If you’re a datacenter systems engineer you have any number of challenges from aging infrastructure, to sprawling tools and features, not to mention the limitations of time, resources and budget. The general expectation is to solve these challenges as soon as they come up, but an outdated technology stack can be inflexible and limited in its scalability.
To build a private cloud that breaks down silos, engineers need to consider a few key factors. First and foremost is the need for a unified infrastructure platform that consolidates disparate systems and fosters collaboration. A full-stack private cloud that deploys as an integrated software stack can play a crucial role in this process.
By implementing a full stack private cloud, engineers can bring together compute, storage, networking, and management capabilities into a single, cohesive solution. This integrated platform enables engineers to streamline their operations and facilitate cross-departmental collaboration. With a common infrastructure platform, engineers can easily share resources, manage workloads, and foster better collaboration and coordination among different teams.
Introducing VMware Cloud Foundation
VMware Cloud Foundation is an integrated software platform designed to simplify the deployment and management of private and hybrid cloud infrastructures. It brings together several key components to provide a complete solution for building and operating a modern cloud environment.
Let’s take a closer look at the main components of the VMware Cloud Foundation solution:

Hosting Your Workloads in VMware Cloud Foundation
Hypervisor (VMware ESXi) – At the core of VMware Cloud Foundation is the industry-leading hypervisor, VMware ESXi. ESXi provides the foundation for virtualization, allowing multiple virtual machines (VMs) to run on a single physical server, but has expanded support for open source compliant, upstream compatible Kubernetes orchestration for containers. vSphere offers robust isolation, resource allocation, and management capabilities, enabling efficient utilization of server resources within the private cloud infrastructure. Of course, most systems engineers already know vSphere inside and out. There’s also VMware Tanzu, but VMware engineering also added a whole suite of services aimed at making it easier to consume infrastructure as a whole.
vSphere has also expanded the range of workloads supported in a data center environment, delivering innovations to support modern compute requirements, including support for hardware accelerators and offload processors (DPU/GPU) for AI/ML workloads. When combined with next-generation storage class memory and NVMe over fabric support, vSphere is well-positioned for the workloads of tomorrow.
Safely Storing Your Data in VMware Cloud Foundation
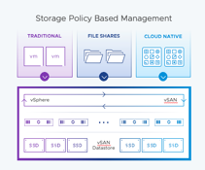
VMware Cloud Foundation incorporates VMware vSAN, a software-defined storage solution. vSAN aggregates the storage capacity of multiple physical servers and presents it as a shared pool of storage resources. This distributed architecture of vSAN enhances storage performance, scalability, and resiliency, simplifying storage management reducing cost and complexity.
vSAN is HyperConverged – that is – storage and compute are derived from the same shared hardware. It integrates with the entire VMware stack. and provides a workload centric data management model. Virtual Machine (VM) storage provisioning and day to day management of storage SLA can all be controlled through policies that can be set or modified on the fly. vSAN delivers enterprise class features scale and performance, making it the ideal storage platform for any foundation.
Go from Siloed Networking and Security to Unlocking True Zero-Trust
VMware NSX is the software-defined networking component of VMware Cloud Foundation. NSX virtualizes networking and security, providing a programmable overlay network that is decoupled from the underlying physical network infrastructure. It enables the creation of virtual networks, micro-segmentation, and network services, allowing engineers to define and manage network policies in a centralized and automated manner.

Networking and Security is the one element of the cloud where VCF enforces an opinion. It delivers on the promise of a private cloud by delivering an end-to-end solution. The problem is that these advanced features and tooling of today adds enough complexity that it often takes days, requiring specialized networking and security knowledge for every task. VMware Cloud Foundation removes the complexity and automates many of these tasks to accelerate time to value.
Unlock Efficiency In The Infrastructure with vRealize Suite (Aria Suite)
VMware Cloud Foundation includes automation and orchestration capabilities through VMware vRealize Suite – now better known as the Aria Suite. These tools enable engineers to automate the deployment, configuration, and management of resources within the private cloud. They provide self-service portals, workflows, and policy-based governance, empowering users to provision and manage their own resources while ensuring compliance and consistency.
Consistency in Upgrades and Streamlining Infrastructure Lifecycle Management
Tasks like patching and upgrading can be daunting tasks in the data center, and the risk of configuration drift and human error can delay patching operations. And with traditional 3 tier architecture and a software stack on top of it, the dependency mapping between multiple hardware, software, and server vendors can leave operation teams planning the upgrades for weeks or even months. To simplify the ongoing management and maintenance of the private cloud infrastructure, VMware Cloud Foundation incorporates the Lifecycle Manager within SDDC Manager.

