Key Points:
- Defining Modern Infrastructure
- Legacy Environments and the Public Cloud
- Building a Future-ready Private Cloud
- Modernizing Core Infrastructure
- Tenant Management
- Operating a Modern Private Cloud
- Self-service Automation
Defining Modern Infrastructure
The term “Modern Infrastructure” is being used to define the next phase of many IT initiatives. What is Modern Infrastructure?
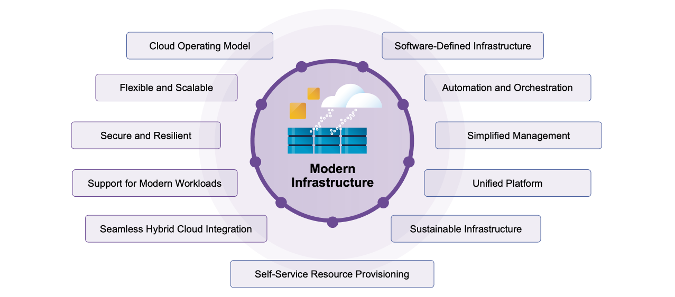
Image: Components of Modern Infrastructure
At its core Modern Infrastructure is software-defined. It is where intelligent software virtualizes compute, storage, and networking. By virtualizing and abstracting infrastructure enables a cloud operating model, bringing all the agility and efficiency of the public cloud to your on-premises environments.
The benefit of a software defined approach is that it is highly flexible. You can easily adapt and expand your resources to best align with your business needs. What drives the agility is automation and orchestration.
Orchestrated wizard-driven workflows and in-built automation streamlines many complex and time-consuming IT processes. This allows IT teams to reduce manual effort in making changes within their environments and therefore accelerates service delivery.
Moreso than ever, modern infrastructure today is also designed with security and reliability at the forefront. It is inherently secure and resilient; it incorporates features to protect against threats and ensures business continuity. It also provides simplified management offering a single pane of glass for monitoring, control, and administration.
A modern platform also supports modern workloads – cloud-native applications, Kubernetes, AI, and big data. Once again it is uniform and seamlessly integrates with hybrid cloud environments, extending your reach and offering deployment flexibility.
Looking ahead, modern infrastructure also incorporates sustainable practices, where resources are optimized and environmental impact is minimized. Users are also empowered with self-service provisioning – and this allows application owners and developers to access the resources they need, when they need it, and without lengthy provisioning times, complex back-end processes and IT involvement. This agility translates directly into faster innovation and time-to-market.
Tradeoffs with Legacy Architecture and the Public Cloud
IT leaders face a key challenge: modernizing infrastructure while dealing with legacy on-premises systems, versus the appeal of the public cloud. Both approaches have their pros and cons.
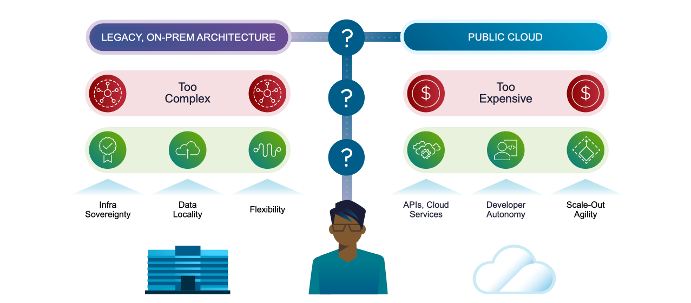
Image: Legacy On-prem Architecture and Public Cloud
Legacy systems and manual processes can be overly complicated and can slow down the business. And while the public cloud offers user-friendly features and speed that excite business teams, IT professionals are concerned about security, data locality (sovereignty), and unpredictable costs. IT teams typically prefer the control and robust security of keeping operations in-house.
So, the real challenge lies in figuring out how to achieve the best of both worlds: maintaining the governance and security of your data center while also gaining the flexibility and new capabilities offered by public cloud.
