloud Foundation Workload Placement.
Discover more from VMware Cloud Foundation (VCF) Blog
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.