SDDC Manager allows engineers to automate the lifecycle management of the entire software stack, including updates, patches, and upgrades. It provides a unified and streamlined approach to ensure the private cloud remains up-to-date and secure.
How to Build a Private Cloud Environment That’s *Any* Future-Ready
The definition of future-ready and infrastructure modernization is in constant change, and it seems like for each new year, there’s a new set of requirements. More than a decade ago, containers were the new technology on the block, demanding everyone’s attention and requiring that future infrastructures support containerized workloads. Then there was the move to public cloud. At the time of this write-up, there is a sense of urgency around the ability to support AI/ML workloads, and a lot of buzz around what is known as Language Modelling as a Service (LMaaS).
But infrastructure also demands operational efficiency, no downtime, a strong security architecture and so on. System architects and engineers are looking at this cornucopia of demands and what makes a private cloud truly any future ready. Let’s go a bit through the requirements:
- Flexibility: Future-proofing the private cloud involves ensuring its flexibility to adapt to emerging technologies and changing business needs. Engineers should design the infrastructure with open standards and compatibility in mind, allowing for easy integration with new technologies and services. VMware Cloud Foundation supports a wide range of hardware and software ecosystems, enabling engineers to leverage the latest innovations without disrupting the entire infrastructure.
- Automation: Building a future-ready private cloud requires embracing automation. Engineers should automate routine tasks and processes to improve efficiency, reduce errors, and enable faster response times. VMware Cloud Foundation offers automation capabilities through its software-defined data center (SDDC) approach, enabling engineers to automate infrastructure deployment, scaling, and management tasks, leading to improved agility and operational efficiency.
- Resiliency: Ensuring high availability and disaster recovery capabilities is essential for a future-ready private cloud. Engineers should implement robust backup and disaster recovery mechanisms to protect data and applications from potential disruptions. VMware Cloud Foundation provides built-in resiliency features such as continuous data protection, automated backups, and site recovery options, enabling engineers to design a private cloud infrastructure that can withstand unforeseen events.
- Security: Security is a critical aspect of any future-ready private cloud. Engineers must prioritize security measures to safeguard sensitive data, protect against cyber threats, and comply with industry regulations. VMware Cloud Foundation offers comprehensive security features, including network segmentation, encryption, role-based access control, and threat detection, providing engineers with the necessary tools to build a secure private cloud infrastructure.
- Monitoring and Analytics: To ensure the future readiness of the private cloud, engineers need robust monitoring and analytics capabilities. These tools enable proactive monitoring, performance optimization, and capacity planning. VMware Cloud Foundation includes monitoring and analytics features that provide real-time visibility into the private cloud infrastructure, helping engineers identify bottlenecks, optimize resource utilization, and make informed decisions for future enhancements.
Conclusions
Implementing VMware Cloud Foundation can significantly simplify the process of building a future-ready private cloud platform. It provides a unified platform that integrates compute, storage, networking, and management capabilities, offering engineers a consistent and scalable infrastructure foundation. The platform’s flexibility, automation, resiliency, security, and monitoring features align with the key considerations for future-proofing a private cloud.
Overall, VMware Cloud Foundation simplifies the implementation and management of a private cloud by bringing together essential components in an integrated platform. Its technical capabilities empower engineers to build a robust, scalable, and any future-ready private cloud infrastructure that meets the evolving demands of the business.
Discover more from VMware Cloud Foundation (VCF) Blog
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.