Building a Future-ready Modern Infrastructure with VMware Cloud Foundation
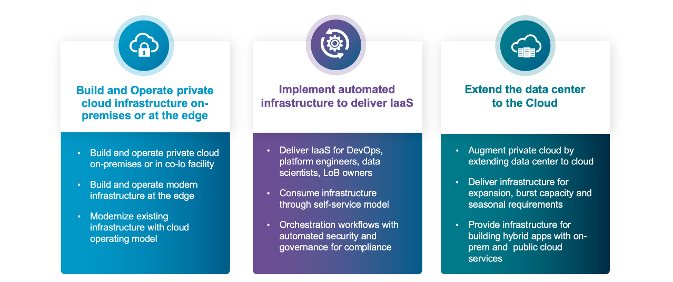
Image: Private Cloud use cases addressed with VMware Cloud Foundation
VMware Cloud Foundation (VCF) provides many benefits for customers who wish to modernize their infrastructure and adopt a cloud operating model to extract greater value from their investments. Infrastructure can be centralized into one or more data centers or it can operate at the edge – where VCF can be tailored to specific industry needs such as manufacturing, industrial IoT, retail, health care, ROBO and much more.
Our recent release of VMware Cloud Foundation 9.0 now makes it even easier for end-users to deploy and consume infrastructure through self-service model… while also ensuring that security and governance guardrails are in place to maintain control.
VCF also provides options to augment private cloud by extending data center to cloud, by delivering infrastructure for expansion, burst capacity and seasonal requirements and hybrid applications.
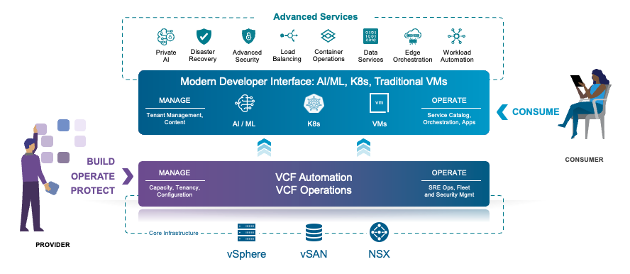
Image: VMware Cloud Foundation platform components and capabilities
This comprehensive platform delivers a scalable, secure, and automated private cloud infrastructure that accommodates a wide range of traditional and container-based applications.
VMware Cloud Foundation can be deployed with a portfolio of advanced services which help customers support an extended set of use cases to further drive innovation and improve operational resilience.
Ultimately, VMware Cloud Foundation provides a modern private cloud experience, simplifies operations, enhances security, and accelerates innovation for your organization.
Modernizing Core Infrastructure
Let’s take a look at the primary components of VMware Cloud Foundation that enable a modern private cloud.
Compute
With the latest release of VCF, vSphere remains the core compute engine within a fully integrated platform that includes networking, storage, management, and security while supporting both traditional VMs and containerized applications with K8s.
Image: vSphere 9.0 enhancements as part of VMware Cloud Foundation 9.0
- The vSphere Lifecycle Manager of vSphere 9.0 supports the configuration of mixed vendor clusters as well as support for multiple hardware support managers (HSM) per cluster. For a mixed vendor cluster to work the base ESX version is static. The vendor addons, firmware, and components of each image definition can be customized to accommodate clusters with mixed hardware.
- Memory Tiering leverages PCIe-based Flash NVMe devices to act as a second tier of memory, increasing your available memory and workload capacity, while improving your TCO and green score. Virtual infrastructure teams can increase VM consolidation by directing VM memory allocations to either NVMe devices or faster DRAM in a host.
- vSphere 9.0 and therefore VCF 9.0 introduces several new features to make working with GPUs easier:
- vGPU profiles can be configured and provide descriptive detail of a GPU type and it’s configuration (GPU or vGPU; timesliced vs MIG) which can be useful for capacity management of these high cost/high demand resources.
- vSphere 9.0 introduces vMotion pre-copy which is a technique used to transfer both hot and cold VM memory to another host while a VM is still running. This eliminates the need to checkpoint and transfer all memory during downtime and can be particularly useful for AI workloads (3x reduction in vMotion time).
- GPU reservations are also new and allow admins to reserve resource pools for vGPU profiles ahead of time. A GPU reservation guarantees capacity for a new VM and can be used to assure that vGPU resources are available to power-on a new VM
- Live Patch for ESX was introduced with vSphere 8.0 Update 3 and is has now been extended. NSX components, now part of the base ESX image, can be patched using the live patch process without hosts entering maintenance mode and without the need for VMs to be evacuated from a host. VMkernel, user-space and vmx (virtual machine execution) components can also leverage live patch.
The new capabilities introduced with the latest release of vSphere allow VMware Cloud Foundation to provide greater scope for a more flexible, cost-effective, and highly available private cloud platform.
Storage
VMware Cloud Foundation with vSAN provides a robust, scalable, and efficient infrastructure. vSAN’s integration at the hypervisor level delivers complete I/O visibility and control, unlike traditional storage arrays that lack this awareness. With this, vSAN can prioritize traffic during contention, therefore ensuring consistent performance.
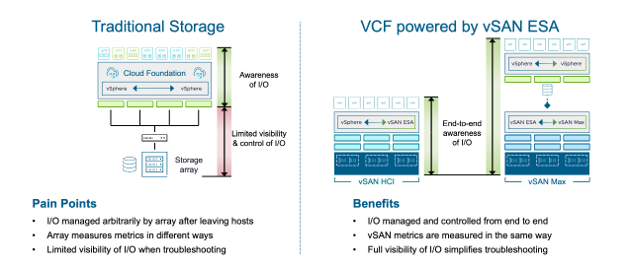
Image: Highlights the pain-points of managing traditional storage (left) and the benefits of vSAN ESA for the private cloud (right)
Additionally, vCenter Server and VCF Operations provide performance tracking, troubleshooting, and monitoring.
Beyond performance, vSAN’s integration with VCF simplifies management and enhances efficiency. Its hyperconverged design reduces I/O delays and enables near-linear scaling.
vSAN Express Storage Architecture (ESA) is the ideal storage for your VCF-powered private cloud. It employs a specialized file system optimized for the speed of modern NVMe drives and was developed to provide exceptional performance, efficiency and reliability. vSAN ESA provides the flexibility to tailor your storage to meet your needs:
- Combine compute and storage together in standard HCI clusters …or
- Separate storage independent of compute into disaggregated vSAN Storage Clusters.
Global Deduplication in vSAN ESA further improves storage efficiency and reduces costs by enabling deduplication across the entire cluster.
vSAN includes data replication and works with vSphere HA and DRS to help ensure uptime and data protection. Storage Policy-Based Management makes storage management easier through automation and central control. vSAN lifecycle management integrates with vSphere, automating updates and maintenance while minimizing operational effort.
vSAN also provides a versatile collection of data services, extending beyond just basic VM storage. vSAN data services enable organizations to adapt vSAN to their evolving needs during modernization providing superior flexibility.
- Erasure coding, snapshots and cloning to balance availability, storage utilization, and data protection.
- Connect older physical servers to vSAN using its iSCSI target service
- vSAN File Services standard SMB and NFS shares for traditional and newer cloud-native applications
- S3-compatible object storage, essential for unstructured data in modern apps.
And not to be overlooked, vSAN’s hyperconverged architecture helps reduce power and cooling requirements, resulting in a much more efficient data center.
Collectively this level of integration provides a streamlined private cloud experience, establishing vSAN as the best option for VMware Cloud Foundation.
Networking
It’s well understood that traditional physical networks hinder agility and scalability which are ESSENTIAL for modern private clouds. VMware NSX addresses this by abstracting network services from hardware facilitating software-defined networking (SDN). This allows provisioning and managing network services such as routing, switching, load balancing, and firewalls through software. NSX, is essential for unlocking several critical use cases in modern private cloud environments, fostering agility, resilience, and seamless connectivity.
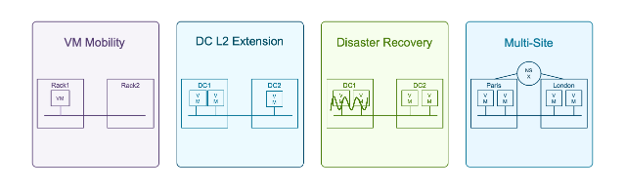
Image: Software Defined Networking (SDN) use cases with NSX in Modern Private Cloud Environments
Virtual machine mobility helps facilitate effortless workload migration between hosts, clusters, and across different data centers. This is accomplished through consistent networking and security policies decoupled from the physical network. So when for example: a VM is moved or relocated, its network configuration and security posture travel with it, simplifying operations and minimizing downtime.
NSX offers a robust and scalable solution for scenarios requiring the extension of layer-2 networks across various physical locations. This can be useful for data center consolidations, mergers, and acquisition projects. Layer 2 Datacenter extension is also a requirement for high-availability solutions such as a stretched cluster or an application migration, where preserving IP addresses and network configurations is essential. NSX achieves this without the complexities and limitations associated with traditional hardware-based layer-2 extensions.
NSX also streamlines disaster recovery orchestration within VCF. By replicating network configurations and security policies, NSX guarantees that applications can be recovered quickly at a secondary site. Being automated this solution helps reduce recovery times and enhancing business continuity.
For organizations managing multiple data centers, NSX also facilitates multi-site federation. This enables the maintenance of consistent network and security policies across all sites, which essentially simplifies management and ensures compliance. Within VCF, this federation delivers a unified network fabric… and this allows for seamless communication and resource sharing across geographically dispersed locations.
These four (4) common network virtualization use-cases help empower organizations to construct a highly agile, resilient, and interconnected infrastructure, many which are not possible using traditional hardware-based solutions.
Tenant Management
VMware Cloud Foundation 9.0 delivers a unified networking framework that aligns with industry standards and supports Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) consumption by vCenter Server, VKS, NSX, and VCF Automation.
A VPC is essentially – a logically isolated, tenant-specific virtual network that provides dedicated routing, switching, and security services.
In VCF 9.0, VPCs are implemented consistently across the entire platform – not just within NSX
VPCs within VCF allow IT teams to deliver a true end-to-end private cloud. The VPC model defines clear roles to support multi-tenancy and enables self-service capabilities for end users.
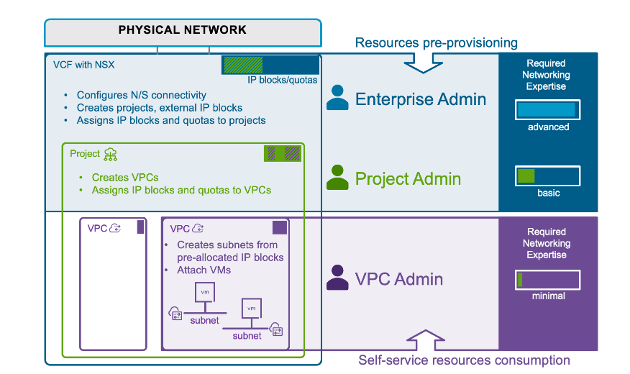
Image: Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) constructs and roles to support multi-tenancy
VPCs are best explained by talking to the roles defined when configuring self-service networking.
The first role is the Enterprise Admin. This role owns the VCF infrastructure and is responsible for coordinating with the physical network to ensure proper connectivity. Enterprise Admins also create “projects,” which represent the first level of tenancy – they also define external IP blocks that allow communication between the virtual and physical networks. These external IP blocks are then distributed to the individual projects. Quotas can be applied as needed. Importantly, the Enterprise Admin maintains full control over all networking resources.
Next, the Project Admin steps in to manage the resources delegated by the Enterprise Admin, but without direct access to the physical infrastructure. The Project Admin is responsible for creating and managing VPCs, which represent this second level of tenancy.
They also allocate resources, such as IP pools, and apply quotas to individual VPCs.
Finally, we have the VPC Admin, who acts as the end user in this model. The VPC Admin can independently create logical networks (subnets) and easily attach workloads to these networks.
A key benefit of this model is that the VPC Admin can fully leverage networking services without requiring in-depth networking expertise.
This is possible because the Enterprise and Project Admins pre-configure all of the underlying network and resource allocations, enabling true self-service capabilities to users.
Operating a Modern Private Cloud
VMware Cloud Foundation 9.0 introduces some significant new enhancements to simplify the ongoing management of modern private cloud infrastructure.
VCF Operations provides admins with a unified and feature rich operations experience which expands upon the familiar capacity management and performance monitoring capabilities included in prior versions of Aria Operations. VCF Health and diagnostics has also been adapted from Skyline and is has now also been integrated.
Private cloud operations and management traditionally serviced from SDDC Manager is now also performed using the VCF Operations console as part of Fleet Management. NEW

Image: The familar capabilities of VCF Operations (left) and the introduction of additional Fleet Management capabilities (right)
Fleet management within VCF Operations allows admins to oversee multiple VCF instances from a single console. This includes centralized lifecycle management and consistent upgrades across environments, identity and access management (IAM and SSO), certificate and password management, tag management, configuration management & drift assessment and license management.
A VCF Fleet can consist of multiple VCF deployments which can leverage common VCF Operations and VCF Automation instances.
VCF Operations is the primary interface for managing the private cloud, while the vSphere Client remains available for detailed host and cluster configuration tasks. Together, they provide centralized control with operational efficiency.
Refer to my earlier blog on VMware Cloud Foundation Deployment Pathways to learn more about how VMware Cloud Foundation can be deployed and scaled and some of the constructs of VCF Fleets.
Self-service Automation
A fully featured Private Cloud provides self-service provisioning of new applications and services to it’s users. VMware Cloud Foundation provides a frictionless, cloud-like experience for teams consuming self-service infrastructure delivered through VCF Automation. This single, unified interface enables IT to deliver an end-to-end private cloud accelerating application delivery including AI, Kubernetes, and VM-based workloads.
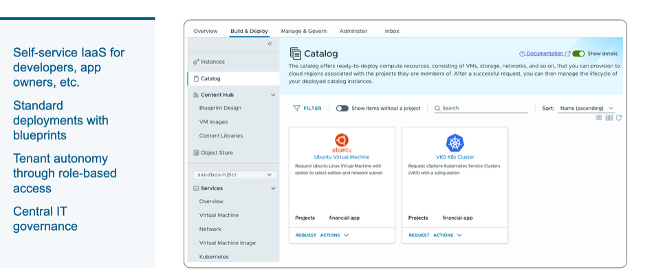
Image: A sample service catalog for self-service provisioning within the VMware Cloud Foundation Automation console
Tenant Management allows IT Admins and the Service Providers to organize, provision and manage allocations of infrastructure to tenants. These tenants could be either end-customers (in the case of a Service Provider) or just internal lines of businesses (in the case of Enterprise IT).
Each tenant can be configured with their own identity providers ensuring secure, role-based access.
When a provider allocates these tenants, utilization can be managed and chargeback functions performed.
Cloud Governance policies are built-in and can be enforced across tenants or the lines of business based upon the infrastructure resources they are allocated. These can be configured based upon quotas, leases, by name or resource-level. Governance can also be applied across users/groups which enforce only the provisioning of specific workload types.
Governance can also be applied to pre-defined blueprints which mandate that certain VMs and components are configured end-to-end in a specific manner. Additionally, workflow orchestration can be applied to simplify provisioning and remove manual overhead ensuring a deployment follows a repeatable process.
For example: A mandate for a specific application team which can deploy and configure a subset of VMs from the service catalog configured with additional software, a load balancer and registered in a CMDB.
IaaS Services are further extended providing built-in automation, governance and elastic scaling, which empowers end-users and developer teams to move fast. Cloud Admin teams can deliver an enhanced End User Experience which include a wide range of extensible services like object storage, data services, and backup, with the vSphere supervisor providing this capability. The centralized resource catalog from VCF Automation ensures consistency across your VCF fleet providing end users and developers the speed and flexibility of public cloud.
Summary
VMware Cloud Foundation 9.0 provides numerous benefits for organizations looking to modernize their infrastructure and streamline operations.
It offers a unified, software-defined approach to compute, storage, networking and management, facilitating a cloud operating model for both traditional and modern workloads.
Inbuilt automation and orchestrated workflows remove manual dependencies and streamline deployment of new infrastructure as well as supporting the capability to import existing infrastructure. Daily operations are streamlined with VCF Operations which provides fleet-level visibility, enhanced performance and lifecycle management across the workload and infrastructure stack while also helping your organization stay compliant with regulatory standards and organisational guidelines.
Key improvements for VMware Cloud Foundation 9.0 includes but is not limited to fleet management, tenancy and VPC consumption.
VCF Automation self-service IaaS allows IT teams to deliver a true end-to-end private cloud to run VMs, containers and AI workloads.
Modernizing your infrastructure with VMware Cloud Foundation allows IT teams to deliver the scale and agility of public cloud together with the security and performance of private cloud.
Resources and Further Reading
Related Blogs:
VMware Cloud Foundation Deployment Pathways
Planning a Successful VMware Cloud Foundation Deployment
Related Short Videos:
VCF 9.0 What’s New Technical YouTube Series
Discover more from VMware Cloud Foundation (VCF) Blog
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.





